مدل LOGMAN: مدلی منطقی در مدیریت برند
چکیده
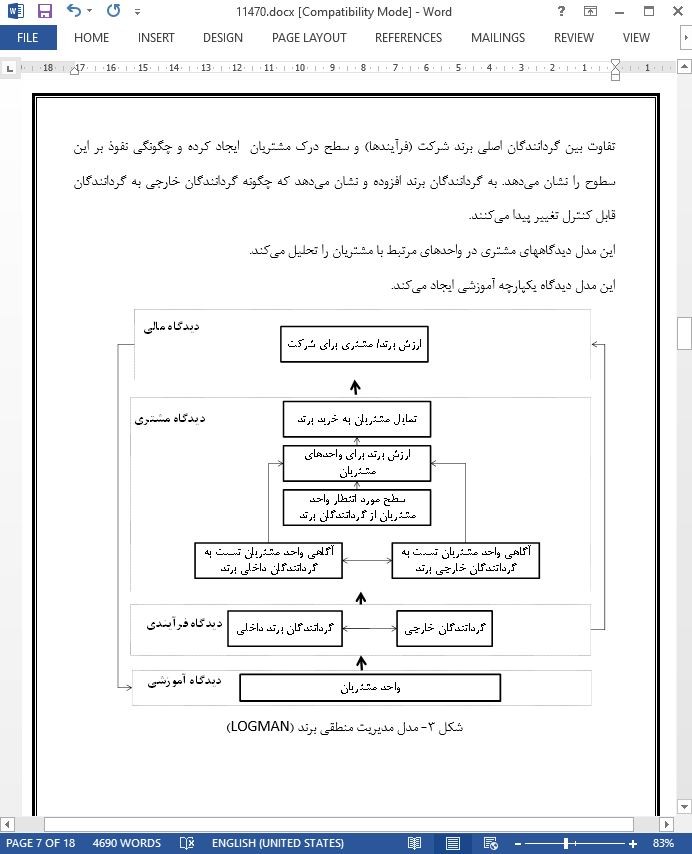
مدلی که ماهیت پویا و انفعالی مدیریت برند را ترکیب میکند؛ ارائه شده است. این مدل، مدل مدیریت منطقی برند نام دارد که بصورت اختصاری مدل LOGMAN شناخته میشود. بصورت اختصاصی این مدل مفاهیم روش کارت امتیاز متوازن Norton و Kaplan، روش تولید ارزش برند BCG، روش تحلیل مسیر، روش تحلیل فاصله، روش مکانی برای کیفیت QFD را ترکیب میکند. این مدل امکان بررسی ثبات یک برند منطقی را در چند سطح فراهم میکند. این مدل میزان آگاهی مشتری از گرداننده برند شرکت یا گردانندگان خارجی برند و اینکه آیا با اهداف برند شرکت هم راستا هستند یا خیر را مشخص میکند. بعلاوه این مدل ثبات منطقی مقررات برند شرکت در برابر انواع مشتریان و در طول زمان را ارزیابی میکند.
1- مقدمه
بازارهای کنونی بسیار آشفته و ناپایدار هستند. این مسئله تنها نیازمند تطبیق نقاط قوت و ضعف با فرصت ها و خطرات واقعی نیست بلکه نیازمند سرهم بندی (مقام و شایستگی هایی که پیوسته در حال تغییر هستند (Eisenhart و Brown 1999) نیز هست. این مسئله تنها به مکان قرارگیری شرکت یا کاری که انجام میدهد؛ محدود نمیشود بلکه چگونگی تغییر آن را بررسی میکند (Eiswnhart و Sull 2001). Saounders و همکاران در خلاصه ای از مطالعه بر برنامه ریزی بازاریابی، مشاهده کردند که طراحی بازاریابی راهبردی، به سازمانها در تطبیق با محیط کمک میکند.
چالش پیش روی تحقیقات آتی
کاملا مشخص است که روشی یکسان جهت یکپارچه سازی روش های متفاوت، نمیتواند در سطح مدیریت منطقی برند اعمال شود اما در سطح مدیریت بازاریابی راهبردی (مشارکتی) امکان بکارگیری آن وجود دارد. برای مثال تحلیل توانمندی ها، ساختار سازمانی و تحلیل عملکرد که گاهی بخشی از آنالیز درونی برنامه بازاریابی راهبردی است؛ وابسته به دیدگاه آموزش و رشد در روش کارت امتیاز متوازن است. تحلیل خارجی برنامه بازاریابی راهبردی با دیدگاه فرآیند خارجی و دیدگاه مشتری هم راستا است. بخش ماهرانه طرح بازاریابی راهبردی (ترکیب فعالیت های بازاریابی)، به دیدگاه فرآیند داخلی مرتبط است. راهبرد کلی و ارزیابی طرح بازاریابی استراتژیک وابسته به مقیاس های مورد استفاده در سطح هر چهار دیدگاه است.
Abstract
Proposes a model that combines the proactive and reactive nature of brand management. It is called the logical brand management model, abbreviated to the LOGMAN model. More specifically it combines insights from: Kaplan and Norton's balanced scorecard method; BCG's brand value creation method; the path analysis method; the gap analysis method; and the house of quality (QFD) method. It allows one to perform a logical brand consistency audit at several levels. It evaluates whether customer perceptions of the company's brand drivers and the external brand drivers are in line with the company's brand objectives. Furthermore, it analyzes the logical consistency of the company's brand policy across multiple customer segments and over time.
Introduction
Today’s markets are very turbulent and unstable. This not only asks for “matching” strengths/weaknesses with the actual opportunities/threats, but also for “patching” (continuously changing portfolios and competencies) (see Eisenhardt and Brown, 1999). It is not only about where a company should be or what it should be, but also about how it should proceed (Eisenhardt and Sull, 2001). In their epilogue (summary) of a special issue on exploring marketing planning, Saunders et al. (1996) observe that strategic marketing planning should help organizations to cope better with the environment.
Challenge for future research
It is quite obvious that a similar exercise in integrating different methods cannot only be applied at the brand management level, but also at the strategic (corporate) marketing management level. For instance, the analysis of competencies, organizational structure and performance analysis, which often form part of the internal analysis of a strategic marketing plan, are related to the learning and growth perspective in the balanced scorecard. The external analysis of the strategic marketing plan can be related to the customer and external process perspective. The tactical part of a strategic marketing plan (marketing mix actions) can be related to the internal process perspective. The overall strategy and the evaluation of a strategic marketing plan are related to measures used at the four perspective levels.
چکیده
مقدمه
توصیف روشهای متفاوت (اساس مدل مدیریت منطقی برند)
مدل LOGMAN: مدلی جهت مدیریت منطقی برند
مفاهیم: سازگاری منطقی در چند سطح
چالش پیش روی تحقیقات آتی
Abstract
Introduction
Explanation of the different methods (underlying the logical brand management model)
The LOGMAN model: a logical brand management model
Implications: logical consistency at several levels
Challenge for future research
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه