آیا تجدید سازمان دارایی های مادی بر هزینه های تامین مالی استقراضی شرکت های اکتساب کننده تاثیر می گذارد؟
چکیده
در مقاله حاضر، ما به بررسی تاثیرگذاری سازمان های مجدد دارایی های مادی (MAR) که شکل خاصی از معاملات ادغام و اکتساب (M&A) می باشد بر هزینه های تامین مالی استقراضی شرکت های اکتساب کننده می پردازیم. افزون بر این، ما تاثیر کیفیت اطلاعات حسابداری شرکت های اکتساب کننده را بر هزینه استقراض و ارتباط بین MAR و هزینه های استقراض را مورد بررسی قرار می دهیم. ما پیش بینی نمودیم که در مقایسه با M&A متعارف، اکتساب های مقیاس بزرگ از طریق MAR منجر به ورود بیشتر دارایی ها از شرکت های هدف می شود. این امر باعث افزایش دارایی های قابل وثیقه شرکت های اکتساب کننده و در نتیجه کاهش هزینه استقراض می گردد. از آنجایی که کیفیت اطلاعات حسابداری، عامل کلیدی موثری بر هزینه استقراض محسوب می شود، ما نشان دادیم که کیفیت اطلاعات حسابداری بر تاثیر هزینه استقراض MAR اثر سرریز دارد. با استفاده از معاملات M&A شرکت های ثبت شده در بازار سهام A چین از 2008 تا 2014 به عنوان نمونه خود، ما دریافتیم که MAR با دارایی های قابل وثیقه بالاتر و هزینه های استقراض تحقق یافته کمتری نسبت به M&A متعارف همراه است. افزون بر این، ما نشان دادیم که کیفیت اطلاعات حسابداری شرکت های اکتساب کننده تاثیر منفی و معنی داری بر هزینه های استقراض داشته و ارتباط منفی بین MAR و هزینه استقراض هنگامی که کیفیت اطلاعات حسابداری بالاتر باشد، بیشتر اعلام می شود.
1. مقدمه
معاملات ادغام و اکتساب (M&A) مبحث بسیار گسترده ای در تحقیقات بازارهاي سرمايه محسوب می شود. تحقیقات علمی اولیه عمدتاً بر انگیزه انجام M&A از جمله دستیابی به هم افزایی کسب و کار، تثبیت موقعیت بازار و ایجاد یک امپراتوری تجاری متمرکز شده اند (جنسن و روبک، 1983؛ مولین، 1995؛ مارتینووا و رنبوگ، 2006). ادبیات اخیر بر ارزش ثروت زایی معاملات M&A در بازارهای سهام متمرکز شده و عوامل تعیین کننده ایجاد ارزش را مورد بررسی قرار می دهد (ژانگ، 2003؛ مارتینووا و رنبوگ، 2011؛ کای و سویلیر، 2012؛ تیان و همکاران، 2013؛ چن و همکاران، a2013؛ کراوت، 2014؛ ماتیو، 2017). با این حال، تحقیقات اندکی درباره پیامدهای اقتصادی M&A در بازارهای استقراضی وجود دارد. در مقاله حاضر، ما به بررسی تاثیرگذاری احتمالی سازماندهی مجدد دارایی های مادی (MAR) که شکل خاصی از معاملات M&A است بر هزینه های تامین مالی استقراضی شرکت های اکتساب کننده و نحوه تاثیر آن می پردازیم.
6. نتیجه گیری
در مقاله حاضر ما بررسی نمودیم که آیا MAR (به عنوان شکل خاصی از معامله M&A) با هزینه های تامین مالی استقراضی شرکت های اکتساب کننده ارتباط دارد. با نمونه ای از معاملات M&A شرکت های ثبت شده در بازار سهام A چین، دریافتیم که اجرای MAR شرکت هیا اکتساب کننده را قادر به کسب جریان عظیمی از دارایی های شرکت های هدف و دارایی های قابل وثیقه قابل توجه می نماید که این امر باعث کاهش هزینه های تامین مالی استقراضی شرکت های اکتساب کننده می گردد. نتایج ما به آشکارسازی پیامدهای اقتصادی معاملات M&A کمک نموده و بر غنای ادبیات کنونی درباره تامین مالی استقراضی می افزاید. هم چنین مقاله حاضر نقش کیفیت اطلاعات حسابداری را در بازار M&A نیز مورد بررسی قرار می دهد. ما نشان دادیم که کیفیت اطلاعات حسابداری شرکت های اکتساب کننده تاثیر معنی داری بر هزینه های تامین مالی استقراضی آن ها دارد. این نتیجه بر اساس مطالعاتی است که ارتباط منفی را بین کیفیت اطلاعات حسابداری و هزینه های استقراضی نشان دادند. افزون بر این، ما دریافتیم که اثر MAR بر هزینه های تامین مالی استقراضی تحقق یافته برای شرکت های اکتساب کننده ای که کیفیت اطلاعات حسابداری بالاتری دارند، قوی تر است. این نتیجه نشان دهنده اثر سرریز کیفیت اطلاعات حسابداری در شرایط M&A بوده و به آشکارسازی مکانیزم تقویتی MAR در هزینه استقراض کمک می کند.
Abstract
In this paper, we investigate whether material asset reorganizations (MARs), a special form of merger and acquisition (M&A) transactions, can affect the acquirers’ cost of debt financing. Further, we examine the effect of acquiring firms’ accounting information quality on the cost of debt and on the association between MARs and debt costs. We predict that compared to conventional M&As, large-scale acquisitions through MARs can generate a much greater influx of assets from target firms. This raises the acquirers’ asset collateral and thus reduces the cost of debt. Because the quality of accounting information is a key factor affecting the cost of debt, we suggest that it has a spillover effect on the debt-cost effect of MARs. Using M&A transactions by listed companies in the Chinese A-share market from 2008 to 2014 as our sample, we find that MARs are associated with a higher asset collateral and lower ex post cost of debt than conventional M&As. Furthermore, we show that the acquiring firms’ accounting information quality has a significant negative effect on debt costs, and the negative association between MARs and the cost of debt is more pronounced when accounting information quality is higher.
1. Introduction
Merger and acquisition (M&A) transactions are a widely discussed issue in research on capital markets. Earlier academic research mainly focuses on the motivation for conducting M&As, including obtaining business synergies, consolidating market position, and building a ‘‘commercial empire” (Jensen and Ruback, 1983; Mullin, 1995; Martynova and Renneboog, 2006). The recent literature focuses on whether M&A transactions create wealth value in stock markets, and explore the determinants of this value-creation (Zhang, 2003; Martynova and Renneboog, 2011; Cai and Sevilir, 2012; Tian et al., 2013; Chen et al., 2013a; Kravet, 2014; Mateev, 2017). However, there is little research on the economic consequences of M&As in debt markets. In this paper, we investigate whether and how material asset reorganizations (MARs),1 a special form of M&A transactions, can affect acquirers’ ex post debt financing costs.
6. Conclusion
In this paper, we investigate whether MARs (as a special form of M&A transaction) are related to acquiring firms’ debt financing costs. Using a sample of listed companies’ M&A transactions in the Chinese A-share market, we find that MAR implementation can enable the acquirers to obtain a massive inflow of assets from target firms and gain significant asset collateral, and this can decrease the acquirers’ debt financing costs. Our results help to reveal the economic consequences of M&A transactions and enrich the current literature on debt financing. This paper also examines the role of accounting information quality in the M&A market. We show that acquiring firms’ accounting information quality has a significant negative effect on their debt financing costs. This result builds on studies that find a negative relationship between accounting information quality and debt costs. In addition, we find that the effect of MARs on the ex post cost of debt financing is stronger for acquiring firms that have higher quality accounting information. This result indicates the spillover effect of accounting information quality in the M&A setting, and helps to reveal the reinforcing mechanism of the MARs on debt cost.
چکیده
1. مقدمه
2. بررسی ادبیات
2.1. انگیزه و ایجاد ارزش معاملات M&A
2.2. عوامل تعیین کننده هزینه های تامین مالی استقراضی
3. توسعه فرضیه
4. طرح پژوهش
4.1. انتخاب نمونه و منابع داده ها
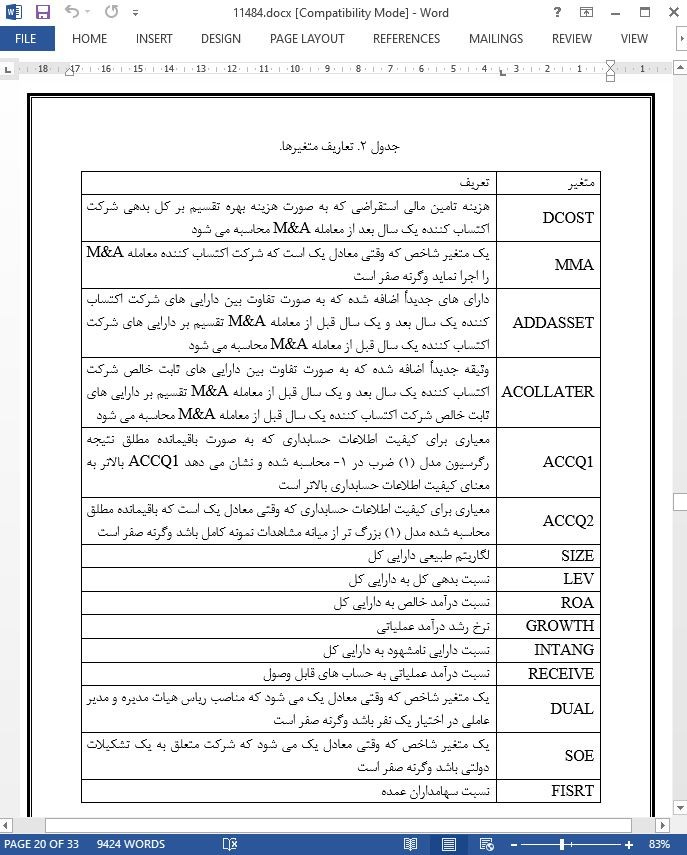
4.2. اندازه گیری متغیر
4.3. مدل های تجربی
5. نتایج تجربی
5.1. آماره های توصیفی
5.2. MAR و هزینه استقراض: نتایج آزمون H1a، H1b و H1c
5.3. کیفیت اطلاعات حسابداری شرکت های اکتساب کننده و هزینه استقراض: نتایج آزمون H2
5.4. اثر تعدیل کننده کیفیت اطلاعات حسابداری: نتایج آزمون H3
5.5. آزمون های استحکام
6. نتیجه گیری
ABSTRACT
1. Introduction
2. Literature review
2.1. The motivation and value-creation of M&A transactions
2.2. The determinants of debt financing costs
3. Hypothesis development
4. Research design
4.1. Sample selection and date sources
4.2. Variable measurement
4.3. Empirical models
5. Empirical results
5.1. Descriptive statistics
5.2. Mars and debt cost: The test results of H1a, H1b and H1c
5.3. Acquiring firms’ accounting information quality and debt costs: The test results of H2
5.4. Moderating effect of accounting information quality: The test results of H3
5.5. Robustness tests
6. Conclusion
- اصل مقاله انگلیسی با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه