آیا قانون بنفورد می تواند حقوق ماهیانه مدیر عامل را شرح دهد؟
چکیده
مسئله / موضوع تحقیق. این پژوهش ویژگی های آماری قانون بنفورد را برای حقوق ماهیانه مدیر عامل بکار می گیرد. "قانون" بنفورد بیان می دارد که در یک مجموعه داده بی طرفانه، با توجه به انتظارات منطقی توزیع برابر، مقادیر اول رقم معمولا نابرابر هستند. در این پژوهش سؤال این است که آیا ویژگی های تجربی منطقی قانون بنفورد می تواند برای تجزیه و تحلیل قدرت مذاکره و اولويتهاي مدیران عامل استفاده شود با خیر. ما استدلال می کنیم که حقوق و دستمزد تعیین شده بر اساس عملکرد و یا بازار باید از قانون بنفورد پیروی کند و هیچ مذاکره مستقیمی از مدیران عامل وجود ندارد. برعکس، انحراف از قانون بنفورد می تواند قدرت و یا حتی اولویت مذاکره مدیران عامل را آشکار نماید.
یافته ها/ بینش تحقیق. تجزیه و تحلیل ما نشان می دهد که "گزینش ارزش منصفانه" مبتنی بر بازار(ارزش دلاری گزینه های سهام زمانی که مورد استفاده قرار می گیرند) ، بر خلاف"حقوق" که به طور کامل مورد مذاکره قرار می گیرد،با قانون بنفورد مطابقت زیادی دارد. "پاداش"، "گزینه جایزه " و " حقوق و دستمزد کلی" نیز عموماً با قانون بنفورد مطابقت دارند، اما با بعضی استثنائات. ما این استثنائات را به عنوان مذاکره مدیران عامل تفسیر می کنیم. به طور شگفت انگیز، ما دریافتیم که مدیران عامل ترجیح می دهند مقادیر عددی گرد شده، به ویژه به سمت 5پرداخت شود. ما از قانون بنفورد برای مطالعه قدرت های مذاکره مدیران عامل در مقابل مدیران دیگر استفاده می کنیم. در نهایت، ما تاکتیک های مذاکره مدیران عامل را قبل و بعد از SOX مقایسه می کنیم و تاثیر اندازه شرکت ها بر حقوق و دستمزد آنها را تحلیل می کنیم.
دستاوردهای تئوری / علمی. این پژوهش قانون بنفورد و کاربردهای آن را در متون تحقیقاتی حاکمیت سازمانی معرفی می نماید.
دستاورد های متخصصان / سیاست پژوهش. این پژوهش می تواند توسط دانشگاهیان، صنایع و قانونگذاران برای کشف الگوهای حقوق و دستمزد در بخش های بزرگ کسب و کار و / یا سازمان ها و یا حتی کل بخش های صنعت استفاده شود.
7. نتیجه گیری و محدودیت هاي پژوهش
در این پژوهش، ما با پیشنهاد استفاده از قانون بنفورد در توضیح حقوق ماهانه مدیر عامل در متون تحقيقاتي در مورد نحوه حاكميت شركتهاي بزرگ مشاركت نموديم. در بخش اول تجزیه و تحلیل، ما ثابت نموديم که قانون بنفورد روش مناسبي برای تمایز بین حقوق مبتنی بر عملکرد و یا مرتبط با بازار و يا حقوق و دستمزد مستقیم بواسطه مذاکره است. پس از اثبات اثربخشی آن استفاده از قانون بنفورد را براي آزمودن برخي مسائل جالب توجه مربوط به حقوق و دستمزد مديران اجرایی پیشنهاد نموديم. بنابراين در بخش دوم پژوهش تجربی خود قانون بنفورد را برای روشن شدن سه مسئله مرتبط اعمال نموديم ، یعنی (1) آیا اختلافي بین قدرت مذاكره در مورد حقوق و دستمزد مدیران عامل و سایر مدیران اجرایی وجود دارد يا خير؟ (2) آیا بين تاکتیکهاي مذاکره حقوق و دستمزد مدیران عامل قبل و بعد از پیاده سازی SOX تفاوتي وجود دارد؟؛ و (3) آیا بین مدیران عامل شرکت های کوچک و مدیران عامل شركتهاي بزرگ در نحوه مذاكره براي حقوق و دستمزد ثابت آنها تفاوتي وجود دارد؟
Abstract
Research Question/Issue This study applies the statistical properties of Benford's Law to CEO pay. Benford's “Law” states that in an unbiased dataset, the first digit values are usually unequally allocated when considering the logical expectations of equal distribution. In this study we question whether the striking empirical properties of Benford's Law could be used to analyze the negotiating power and preferences of CEOs. We argue that performance‐based or market‐ determined compensations should follow Benford's Law, demonstrating no direct negotiation by the CEOs. Conversely, deviation from Benford's Law could reveal CEO negotiating power or even preference.
Research Findings/Insights Our analysis shows that market‐determined “Option Fair Value” (the dollar value of stock options when exercised) conforms closely to Benford's Law, as opposed to “Salary”, which is fully negotiated. “Bonus”, “Option Award”, and “Total Compensation” are generally also largely consistent with Benford's Law, but with some exceptions. We interpret these exceptions as negotiation by the CEOs. Surprisingly, we found that CEOs prefer to be paid in round figure values, especially “5”. We use Benford's Law to study the negotiating powers of CEOs vs. that of other executives. Finally, we compare the negotiating tactics of CEOs before and after SOX and analyze the impact of firm size on their compensation.
Theoretical/Academic Implications This study introduces Benford's Law and its applications within the corporate governance literature.
Practitioner/Policy Implications This method could be used by academics, industry and regulators to uncover compensation patterns within large business departments and/or organizations or even entire industry segments.
7 | CONCLUSIONS AND LIMITATIONS
In this study, we contributed to the corporate governance literature by proposing the usage of Benford's Law in explaining CEO pay. In the first part of the analysis, we established that Benford's Law is a suitable method for differentiating between performance‐based or market‐linked pay and directly negotiated compensation. Having proven its effectiveness, we next proposed the usage of Benford's Law in testing some interesting executive compensation‐related problems. In the second part of our empirical study we therefore applied Benford's Law to shed light on three specifically related issues, namely (1) Is there a difference between the compensation negotiating powers of CEOs and those of Other Executives?; (2) Is there a difference between the compensation negotiating tactics of CEOs before and after the implementation of SOX; and (3) Is there a difference between small‐firm CEOs and large‐firm CEOs in the way in which they negotiate their fixed compensation?
چکیده
1. مقدمه
2. مطالعه حقوق ماهانه مدیر عامل شرکت با استفاده از قانون بنفورد
2 .1. قانون بنفورد
2 .2. قانون بنفورد در عمل
3. چارچوب تحلیلی و فرضیههاي تحقيق
4. داده هاي پژوهش
5. روش پژوهش
6. تجزيه و تحلیل عملي
6 .1. متغیرهای حقوق و دستمزد از سود
6. 2. خلاصه آماري
6. 3. آيا قانون بنفورد می تواند حقوق ماهانه مدیر عامل را توضيح دهد؟
6. 4. برخی کاربردهای دیگر قانون بنفورد با استفاده از داده های حقوق ماهیانه مدیر عامل شرکت
7. نتیجه گیری و محدودیت هاي پژوهش
Abstract
1 .INTRODUCTION
2 .STUDYING CEO PAY USING BENFORD'S LAW
2.1 .Benford's Law
2.2 .Benford's Law in practice
3 .ANALYTICAL FRAMEWORK AND HYPOTHESES
4 .DATA
5 .METHODOLOGY
6 .EMPIRICAL ANALYSIS
6.1 .Compensation variables of interest
6.2 .Summary statistics
6.3 .Can Benford's Law explain CEO pay?
6.4 .Some other applications of Benford's Law using CEO pay data
7 . CONCLUSIONS AND LIMITATIONS
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
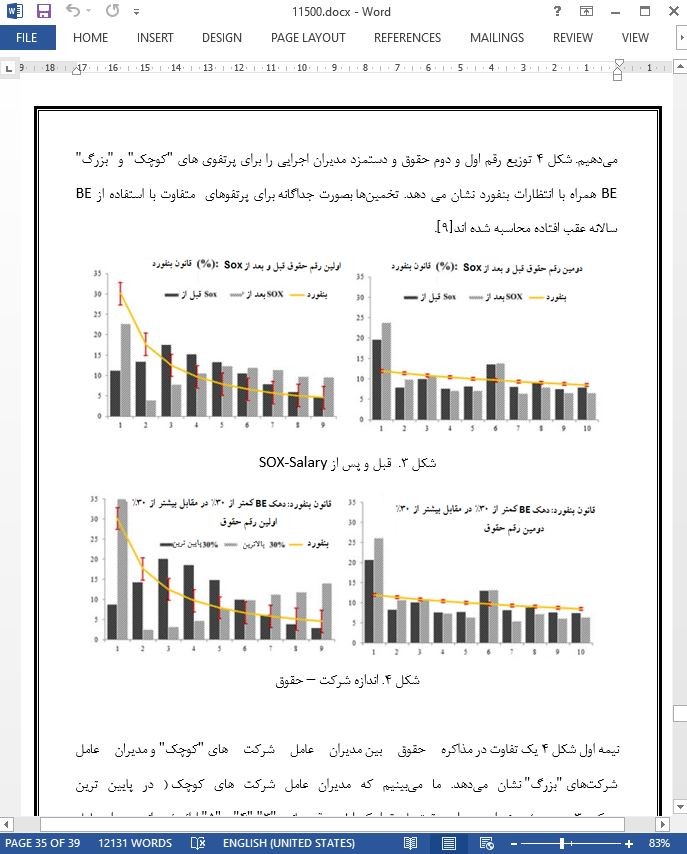
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه