تاثیر تولید پراکنده بر روی حفاظت سیستم قدرت
چکیده
تقاضای برق روز به روز در حال افزایش است؛ بنابراین ما بهمنظور تحقق این تقاضا نیاز داریم تا تولید انرژی را بیشتر کنیم. بهدلیل این افزایش تقاضا، منابع انرژی تجدیدناپذیر در آستانهی انقراض قرار دارند، بنابراین برای حل این مشکل، بایستی از منابع انرژی تجدیدپذیر استفاده نمود. یکی از مشکلات اتصال DG، وجود منابع انرژی تجدیدپذیر بر روی یک سیستم قدرت میباشد. اما اضافه نمودن DG دارای اثر مشخصی بر روی یک سیستم قدرت نیز میباشد.
این پژوهش به ارزیابی اثر DG بر روی حفاظت سیستم قدرت میپردازد. کار ارائه شده در این پژوهش شامل شبیهسازی سیستم قدرت شعاعی در نرمافزار PSCAD /EMTDC بوده است. در این شبیهسازی، خطای جریان و بار جریان مورد بررسی قرار گرفته است. تأثیر DG بر روی خطای جریان تحت تأثیر خطای LG، LL و LLLG در حالت حاوی و بدون محافظت مورد مطالعه قرار گرفته است. در حالت خطای LLLG، حداکثر مقدار خطای جریان مشاهده شده است. تأثیر محدودکنندهی خطای جریان مقاومتی نیز بر روی مقدار خطای جریان بررسی شده است. هم DG و هم منبع در برابر خطای جریان با استفاده از محافظت جریان زیاد به ترتیب با انتخاب مقدار 2kA و 4kA محافظت میشوند.
1- مقدمه
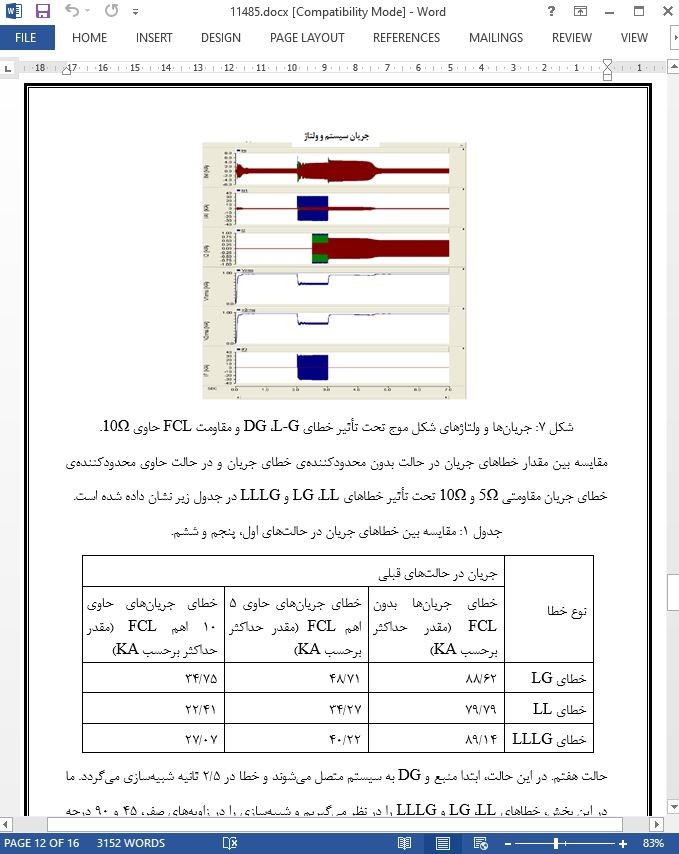
عملکرد سیستم توزیع بهوسیلهی تولید پراکنده در روشهای متنوع تحت تأثیر قرار میگیرد. در حالتیکه DG با انرژی تجدیدپذیر برای کم نمودن اثر محیط زیستی تولید انرژی ارتباط پیدا کند، نشاندهندهی یک هدف بزرگ برای DG در آینده میباشد. سیستم DG باعث بهبود پروفیل ولتاژ میشود، اما باعث اختلال در تنظیم ولتاژ میگردد ]1[، ]2[. اگر DG نزدیک به بار متصل گردد، تلفات در یک مدار میتواند بهحداقل برسد. سیستم موجود با تولید در ایستگاه توزیع بر روی دستگاه تغذیهکنندهی شعاعی سر و کار ندارد، بنابراین اینگونه سیستم برای مدیریت این انرژی که بایستی به منبع فرستاده شود، طراحی نگردیده است. از اینرو، اثر قابلتوضیح بر روی عملیات محافظت موجود ممکن است بر روی هم قطع نادرست و هم بر روی دستگاههای محافظ غیرعملیاتی که محتمل میباشند، رخ دهد ]3[.
8- نتیجهگیری
حضور تولید پراکنده ممکن است سبب افزایش خطاهای جریان حتی بیش از ظرفیت مدارشکن شود. بنابراین انتظار میرود که دستگاههای محافظت موجود دارای تنش الکتریکی بیشتری نسبت به معمولیها باشند.
حالتهای ارائه شده در این پژوهش نشان میدهد که اضافه کردن DG بهوسیلهی موتور القایی باعث ایجاد جریان میگردد که هم منبع و هم DG در این حالت مشارکت دارند. همچنین مشاهده شده است که مشارکت DG بر روی خطا با اضافه نمودن DG باعث بیشتر شدن مقدار خطای جریان گردیده است. با استفاده از محافظت بیش از حد جریان لحظهای، هم منبع و هم DG محافظت شدهاند.
Abstract
Day by day demand of Electricity is increasing so, in order to fulfill this demand we need to increase generation of power. Because of this increasing demand, non-renewable energy sources are on the verge of extinction so the solution is to use renewable energy sources. One such solution is to connect DG having renewable energy sources in power system. But the insertion of DG has some impact on a power system.
This paper deals with the evaluation of the impact of DG on the protection of power system. The work presented in this paper consists of a simulation of a radial power system in PSCAD /EMTDC software. Monitoring of both fault current and the load current is done in the simulation. The impact of DG on fault current under the influence of LG, LL and LLLG fault with and without protection is studied Maximum magnitude of fault current is found in case of LLLG fault. Also, the impact of resistive fault current limiter on the magnitude of fault current is studied. Both DG and source is protected from fault current by using overcorrect protection with pick up value of 2kA and 4kA respectively.
I. Introduction
The performance of distribution system is affected by distributed generation in various ways. As DG is related to renewable energy for lowering the environmental impact of power generation indicate a large scope for DG in future. DG improves voltage Profile but interfere with voltage regulation [1],[2]. The losses in a circuit can be minimized if DG is connected near to the load. The existing system did not deal with generation at distribution substation on radial feeder so such system where not designed to handle such power would be sent back to the source. Hence, accountable effect on the operation of existing protection may occur both false tripping and non-operations of protective devices are possible [3].
VIII. CONCLUSION
The presence of Distributed Generation may cause higher fault currents that are over the breaking capacity of circuit breakers. Therefore, existing protection devices are exposed to more electrical stress than normal.
The cases presented in this paper shows that by adding DG the current drawn by the induction motor is contributed by both source and DG. Also, the DG contributes to the fault so it is found that magnitude of fault current increases with the insertion of DG. By providing instantaneous overcurrent protection both source and DG are protected.
چکیده
1- مقدمه
2- تولید پراکنده
3- انواع تولید پراکنده
الف) فتو ولتائیک
ب) توربین بادی
ج) پیلهای سوختی
د) میکرو توربینها
ه) ماشینهای دوار
4- اثر تولید پراکنده بر سیستم قدرت
الف) تأثیر DG بر روی تنظیمکنندهی ولتاژ
ب) تأثیر DG بر روی تلفات
ج) تأثیر DG بر روی هارمونیکها
د) تأثیر DG بر روی سطحهای اتصال کوتاه شبکه
5- تأثیر تولید پراکنده بر روی محافظت
الف) قطع نادرست تغذیهکننده
ب) مشکلات قطع تغذیهکننده
ج) جزیرهای شدن ناخواسته
6- سیستم مورد مطالعه
7- شبیهسازی نتایج
8- نتیجهگیری
9- ضمیمه
Abstract
I. Introduction
II. Distributed generation
III. Types of Distributed Generation
A. Photo voltaic
B. Wind Turbine
C. Fuel Cells
D. Micro-Turbines
F. Rotating Machines
IV. Impact of Distributed Generation on Power System
A. Impact of DG on Voltage Regulation
B. Impact of DG on Losses
C. Impact of DG on Harmonics
D. Impact of DG on Short Circuit Levels of the Network
V. Impact of Distributed Generation on Protection
A. False Tripping of feeder
B. Nuisance Tripping Of Feeder
C. Unintentional Islanding
VI. System under Study
VII. Simulation Results
VIII. CONCLUSION
IX. APPENDIX
- اصل مقاله انگلیسی با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه