ارزیابی تاثیر محیطی و عملکرد مقاومت بلند مدت شیار شدگی فناوری های ترکیب آسفالت گرم
چکیده
استفاده از فناوری های ترکیب آسفالت گرم (WMA) بدلیل وجود مزایای موثر محیطی به خوبی پذیرفته شده اند. به هر حال، عملکرد بلند مدت میدانی این چسباننده به خوبی درک نشده است. تاکید این مقاله متمرکز بر مقاومت بلند مدت شیار شدگی ترکیب آسفالت گرم (WMA) وترکیب آسفالت داغ (HMA) همراه با آن بر اساس 83 نمونه میدانی گردآوری شده از 28 پروژه میدانی در آمریکا در چهار ناحیه آب و هوایی و همچنین تاثیرات محیطی اندازه گیری شده برای فناوریهای مختلف آسفالت گرم مرکب (WMA) در مقایسه با آسفالت ترکیب داغ (HMA) می باشد. هسته های میدانی در حالت های دینامیک با استفاده از ارزیابی تطابق خزش و آزمایش های ابزار ردیابی چرخ هامبورگ ارزیابی شده اند. چسباننده آسفالت بدست آمده از هسته های میدانی با درجه بندی پیوسته عملکرد (PG)، بازیابی خزش تنش های متعدد (MSCR) و آزمایشات کشش مونوتونیک ارزیابی شده اند. نتایج نشان داد که چسباننده ترکیب آسفالت گرم (WMA) دارای مقاومت شیارشدگی مشابه با چسباننده ترکیب آسفالت داغ(HMA) بعد از فرسایش بلند مدت هستند. وجود پلیمر در چسباننده آسفالت ار طریق نمودار تطابق خزش قابل بازیابی و بازیابی درصدی نمایش داده می شود. چسباننده پلیمر اصلاح شده با قدمت بلند مدت در ترکیب آسفالت گرم (WMA) و ترکیب آسفالت داغ (HMA) قابل مقایسه هستند. همچنین نتایج نشان داد که کاهش دی اکسید کربن با استفاده از ترکیب آسفالت گرم(WMA) با توجه به نوع ماده ترکیب آسفالت گرم (WMA) در بازه 89.09 تا 42.79% قرار می گیرد. به طور میانگین، انتشار دی اکسید کربن با استفاده از فناوریهای ترکیب آسفالت گرم (WMA) با کاهش 66.98 درصدی همراه است. در نهایت، نتایج تحلیل تاثیر محیطی و عملکرد بلند مدت تائید کننده استفاده مطمئن از فناوریهای ترکیب آسفالت گرم (WMA) می باشد.
5. نتیجه گیری ها
این تحقیق به ارزیابی تاثیرات محیطی فناوری ترکیب آسفالت گرم(WMA) در مقایسه با ترکیب آسفالت داغ (HMA) برای 28 پروژه میدانی در آمریکا و همچنین مقاومت شیار شدگی در برابر تغییرات دائمی چسباننده ترکیب آسفالت گرم(WMA) و ترکیب آسفالت داغ (HMA) و مصالح دانه ای مختلف آسفالت بر اساس 83 نمونه میدانی پرداخته است. نتایج این تحقیق برای انتخاب آزمایش ها و ویژگی های مناسب جهت توصیف مقاومت در برابر تغییرات دائمی چسباننده مختلف آسفالت ها مفید می باشند. یافته های اصلی این تحقیق به صورت زیر خلاصه می شوند:
• با توجه به نوع چسباننده ترکیب آسفالت گرم(WMA)، کاهش CO2 در بازه 89.09 تا 42.79% قرار می گیرد. به طور میانگین، انتشار دی اکسید کربن می تواند با استفاده از فناوری چسباننده ترکیب آسفالت گرم(WMA) کاهش 66.89 درصدی داشته باشد.
Abstract
The adoption of warm mix asphalt (WMA) technologies is well accepted due to its promising environmental benefits, however, their long-term field performance is not well understood. This study focused on the long-term rutting resistance of WMA and their companion hot mix asphalt (HMA) based on 83 field samples collected from 28 field projects across the United States covering four climate zones, and quantified environmental impacts for various WMA technologies as compared to HMA. Field cores were evaluated by dynamic modulus, creep compliance, and Hamburg wheel-tracking device tests. Asphalt binders extracted from field cores were evaluated by continuous performance grading (PG), multiple stress creep recovery (MSCR), and monotonic shear tests. The results showed that WMA binders exhibited similar rutting resistance compared with the HMA binders after long-term field aging. Existence of polymer in the asphalt binder was displayed through the plot of non-recoverable creep compliance and percent recovery. The long-term field aged polymer modified asphalt binders for WMA and HMA were comparable. The results also showed that the CO2 reduction by using WMA ranged from 89.09% to 42.79% depending on WMA type. On average, the CO2 emission was reduced to 66.89% by using WMA technologies. Overall, environmental impact analysis and long-term field performance results validated the confident use of WMA technologies.
5. Conclusions
This study evaluated the environmental impacts of WMA technologies as compared to HMA for 28 field projects across U.S., as well as permanent deformation resistance for extracted HMA and WMA binders and asphalt mixtures based on 83 field samples. The outcome of this study would be helpful to select appropriate testing and properties to characterize long-term permanent deformation resistance for various asphalt materials. The major findings in this study are summarized as follows:
Depending on the WMA type, the CO2 reduction ranged from 89.09% to 42.79%. On average, the CO2 emission could be reduced to 66.89% by using WMA technologies.
چکیده
1.مقدمه
2. اهداف
3.روش شناسی تحقیق
3.1 توصیف پروژه و گردآوری چسباننده
3.2 تاثیر فناوریهای ترکیب آسفالت گرم بر تولید دی اکسید کربن
3.3 توصیف چسباننده
4. نتایج و بحث
1-4. نتایج آزمایش PG چسباننده و مصالح دانه ای
2-4. نتایج آزمایش MSCR
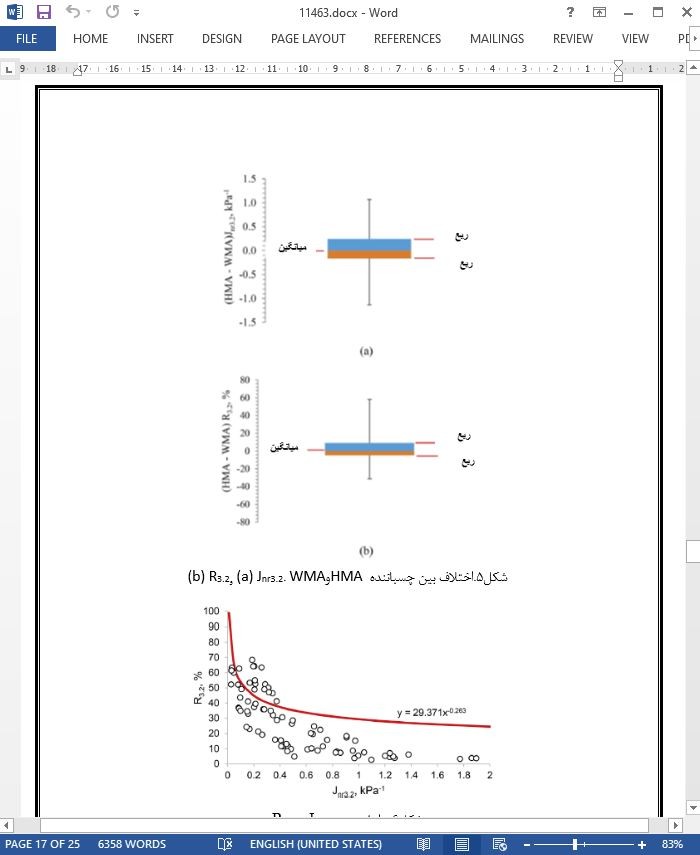
3-4. رابطه بین Jnr3/2 و R3/2
4.4 نتایج آزمایش ترکیبات هسته های میدانی
5-4. همبستگی ویژگی های چسباننده و ویژگیهای مصالح دانه ای آسفالت
4.6 همبستگی میان ویژگیهای چسباننده
4.7 تحلیلی تاثیر محیطی
5. نتیجه گیری ها
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Objectives
3. Research methodology
3.1. Project description and material collections
3.2. Effect of WMA technologies on the production of CO2
3.3. Material characterization
4. Results and discussions
4.1. Extracted binders’ PG test results
4.2. MSCR test results
4.3. Relationship between Jnr3.2 and R3.2
4.4. Field cores mixtures test results
4.5. Correlation of binders’ properties and asphalt mixtures’ properties
4.6. Correlation among binders’ properties
4.7. Environmental impact analysis
5. Conclusions
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه