توسعه فناوری ها برای انجام محاسبات مه در سیستم های اینترنت اشیا مرتبط با بخش سلامت
چکیده
موضوع: معماری محاسبات مِه دارای توزیع جغرافیایی است و بر این اساس انواع مختلفی از دستگاههای گوناگون در هر مکانی به این شبکه متصل میگردد تا باعث ایجاد ارتباطات یکپارچه متنوع و انعطافپذیر، محاسبه، و دستگاههای ذخیرهسازی گردد. محاسبات مِه دارای مزیتهای زیادی بوده و برای برنامههای کاربردی مناسب است که در آنها زمان واقعی، زمان واکنش سریع، و تاخیر کم، به ویژه در حوزه سلامت دارای اهمیت بالایی است. اهداف: هدف از این پژوهش، معرفی پژوهشهای پیشین نظامند در مورد فناوریهای محاسبات مِه در حوزه سیستمهای IOT بخش سلامت و تحلیل موضوعات آن است. همچنین به تعریف انگیزه، و محدودیتهایی که محققان با آن روبرو میشوند، و پیشنهادات ارائه شده به تحلیلگران برای بهبود این حوزه پژوهشی مهم پرداخته میشود. روشها: این پژوهشها به صورت نظامند در مورد محاسبات مِه در بخشهای مراقبت بهداشتی توسط مطالعات دیگر صورت میگیرد؛ همچنین از چندین سایت علمی بانک اطلاعاتی (WoS) همچون ساینسدایرکت ، کتابخانه دیجیتال IEEE ، و اسکوپوس بین سالهای 2007 تا 2017 مورد استفاده قرار گرفته است تا به تجزیه و تحلیل این طرح، برنامههای کاربردی، و ارزیابی عملکرد آن بپردازیم.
1. مقدمه
چند نمونه از سرویسهای اینترنت اشیا (IOT) همچون منابع محاسباتی، قابلیت ذخیرهسازی، ناهمگنی، پردازش بالا، و موارد دیگر که باعث ایجاد تحول فناوری میگردد، توسط محاسبات ابری انجام میگیرد. این محاسبات ابری منجر به مجازیسازی منابع محاسباتی در سطوح مختلف میگردد. تقریبا تمام حوزههای زندگی بشر با محاسبات ابری وفق پیدا کرده است [2]. به هر حال، محاسبات ابری دارای موانعی از نقطهنظر تاخیر بالا است که دارای تاثیرات معکوسی روی فعالیت IOT دارد که این خود نیازمند پاسخ در زمان واقعی است. علاوه بر این، محاسبات ابری در تطبیق با با سیستمهای کنترل صنعتی که مستلزم زمان پاسخ با کمترین تاخیر میباشد، نیست. [1]. در سال 2012، شرکت سیسکو ، الگوی زیرساختی را تحت عنوان محاسبات مِه معرفی نمود، که به عنوان یک مفهوم محاسباتی جدید به منظور ردیابی محدودیتهای محاسبات ابری است [3].
7. درسهای فراگرفته شده
مباحث زیادی در ارتباط با محاسبات مِه آموخته شده است. بدون شک محاسبات مِه، در مقایسه با محاسبات ابری باعث کاهش تاخیر در سیستمهای IOT بخش سلامت میگردد. پژوهشگران نشان دادهاند که شبیهسازی و نسبتهای تجربی، مزایای زیادی را همچون پردازش توزیعی، حریم خصوصی، امنیت، مقیاسپذیری، تحمل خطا، و تاخیر کم ایجاد میکند. این مزایا برای سیستم مانیتورینگ نشانههای حیاتی بیمار، مفید است، که مستلزم قابلیت اطمینان، تحرکپذیری، شناخت بافت، و پردازش در زمان واقعی است.
Abstract
Context: A fog computing architecture that is geographically distributed and to which a variety of heterogeneous devices are ubiquitously connected at the end of a network in order to provide collaboratively variable and flexible communication, computation, and storage services. Fog computing has many advantages and it is suited for the applications whereby real-time, high response time, and low latency are of the utmost importance, especially healthcare applications. Objectives: The aim of this study was to present a systematic literature review of the technologies for fog computing in the healthcare IoT systems field and analyze the previous. Providing motivation, limitations faced by researchers, and suggestions proposed to analysts for improving this essential research field. Methods: The investigations were systematically performed on fog computing in the healthcare field by all studies; furthermore, the four databases Web of Science (WoS), ScienceDirect, IEEE Xplore Digital Library, and Scopus from 2007 to 2017 were used to analyze their architecture, applications, and performance evaluation.
1. Introduction
A number of IoT services, such as computation resources, storage capabilities, heterogeneity, high processing, and others that brought a technological revolution, are provided by cloud computing. The cloud provides the virtualization of computing resources at various levels [1]. Almost all the human life domains have adopted cloud computing [2]. However, cloud computing has drawbacks in terms of high delays which have an adverse effect on the IoT tasks that require a real-time response. Furthermore, it does not match industrial control systems which require a lowdelay response time [1]. In 2012, Cisco announced an infrastructure paradigm called fog computing, which is a new computing concept, so as to tackle the limitations of cloud computing [3].
7. Learned lessons
Numerous lessons related to fog computing have been learned. Fog computing, without a doubt, decreased latency in contrast to cloud computing in healthcare IoT systems. Researchers show that simulation and experimental proportions provide many advantages such as distributed processing, privacy, security, scalability, fault tolerance, and low latency. These advantages are beneficial for vital signs patient monitoring systems, which demand substantial reliability, mobility, context awareness, and processing in realtime.
نکات
چکیده
1. مقدمه
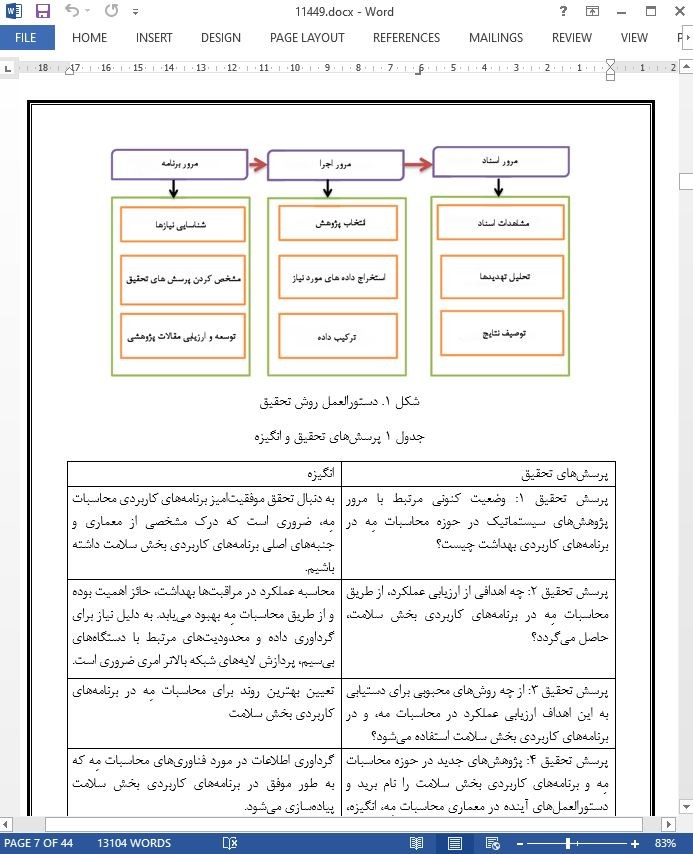
2. روش تحقیق
2.1 منایع اطلاعات
2.2 انتخاب مورد پژوهشی
2.3 جستجوی SLR
2.4 معیار شایستگی انتخاب
2.5 نتایج جستجوی مقاله
3. محاسبات مِه در سیستمهای IOT بخش سلامت
4. مقالات مرتبط
4.1 روشها
4.2 توسعه سیستم
4.3 مرور و بررسی
5. محدودیتها
6. بحث و موضوعات پیرامونی
6.1 ارزیابی عملکرد
6.2 انگیزه
6.3 چالشها و موضوعات
6.4 پیشنهادات
7. درسهای فراگرفته شده
8. نتیجهگیری
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Research methodology
2.1. Sources of information
2.2. Study selection
2.3. The SLR search
2.4. Eligibility criteria
2.5. Article search results
3. Fog computing in healthcare IoT systems
4. Related works
4.1. Methods
4.2. System development
4.3. Review and survey
5. Limitations
6. Discussion and open issues
6.1. Performance evaluation
6.2. Motivation
6.3. Challenges and issues
6.4. Recommendations
7. Learned lessons
8. Conclusion
- اصل مقاله انگلیسی با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه