مطالعه یک ژنراتور القایی دو بار تغذیه شده با استفاده از مبدل ماتریس
چکیده
با توجه به رشد روز افزون الکترونیک قدرت، استفاده از نسل جدید مبدل های توان مورد توجه ویژه قرار گرفته است، مبدل ماتریس AC/AC که مبدل توان مستقیم AC/AC را فراهم می کند، جریان توان دو طرفه، شکل موج تقریبا سینوسی ورودی و خروجی. در این مقاله، ما به ارائه مطالعه عملکرد و کارایی توربین بادی با سرعت متغیر مبتنی بر ژنراتور القایی دو بار تغذیه شده توسط مبدل ماتریس با استفاده از روش ردیابی نقطه دارای حداکثر توان برای به دست آوردن حداکثر توان در دسترس، می پردازیم. کل سیستم در چهارچوب مرجع همگام d-q ارائه شد. طرح کنترل تست شده و عملکرد آن با استفاده از نتایج شبیه سازی مورد بررسی و ارزیابی قرار گرفت. نتایج شبیه سازی بدست آمده تحت سیمولینک نرم افزار متلب اثربخشی و اعتبار کنترل مورد نظر را نشان می دهد.
مقدمه
با شروع از اصل Lavoiser: هیچ چیز از دست نرفته است، هیچ چیز ایجاد نشده است، همه چیز تغییر پیدا کرده است. انرژی، به منزله موتور آثار یا پدیده های طبیعی می باشد و می تواند از شکلی به شکل دیگر تغییر پیدا کند. انرژی بادی یکی از پاک ترین منابع انرژی می باشد چراکه در حال تولید برق هیچگونه گاز گلخانه ای تولید نمی کند و همچنین باعث نامطلوب شدن کیفیت هوا نمی شود (هوا را آلوده نمی کند) و همچنین باعث آلودگی خاک و آب نیز نمی شود. علاوه بر این، زباله سمی یا رادیواکتیو نیز تولید نمی کند [5-1]. امروزه، با در نظر گرفتن افزایش آلودگی محیط زیست و اتمسفر، کوشش های زیادی در راستای ارتقا سطح سیستم های تبدیل انرژی باد یا WECS بمنظور کاهش هزینه ها و افزایش قابلیت اطمینان و اعتبار و همچنین استحکام، صورت گرفته است [6].
نتیجه گیری
در این مقاله، مدل سازی و کنترل سیستم مبدل باد مبتنی بر DFIG تغذیه شده توسط مبدل ماتریس در نظر گرفته شد. در حقیقت کنترل جداگانه این توان ها اجازه تنظیم مشخصه توان نصب و در نتیجه رسیدن به یک عملکرد مطلوب را می دهد. مدل زنجیره تبدیل انرژی بادی گسترش داده شده است و تکنیک ردیابی حداکثر نقطه توان بمنظور فراهم کردن تمامی توان فعال تولید شده به شبکه با مشخصه توان واحد اعمال شده است. نتایج شبیه سازی نشان می دهند که توان فعال و غیر فعال انرژی باد کیفیت بالایی را ارائه می دهد (دارای کیفیت بالایی می باشد).
Abstract
Due to the growing of the power electronics, especial attention has been given to the use of new generation of power converters, AC/AC matrix converter to which provide a direct power converter AC/AC, bi-directional power flow, almost sinusoidal input and output waveform. In this paper, we present the performance study of a variable-speed wind turbine based on doubly fed induction generator fed by matrix converter using the maximum power point tracking method to extract the maximum power available. The whole system is presented in d-q-synchronous reference frame. The control scheme is tested and the performances are evaluated by simulation results. The simulation results obtained under MatLab/Simulink show the effectiveness and validity of the considered control.
Introduction
Starting from the principle of Lavoisier: Nothing is lost, nothing is created, everything is transformed. Energy is the motor of natural phenomena, it can be transformed from one form to another. Wind energy is one of the cleanest sources of energy because while producing electricity it does not generate any gas greenhouse effect, does not degrade air quality and does not pollute soils or water. Furthermore, it does not produce toxic or radioactive waste [1e5]. Nowadays, Owing to the increasing pollution of environment and atmosphere, huge efforts have been made in promoting the wind energy conversion systems WECS to reduce costs and increase reliability and robustness [6].
Conclusion
In this paper, the modeling and control of wind conversion system based on DFIG fed by matrix converter has been considered. The fact of the control of these powers separately permits to adjust the power factor of the installation and in consequence obtain better performance. The model of wind conversion chain is developed and the technique of maximum power point tracking has been applied to provide all of the active power generated to the grid with unity power factor. The simulation results showed that the active and reactive power of the wind energy present a high quality.
چکیده
مقدمه
مدل سازی سیتم بادی
مدل سازی توربین بادی
مدل سازی بخش مکانیکی
مدل سازی DFIG
مدل سازی و کنترل مبدل ماتریس
ساختار کنترل
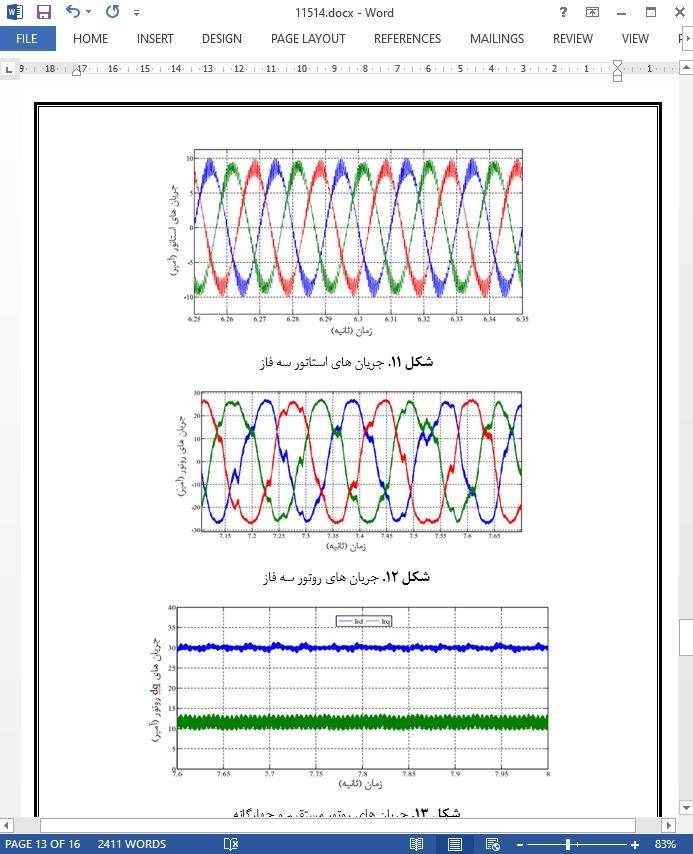
نتایج شبیه سازی
نتیجه گیری
فهرست علائم و اختصارات
Abstract
Introduction
Wind system modeling
Wind turbine modeling
Modeling of the DFIG
Modeling and control of matrix converter
Control structure
Simulation results
Conclusion
Nomenclature
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه