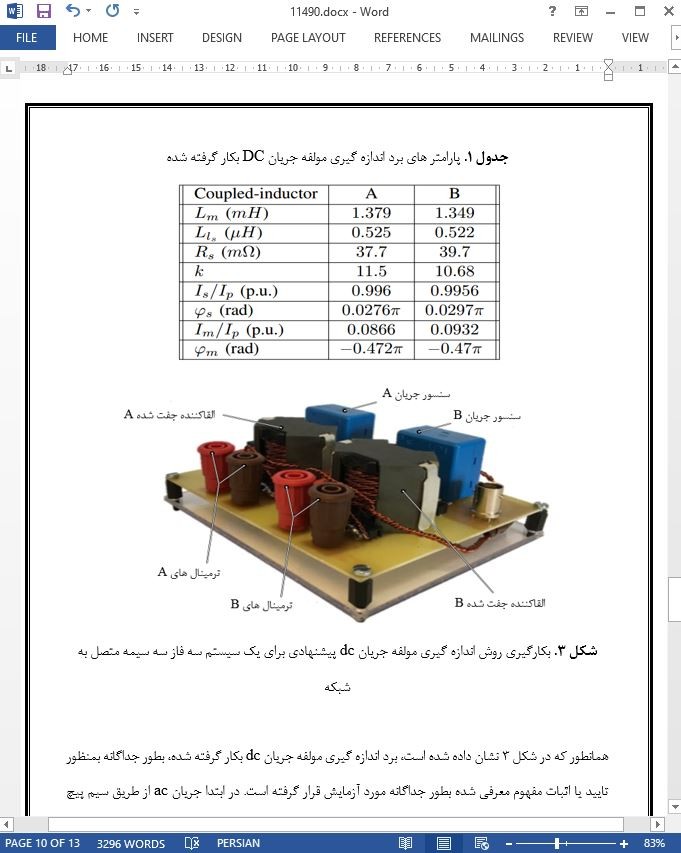
القا کننده جفت شده بر مبنای روش اندازه گیری جریان مستقیم برای مبدل های بدون ترانسفورماتور متصل به شبکه
چکیده
مبدلهای فتوولتائیک (PV) متصل به شبکه باید چندین تقاضا را برآورده کنند، این تقاضا ها شامل کارایی بالا و کاهش هزینه و پیچیدگی سیستم کلی میباشد. از این رو عملیات بدون ترانسفورماتور برای دستیابی به تقاضا های ذکرشده مفید میباشد. در ضمن، چنین عملیاتی منجر به ناکارامدی های متعددی مانند تزریق مولفه جریان مستقیم به داخل شبکه میشود، این مولفه باید بمنظور اجتناب از برخی اثرات مانند اشباع ترانسفورماتور ها در شبکه توزیع، بطورموثری کاهش یابد. از سوی دیگر محدود کردن این مولفه تا چند میلیآمپر با توجه به خطای اندازهگیری مختلف، یک مشکل چالش برانگیز میباشد. بر این اساس، روشهای مختلف مسدود سازی و اندازهگیری پیشنهاد شده جهت غلبه بر این مشکل مورد مطالعه قرار گرفته است، که برخی از معایب در کنار هر روش، مانند پیچیدگی پیادهسازی، مشکلات ولتاژ حالت مشترک و فیلتر مورد نیاز زیاد مشاهده میشوند. علاوه بر این، هیچکدام از آنها مستقیما مولفه dc را اندازهگیری نمیکنند، اما با استفاده از روشهای مختلف، مقدار آن را پیشبینی میکنند. از اینرو، این مقاله یک روش جدید برای اندازهگیری مولفه dc با دقت بالا، با استفاده از القاکننده جفتشده همراه با حسگر جریان اثر هال با رنج کم بمنظور دستیابی به حداقل هزینه ههکن با حداکثر دقت ممکن را پیشنهاد میدهد. این روش پیشنهادی بمنظور بررسی و تایید اصل عملیات مورد بررسی، تجزیه و تحلیل قرار گرفته و بصورت تجربی آزمایش شدهاست. همچنین اندازهگیری تجربی مولفه جریان مستقیم با استفاده از مبدل منبع ولتاژ (VSI) متصل به شبکه بدون ترانسفورماتور 5 کیلوولتآمپر با و بدون روش پیشنهادی به منظور تایید عملیات، توصیف شده است.
نتیجه گیری
این مقاله روش اندازه گیری مولفه جریان dc بر مبنای القاکننده جفت شده را برای مبدل های بدون ترانسفورماتور های متصل به شبکه پیشنهاد کرد. مزیت های در کنار این روش، هزینه کم، سادگی و دقت بالا می باشد. در همین حال، حسگر های جریان اضافی مورد استفاده قرار می گیرند، این حسگر ها دارای رنج یا دامنه کوچکی می باشند. برخلاف همه روش های اندازه گیری مرسوم، روش اندازه گیری پیشنهاد شده قادر به اندازه گیری مولفه dc خود می باشد، یعنی مقدار آن از آفست dc اندازه گیری شده بین خروجی های مبدل را پیش بینی نمی کند. روش اندازه گیری پیشنهاد شده بصورت آزمایشی تایید شد و در یک مبدل منبع ولتاژ 5 کیلو ولت آمپر سه فاز سه سیمه بدون ترانسفورماتور متصل به شبکه آزمایش شد که در آن مولفه dc بطور موثر از 60 میلی آمپر به 2 میلی آمپر، کاهش یافت.
Abstract
Grid-tied photovoltaic inverters must fulfill several requirements, including high efficiency and reduced cost and complexity of the overall system. Hence, transformerless operation is advantageous in order to achieve the prior requirements. Meanwhile, such operation results in several demerits, such as the dc current component injection into the grid. This component should be effectively mitigated in order to avoid some impacts, such as the saturation of the transformers in the distribution network. On the other hand, limiting this component up to few milliamperes is a challenging issue due to the various measurement errors. Accordingly, different blocking and measurement techniques have been proposed and studied to overcome this issue, where some demerits are seen behind each technique such as the implementation complexity, the common-mode voltage problems, and the high filter requirements. Moreover, none of them measures the dc component directly, but predicts its value using different approaches. Hence, this letter proposes a new technique to measure this dc current component with high accuracy using a coupled inductor combined with a small-range Hall effect current sensor in order to achieve the lowest possible cost with the highest possible accuracy. The proposed technique is introduced, analyzed, and tested experimentally to verify its principle of operation. Also experimental measurement of the dc current component using a 5-kVA transformerless grid-tied voltage-source inverter is introduced with and without the proposed technique in order to validate its operation.
V. CONCLUSION
This paper has proposed a coupled-inductor-based dc current component measurement technique for transformerless grid-tied inverters. The merits behind this method are low cost, simplicity, and high accuracy. Meanwhile, additional current sensors are used, but these sensors has a small range. Unlike all the conventional measurement techniques, the proposed one is able to measure the dc component itself, i.e. it does not predict its value from the measured dc offset between the inverter outputs. The proposed measurement technique is verified experimentally and tested in a 5 kV A three-phase three-wire transformerless grid-tied voltage source inverter, in which the dc component has been effectively reduced from 60 mA to 2 mA.
چکیده
1. مقدمه
2.روش اندازهگیری جریان DC پیشنهاد شده
3. طرح کنترل مبدل PV در حالت متصل به شبکه با روش پیشنهادی
4. تایید یا اثبات تجربی
5.نتیجه گیری
Abstract
I. INTRODUCTION
II. PROPOSED DC CURRENT MEASUREMENT TECHNIQUE
III. PV INVERTER CONTROL SCHEME IN GRID-TIED MODE WITH THE PROPOSED TECHNIQUE
IV. EXPERIMENTAL VERIFICATION
V. CONCLUSION
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه