تحقیق قیاسی فیزیوتراپی رایج و فیزیوتراپی روباتی برای آموزش راه رفتن در افراد مبتلا به اختلال آتاکسی بعد از سکته
اهداف : ارزیابی تاثیر RAGT بر تعادل – هماهنگی و استقلال فعالیت های روزمره افراد متاثر از سکته حاد و مبتلا به آتاکسی در بازه حداقل یک سال بعد از سکته .
روش ها : این تحقیق یک تحقیق کنترل شده تصادفی است. هر کدام از بیماران برنامه درمان آموزش های راه رفتن با کمک تراپیست TAGT و آموزش راه رفتن با کمک روبات RAGT را دریافت می کنند. هر دو گروه 3 جلسه فیزیوتراپی در هفته را با مدت تخمینی 60 دقیقه برای هر جلسه دریافت می کنند و ورزش خانگی برای آنها تجویز می شود.
شاخص های زیرقبل و بعد از تکمیل دوره 5 ماهه درمان ارزیابی می شوند : BBS – SARA – آزمون TUG و FIM . برای انجام مقایسه داخل گروه ، آزمون ویلکوسان مورداستفاده قرار می گیرد و از آزمون مان ویتنی برای مقایسه بین گروه استفاده می شود.
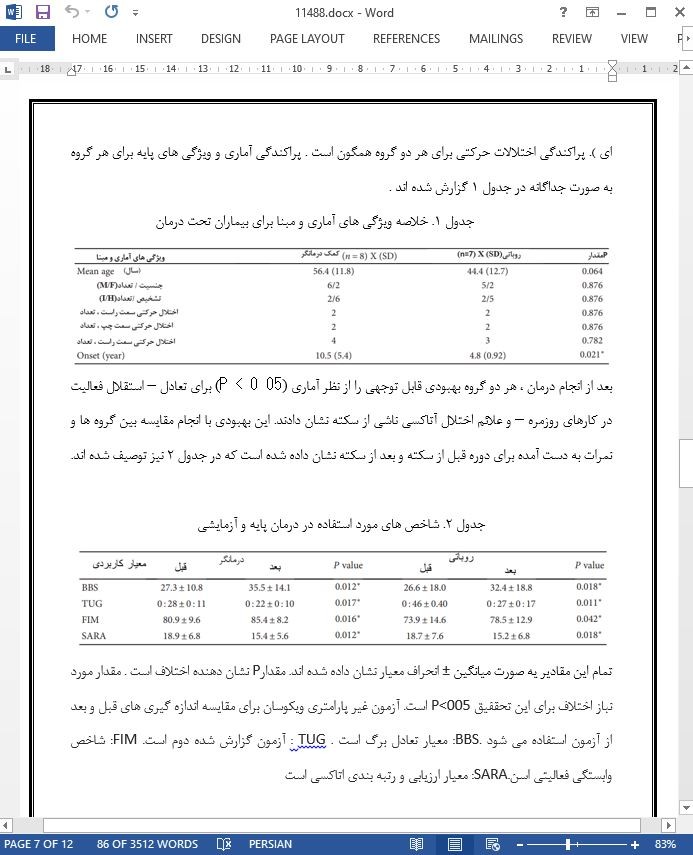
نتایج : 19 بیمار نبتلا به اختلال آتاکسی ناشی از سکته حاد بعد از یک سال از سکته در تحقیق شرکت کرده اند.هر دو گروه بهبودی قابل توجه (P < 0 05) در تعادل – استقلال فعالیت و علائم عمومی آتاکسی را نشان داده اند . اختلاف آماری قابل توجه (P < 0 05) برای مقایسه های بین گروه در مبنا و بعد از تکمیل دوره درمان مشاهده نشده است.
نتیجه گیری ها : بیماران دارای اختلال آتاکسی ناشی از سکته حاد بهبودی قابل توجه در تعادل و استقلال در فعالیت های روزمره را بعد از تکمیل دوره درمان RAGT و درمان مرسوم و ورزش های خانگی نشلن می دهند. این آزمایش با شماره ثبت39862414.6.0000.5505. ثبت شده است.
5. نتیجه گیری ها
این تحقیق نتیجه گیری می کند که بیماران مبتلا به اختلال آتاکسی ناشی از سکته ، بعد از درمان با RAGT همراه با اقدامات مرسوم و ورزش ، بهبود قابل توجه در تعادل و استقلال در فعالیت های روزمره نشان داده اند. برای تعداد کم نمونه ها ، نتایج بدون در نظر گرفتن روش های RAGT یا TAGT مشابه هستند. هر دو روش درمانی باید به عنوان گزینه ای در برنامه توانبخشی تعادل بیماران مبتلا به اختلال آتاکسی در نظر گرفته شوند.
Objectives. To assess the influence of RAGT on balance, coordination, and functional independence in activities of daily living of chronic stroke survivors with ataxia at least one year of injury.
Methods. It was a randomized controlled trial. The patients were allocated to either therapist-assisted gait training (TAGT) or robotic-assisted gait training (RAGT). Both groups received 3 weekly sessions of physiotherapy with an estimated duration of 60 minutes each and prescribed home exercises. The following outcome measures were evaluated prior to and after the completion of the 5-month protocol treatment: BBS, TUG test, FIM, and SARA. For intragroup comparisons, the Wilcoxon test was used, and the Mann–Whitney test was used for between-group comparison.
Results. Nineteen stroke survivors with ataxia sequel after one year of injury were recruited. Both groups showed statistically significant improvement (P < 0 05) in balance, functional independencein, and general ataxia symptoms. There were no statistically significant differences (P < 0 05) for between-group comparisons both at baseline and after completion of the protocol.
Conclusions. Chronic stroke patients with ataxia had significant improvements in balance and independence in activities of daily living after RAGT along with conventional therapy and home exercises. This trial was registered with trial registration number 39862414.6.0000.5505.
5. Conclusions
This study concluded that chronic stroke patients with ataxia sequela had a significant improvement in balance and independence in activities of daily living after treatment with RAGT along with conventional therapy and home exercises. For this sample size, the outcomes were similar regardless of the applied treatment strategy, that is, RAGT or TAGT. Both treatment approaches should be included as options in balance rehabilitation programs for ataxic patients.
1. مقدمه
2. روش ها
2.1 شرکت کننده ها
2.2 پروتکل ارزیابی
2.3 پروتکل آموزش
2.4 تحلیل آماری
3. نتایج
4. بحث
5. نتیجه گیری ها
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Subjects
2.2. Evaluation Protocol
2.3. Training Protocol.
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- اصل مقاله انگلیسی با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه