تخصیص منبع چندمرحله ای در شبکه های 25G-EPON و LTE-Advanced Pro FiWi برای سیستم های 5G
چکیده
نگرش 5G صرفا محدود به دامین بیسیم نیست و الزامات چالش برانگیز آن نمی توانند بدون ادغام موثر تکنیکهای نوآورد (پیشرفته) در تمام بخش های زیرساختار ارتباطات از راه دور برآورده شوند. معماریهای ارتقاء یافته برای سیستم های ارتباطات از راه دور نسل بعد شامل دامین های شبکه با ظرفیت بالا هستند که به طور انعطاف-پذیر و یکپارچه جهت ارائه کیفیت تجربه کامل برای تمام انواع مشترکین فعالیت می کنند. ازدیاد خدمات چندرسانه ای با تقاضای بالا و خصوصیات دستگاههای ارتباطی مدرن توسعه طرحهای پایان به پایان را به ضرورت تبدیل کردند که می توانند به طور موثر میزان عظیمی از منابع شبکه در هرجا و هر زمان که نیاز باشد، توزیع کنند. این مطالعه یک طرح تخصیص منبع جدید برای شبکه های بیسیم فیبری نوآورد (پیشرفته) معرفی می کند که می تواند در بخش فرانت هال معماریهای دارای توانمندی 5G به کار گرفته شود. تکنولوژیهای مورد استفاده عبارتند از شبکه نوری نافعال اترنت 25G (EPON) برای دامین نوری و تکامل طولانی مدت 5G پرو پیشرفته آماده برای دامین بیسیم. طرح پیشنهادی تصمیمات تخصیص را براساس نتیجه یک مسئله بهینه سازی چندمرحله-ای قابل تنظیم انجام می دهد. فاکتورهای بهینه سازی مستقیما مرتبط با ملاحظات اصلی در توزیع پهنای باند یعنی تفکیک ترافیک مبتنی بر اولویت، آگاهی از توان و تدارک انصاف هستند. ارزیابیهای انجام شده اثبات می کنند که این رویکرد قادر به تضمین کارایی بالا در عملیاتهای شبکه است.
1-مقدمه
با ازدیاد خدمات شبکه پیشرفته و خصوصا اپلیکیشنهای چندرسانه ای پرتقاضای مدرن ارائه شده به کاربران موبایل، نیاز برای شبکه دسترسی با کارایی بالا ظهور یافته است. هدف اولیه ارائه کیفیت تجربه پیشرفته به مشترکین و توانایی برای بهره گیری کامل از مزایای دستگاههای هوشمند نوین آنها (برای مثال گوشیهای هوشمند با صفحه نمایش بزرگ دارای رزولوشن بالا) به منظور استفاده و تولید حجم های ترافیک زیاد با استقلال انرژی گسترده در هر کجا و هر زمان است. در سمت ارائه کننده ارتباطات از راه دور، این آشکار است که یک تغییر (شیفت) واضح به سمت خدمات چندرسانه ای، شبکه های تحویل محتوی و اجاره منابع وجود دارد. از این رو، این آشکار است که زیرساختار اصلی با گنجایش بالا در شبکه بک هال نیاز است یکپارچه (بدون درز)، انعطاف پذیر و دارای اتصال درونی کارآمد با شبکه های فرانت هال و شبکه های دسترسی رادیویی باشد. هدف نهایی توانمندسازی مدیریت پایان به پایان منابع شبکه است که بتواند به طور موثر و کارآمد به مشترکین (با تمرکز روی کاربران موبایل) با تضمین عملکرد بالا، کارایی توان و منصفانه تخصیص داده شود.
6- نتیجه گیری
یک طرح تخصیص منبع کارآمد، منصف و آگاه از توان برای شبکه های فای وای نوآورد در این مقاله پیشنهاد شده است. یک تکنیک بهینه سازی چندمرحله ای قابل تنظیم برای اولویت بندی ترافیک و توزیع موثر پهنای باند با در نظرگیری مصرف انرژی UEs معرفی گردید. برطبق معماری مورد استفاده، OLT مسئله بهینه سازی مربوطه را جهت تخصیص منابع به کاربران نهایی از طریق ONUs/eNBs حل می کند. این طرح از طریق سناریو شبکه هیبرید 25G-EPON و Advanced Pro hybrid شبیه سازی شده مورد ارزیابی قرار گرفت. نتایج نشان دادند که این طرح می تواند به استفاده کانال بالا دست پیدا کند، خدمات برای جریان های اولویت بالا را تضمین کند، منابع را به طور منصفانه تخصیص دهد و مطلوب انتقال های دارای توان پایین باشد. این نیز نشان داده شد که با در نظرگیری/عدم در نظرگیری فاکتورهای بهینه سازی خاص، این محتمل است تا به طور دینامیک رفتار شبکه را تنظیمکرد. با در نظرگیری فرآیند راه حل مسئله بهینه سازی، امکانپذیری فنی براساس ادله هایی که مسئله به مسائل فرعی برنامه ریزی خطی و درجه دوم دارای پیچیدگی پایین تجزیه گردیده است، توجیه شد. مفهوم مورد استفاده کلی مطابق با معماری C-RAN برای فرانت هال شبکه های هیبرید 5G است.
Abstract
The 5G vision is not restricted solely to the wireless domain and its challenging requirements cannot be fulfilled without the efficient integration of cutting-edge technologies in all portions of the telecommunications infrastructure. The promoted architectures for next generation telecommunications systems involve high capacity network domains, which operate flexibly and seamlessly to offer full quality of experience to all types of subscribers. The proliferation of highly demanding multimedia services and the features of modern communication devices necessitate the development of end-to-end schemes which can efficiently distribute large amount of network resources anywhere and whenever needed. This study introduces a new resource allocation scheme for cutting-edge fibre-wireless networks is introduced that can be applied in the fronthaul portion of 5G-enabled architectures. The adopted technologies are the forthcoming 25G-Ethernet Passive Optical Network (EPON) for the optical domain and the 5G-ready long-term evolution -Advanced Pro for the wireless domain. The proposed scheme performs allocation decisions based on the outcome of an adjustable multi-stage optimisation problem. The optimisation factors are directly related to the major considerations in bandwidth distribution, namely priority-based traffic differentiation, power awareness, and fairness provision. The conducted evaluations prove that this approach is able to ensure high efficiency in network operations.
1 Introduction
With the proliferation of advanced network services and especially the modern demanding multimedia applications offered to mobile users, the need for highly efficient access networks has emerged. The primary aim is to provide subscribers with advanced quality of experience and the ability to take full advantage of their state-ofthe-art smart devices (e.g. high-resolution big screen smartphones) in order to consume and generate large volumes of traffic with extensive energy autonomy anywhere at any time. On the telecommunications provider side, it is evident that there is a clear shift towards multimedia services, content delivery networks, and resource tenancy. Hence, it becomes apparent that the high capacity core infrastructure at the backhaul network needs to be seamlessly, flexibly, and efficiently interconnected with the fronthaul and the radio access networks. The ultimate objective is to enable end-toend management of the network resources, which can be effectively assigned to subscribers (focusing on mobile users) ensuring high performance, power efficiency, and fairness.
6 Conclusion
An efficient, fair, and power-aware resource allocation scheme for cutting-edge FiWi networks was proposed in this paper. An adjustable multi-stage optimisation technique was introduced for prioritising traffic and effectively distributing bandwidth considering UEs' energy consumption. According to the adopted architecture, the OLT solves the corresponding optimisation problem to assign resources to end-users through ONUs/eNBs. The scheme was evaluated via a simulated 25G-EPON and LTEAdvanced Pro hybrid network scenario. The results have shown that it can achieve high channel utilisation, guarantee service for high priority streams, fairly assign resources, and favour lowpower transmissions. It was also demonstrated that by considering/ ignoring specific optimisation factors it is possible to dynamically tune network behaviour. Regarding the solution process of the optimisation problem, technical feasibility has been justified on the grounds that the problem is broken down to low complexity linear and quadratic programming sub-problems. The overall adopted concept is in line with the C-RAN architecture for the fronthaul of 5G hybrid networks.
چکیده
1-مقدمه
2- پیشینه
3- کارهای مرتبط
3-1- معماری فای وای
3-2- رویکردهای تخصیص منبع برای شبکه های هیبرید
4- بهینه سازی چندمرحله ای برای تخصیص منبع
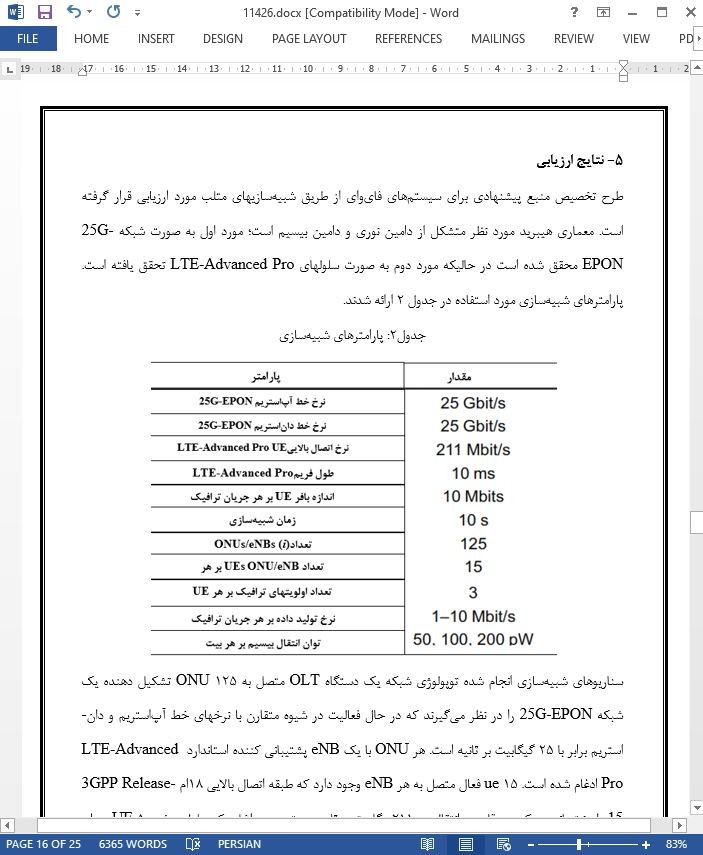
5- نتایج ارزیابی
6- نتیجه گیری
Abstract
1 Introduction
2 Background
3 Related work
3.1 FiWi architectures
3.2 Resource allocation approaches for hybrid networks
4 Multi-stage optimisation for resource allocation
5 Evaluation results
6 Conclusion
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه