خرده فروشی لوکس تا چه حدی میتواند هوشمند باشد؟
چکیده
هدف این مقاله، بررسی نحوه استفادۀ برندهای لوکس از فن آوریهای جدید در زمینه خرده فروشی هوشمند است. تجزیه و تحلیل ما بر اساس دادههای کیفی بدست آمده از صنایع لوکس متعدد، نشان میدهد که این بخش نسبت به مزایای استفاده از فن آوریهای هوشمند به عنوان یک ابزار بازاریابی آگاهی دارد، در حالی که استفاده مؤثر از این فن آوریها در سیستمهای نوآورانه هنوز محدودیتهایی دارد. با این حال، هنوز هم مطالعات اندکی درباره نیروهای نوآوری تاثیرگذار بر صنعت خرده فروشی در بخشهای لوکس وجود دارد. این مطالعه، با ارائه یک نوآوری تجربی برای عنوان نوظهور خرده فروشی هوشمند و بررسی دقیق آن در مورد استفاده از فن آوریهای هوشمند توسط شرکتهای مورد مطالعه، بر بخش لوکس تاکید میکند.
1. مقدمه
در سالهای اخیر، صنعت خرده فروشی شاهد افزایش روزافزون فن آوریهایی بوده است که قادر به بهبود فرایندها هستند، و در عین حال مشتریان را سرگرم میکنند (Dacko، 2017، Demirkan و Spohrer، 2014؛ Hristov و Reynolds، 2015؛ Kumar و همکاران، 2014؛ Pantanoو همکاران، 2017؛ Willems و همکاران، 2017). این فن آوریها را میتوان به سه دسته اصلی تقسیم کرد: (i) فن آوریهای دیجیتال که شامل رسانههای اجتماعی و کانالهای آنلاین برای تجارت الکترونیک هستند (Gao و همکاران، 2013؛ Groß، 2015؛ Hsiao، 2009؛ Pantano و Verteramo، 2015)؛ (ii) فن آوریهای موبایل که شامل نرم افزارهای کاربردی موبایل برای خرده فروشان هستند (برای مثال، نرم افزار Hermés برای دستیابی به هماهنگی مطلوب بین کراوات و پیراهن) (Pantano و Priporas، 2016؛ Varnali و Toker، 2010)؛ و (iii) فن آوریهای گسترده/فراگیر درون فروشگاهی که شامل ibeaconها، ویترینها و نمایشگرهای تعاملی و غیره هستند (Pantano و Verteramo، 2015؛ Papagiannidis و همکاران 2017).
5. بحث و نتیجه گیری
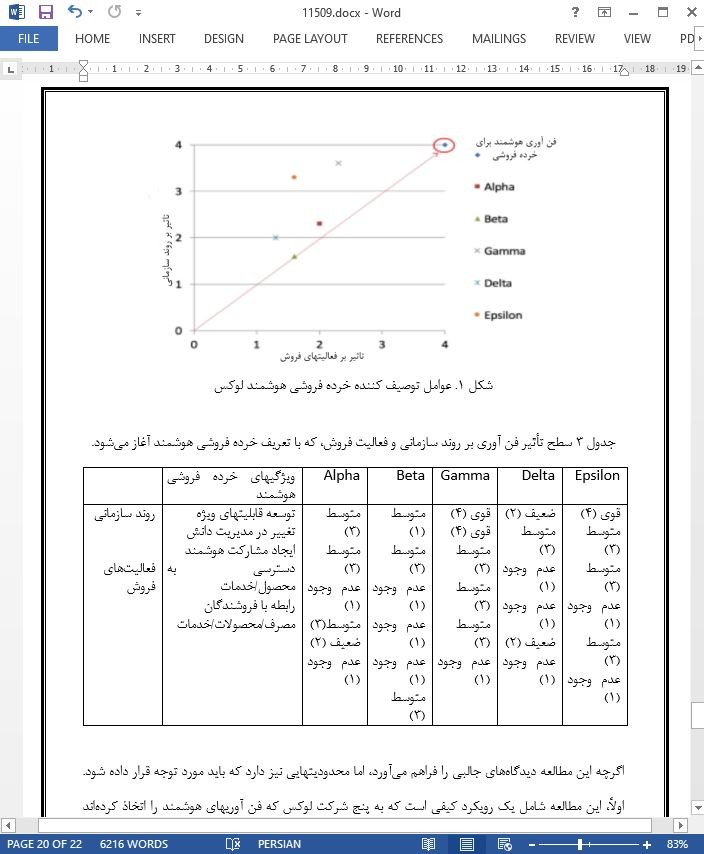
با توجه به جدول 3، استراتژیهای خرده فروشی هوشمند در شرکتها را میتوان بر یک سیستم دکارتی x y قرار داد، در نظر داشته باشید که x سطح تأثیر فن آوری بر فعالیتهای فروش، و y سطح تأثیر بر روند سازمانی است (شکل 1).
از آنجاییکه هیچ یک از شرکتهای مورد بررسی، در واقع به تاثیرگذاری قوی بر تمام مؤلفههای خرده فروشی هوشمند دست نمییابند، ما ممکن است فرض کنیم که خرده فروشی هوشمند کار مناسبی است، اما هنوز به دلیل کمبود فن آوریهای هوشمندی که بتوانند بر فعالیتهای فروش و روند سازمانی تأثیر بگذارند (آنها را بهبود بخشند)، مورد تأیید قرار نگرفته است. در واقع، تنها یک شرکت در جهت معرفی فن آوریهای پشتیبانی کننده از یک فرایند هوشمند سرمایه گذاری میکند که تاکنون به تأثیر قدرتمندی بر هر دو مؤلفه خرده فروشی هوشمند دست یافته است. در واقع، فن آوریهای پذیرفته شده، به شدت عوامل مختلف را تحت تأثیر قرار میدهند، اما نه بطور همزمان، بنابراین خرده فروشی ممکن است با وجود یک فن آوری تاثیرگذار بر همه آنها بطور همزمان، به یک خرده فروشی هوشمند تبدیل شود.
Abstract
The aim of this paper is to explore how luxury brands use new technologies in the context of smart retailing. Building on qualitative data from multiple cases from the luxury industry, our analysis reveals that this sector is conscious of the benefits of using smart technologies as marketing tools, while the effective use of these innovative systems is still limited. However, studies on innovation forces affecting the retail industry are still limited in luxury sectors. The study provides an empirical contribution to the emerging topic of smart retailing with an emphasis on the luxury sector through its in-depth investigation of the usage of smart technologies by the firms studied.
1. Introduction
In recent years, retail industry has witnessed an increasing number of technologies able to largely improve processes while entertaining consumers (Dacko, 2017; Demirkan and Spohrer, 2014; Hristov and Reynolds, 2015; Kumar et al., 2014; Pantano et al., 2017; Willems et al., 2017). These technologies can be classified into 3 main typologies: (i) digital technologies, which include social media and the online channel for e-commerce (Gao et al., 2013; Groß, 2015; Hsiao, 2009; Pantano and Verteramo, 2015); (ii) mobile technologies, which include retailers’ mobile app (i.e. Hermés app to find the perfect match between the tie and the shirt) (Pantano and Priporas, 2016; Varnali and Toker, 2010); and (iii) immersive/pervasive in-store technologies, which include ibeacons, interactive storefronts and displays, etc. (Pantano and Verteramo, 2015; Papagiannidis et al., 2017).
5. Discussion and conclusion
Drawing upon Table 3, companies’ smart retailing strategies might be placed on a Cartesian system x y, considering x the level of influence of the technology on selling activities and y the level of influence on the organizational process (Fig. 1).
Since none of the investigated companies are actually reaching a strong influence on all the components of smart retailing, we might assume that smart retailing is suitable but not yet adopted, due to the lack of smart technologies influencing (improving) selling activities and organizational process. Indeed, only one company is investing towards the introduction of technologies supporting a smart process, achieving so far, a strong impact on two of the components of smart retailing. Indeed, the adopted technologies strongly influence different factors, but not simultaneously, thus retailing might be smart with a technology able to influence all of them at the same time.
چکیده
1. مقدمه
2. پیش زمینه نظری
2.1. خرده فروشی هوشمند
2.2. خرده فروشی لوکس
3. روش تحقیق
3.1. انتخاب مطالعه موردی
3.2. جمع آوری دادهها
4. یافتههای کلیدی
4.1. Alpha
4.2. Beta
4.3. Gamma
4.4. Delta
4.5. Epsilon
5. بحث و نتیجه گیری
ABSTRACT
1. Introduction
2. Theoretical background
2.1. Smart retailing
2.2. Luxury retail
3. Methodology of research
3.1. Selection of the case study
3.2. Data collection
4. Key findings
4.1. Alpha
4.2. Beta
4.3. Gamma
4.4. Delta
4.5. Epsilon
5. Discussion and conclusion
- اصل مقاله انگلیسی با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه