شناسایی حرکت دست ها با استفاده از تکنیک های پردازش تصویر و استخراج خصیصه
چکیده
شناسایی تصویر در حال تبدیل شدن به یک مرحله بسیار مهم در اکثر سیستمهای حل مسئله دنیای مدرن میباشد. روشهای دریافت، آنالیز و دسته بندی تصویر به تعداد فراوان در دسترس هستند، اما تفاوت میان این قبیل روشها هنوز نامعلوم است. لازم است که بین این تکنیکها تمییزگذاریهای مناسبی انجام شده و آنالیز شوند. تصاویر زبان اشاره آمریکایی استاندارد (ASL) از دست یک فرد که تحت شرایط محیطی مختلف عکسبرداری شده اند بعنوان مجموعه داده ها در نظر گرفته شده اند. هدف اصلی، شناسایی و دسته بندی حرکات دست برحسب معنی صحیح آنها و با حداکثر صحت ممکن میباشد. یک روش جدید برای همین کار ارائه شده و چند مدل پرطرفدار دیگر با آن مقایسه شده اند. تکنیکهای پیش پردازش متفاوتی که استفاده شده اند، هیستوگرام گرادیانها ، تحلیل مؤلفه اصلی ، و الگوهای دودوئی موضعی یا محلی هستند. مدل جدید با استفاده از آشکارسازی لبه کنی ، ORB و تکنیک کوله کلمات ساخته شده است. داده پیش پردازش شده از میان چندین دسته کننده (جنگل تصادفی ، ماشینهای بردار پشتیبان ، نیو بیس ، رگرسیون لجستیک ، نزدیکترین همسایگیهای K ، پرسپترون چندلایه ای ) عبور داده میشود تا نتایج موثری دریافت شود. مشخص شد که صحت مدل جدید بطور چشمگیری بالاتر از مدلهای موجود است.
1- مقدمه
فهم زبان اشاره یک کار دشوار بوده و مهارتی است که باید با تمرین کردن فرا گرفته شود. ولی ما میخواهیم در این مقاله چندین نقشه و رویه برای شناسایی و فهم این حروف، بدون یاد گرفتن زبان اشاره، فراهم آوریم. ما در وهله اول روی توسعه رویه های جدید برای فهم زبان اشاره، و یافتن تفاوتهای بین روشها و بهترین روش تشخیص زبان اشاره متمرکز میشویم. دشواریهای متعددی در توسعه یک روش بهتر برای تشخیص اشاره وجود دارد. مثلا، در زندگی واقعی عکسهایی که گرفته میشوند بیش از حد نویزی و خش دار بوده و نیاز به سطوح پیش پردازش زیادی دارند؛ مجموعه داده هایی که بصورت آنلاین در دسترسند معمولا چنان فاقد خش هستند که کار کردن روی آنها سبب توسعه مدلهایی میشود که فقط برای سر و کار داشتن با تصاویر کم یا تقریبا بدون خش آموزش دیده اند، لذا برای کاربری در زندگی واقعی بیهوده اند. بدین ترتیب، لازم است مدلی خلق نمود که بتواند با تصاویر پر خش کار کرده و همچنین نتایج مثبتی تولید کند.
6- نتیجه گیری و چشم انداز آینده
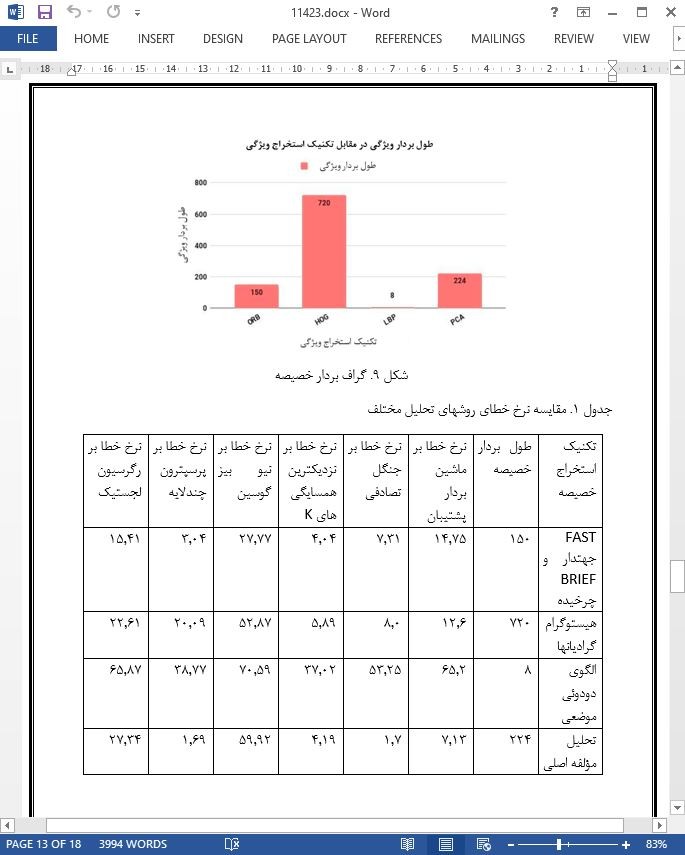
در مقاله حاضر، تکنیک استخراج خصیصه ORB پیشنهادی در مقابل تعداد زیاد و متفاوتی از تکنیکهای پیش پردازش نظیر هیستوگرام گرادیانها، LBP و PCA، روی مجموعه داده های یکسان مورد آزمون قرار گرفته است. این روشها بطور موفقیت آمیزی از دسته کننده های برجسته مختلفی مانند KNN، SVM، جنگل تصادفی، نیو بیز، رگرسیون لجستیک و پرسپترون چندلایه عبور کرده اند. روش پیشنهادی عملکرد بهتری نسبت به تمام تکنیک های پیش پردازش دیگر برای دسته کننده های نیو بیز، رگرسیون لجستیک و KNN دارد، درحالیکه PCA بهترین عملکرد را نسبت به سایر تکنیکها برای دسته کننده های MLP، جنگل تصادفی و SVM دارد. گرچه این روش اساسا صحت بالایی در شناسایی حرکات ارائه میدهد.
Abstract
Image identification is becoming a crucial step in most of the modern world problem-solving systems. Approaches for image detection, analysis and classification are available in glut, but the difference between such approaches is still arcane. It essential that proper distinctions between such techniques should be interpreted and they should be analyzed. Standard American Sign Language (ASL) images of a person’s hand photographed under several different environmental conditions are taken as the dataset. The main aim is to recognize and classify such hand gestures to their correct meaning with the maximum accuracy possible. A novel approach for the same has been proposed and some other widely popular models have compared with it. The different preprocessing techniques used are Histogram of Gradients, Principal Component Analysis, Local Binary Patterns. The novel model is made using canny edge detection, ORB and bag of word technique. The preprocessed data is passed through several classifiers (Random Forests, Support Vector Machines, Naïve Bayes, Logistic Regression, K-Nearest Neighbours, Multilayer Perceptron) to draw effective results. The accuracy of the new models has been found significantly higher than the existing model.
1. Introduction
Understanding sign language is an arduous task and it is a skill that has to be learned with practice. But with this paper, we aim to provide several schemes of identifying and understanding such letters without learning the sign language. We focus primarily on the development of new procedures to understand sign language, and to find differences between the approaches and best method of recognition of the sign language. There are several difficulties in developing a better method for sign recognition such as, in real life the images captured are so excessively noisy that high level of pre-processing is required, the datasets available online are generally so noiseless, that working on them leads to the development of models trained only to handle images with less or nearly no noise, hence being impractical for real-life application. Thus, it is imperative to create a model that can handle noisy images and also be able to produce positive results.
Conclusion and Future
ScopeIn the presented paper, the proposed technique of ORB feature extraction has been tested against many different pre-processing techniques such as Histogram of Gradients, LBP and PCA on the same dataset. These approaches have been successfully passed through various prominent classifiers such as KNN, SVM, Random Forest, Naïve Bayes, Logistic Regression and Multi-Layer Perceptron. The proposed technique outperforms all the other pre-processing techniques for Naïve Bayes, Logistic Regression and KNN classifiers while PCA outperforms all the other techniques for MLP, Random Forest and SVM classifiers. Although the approach gives substantially high accuracy for recognition of gestures.
چکیده
1- مقدمه
2- کار مرتبط
3- پیش زمینه
1. الگوهای دودوئی موضعی (LBP)
3-1- هیستوگرام گرادیانها
3-2- تحلیل مؤلفه اصلی (PCA)
3-3- الگوی دودوئی موضعی (LBP)
4- متودولوژی
4-1- قسمت بندی
4-2- استخراج خصیصه
4-3- ایجاد هیستوگرام مجموعه واژگان بصری
4-4- دسته بندی
5- نتیجه و بحث
6- نتیجه گیری و چشم انداز آینده
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
3. Background
3.1 Histogram of Gradients
3.2 Principal Component Analysis (PCA)
3.3 Local Binary Pattern
4. Methodology
4.1. Segmentation
4.2. Feature Extraction
4.3. Generation of Histogram of Visual Vocabulary
4.4. Classification
5. Result and Discussion
6. Conclusion and Future Scope
- اصل مقاله انگلیسی با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه