رفتار سازه ستون های فولادی مربعی شکل سرد با ضخامت دیواره بی نهایت
چکیده
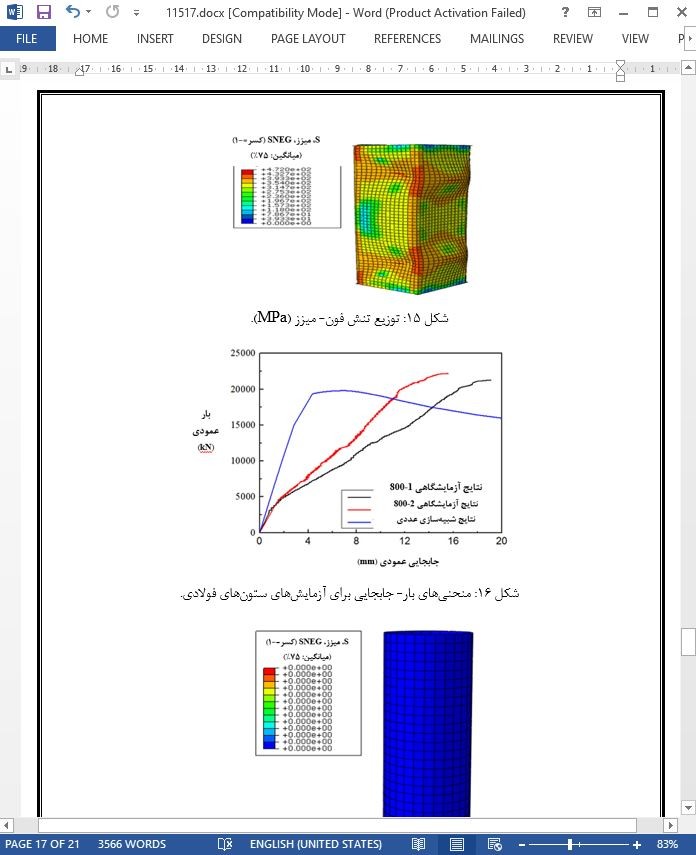
این پژوهش به بررسی ستون های مربعی شکل سرد با ضخامت دیواره بی نهایت پرداخته است که ستون ها از طریق دایره به شکل یک مربع تولید میشوند که دارای عرض 800 میلیمتر و ضخامت 22 میلیمتر میباشند. بررسی متقارن بودن رفتار ماده، توزیع تنش باقی مانده و عملکرد فشار محوری بهصورت عددی و تجربی مورد بررسی قرار گرفته است. نتایج به دست آمده نشان میدهد که (1) خواص مواد در ستون های سرد که از طریق روش غیرمستقیم تولید میشوند، بهدلیل انجام فرآیندهای سرد کاملا تغییر میکنند و نسبت به ستون های سرد که بهوسیله روش مستقیم تولید میگردند، بیشتر یکنواخت هستند. (2) ستون های مربعی شکل سرد با ضخامت دیواره بی نهایت تحت فشار محوری به صورت مطلوب کار میکنند. (3) تنش های باقی مانده در قسمت های میانه و گوشه ستون های مربعی شکل سرد با ضخامت دیواره بی نهایت تقریبا بهترتیب 95 و 210 Mpa میباشد.
1- مقدمه
از اجزای فولاد سرد به صورت گسترده در مهندسی عمران استفاده میشود، چون این فولادها دارای نسبت وزن به مقاومت زیادی می باشند؛ بهدلیل محدودیت های فنآوری شکلدهی سرد در مرحلهی اولیه، ضخامت آنها تقریبا بهصورت کلی به 3 میلیمتر محدود شده است. این ضخامت نسبت به مقطع فولادی نورد گرمشده بسیار نازکتر است. امروزه از مقطعهای شکلگرفتهی سرد با ضخامت دیوارهی بیشتر از 6 میلیمتر استفاده میشود که بهنام دیوارهی ضخیم شناخته میشوند، تولید آنها بسیار متداول میباشد و در مهندسی عمران مورد استفاده قرار میگیرند ]1[. آنها بهصورت متداول از شکلهای بسته مانند مقطعهای توخالی مربعی یا دایرهای ساخته میشوند و بهصورت گسترده در ستونهای ساختمانهای بلند استفاده میشوند. حداکثر اندازه برای مقطع توخالی مربعی شکل، دارای عرض 800 میلیمتر و ضخامت 22 میلیمتر میباشد؛ از این نوع مقطع در پروژهی مربع وانوی تیانجین در چین استفاده شده است.
6- نتیجهگیری
از طریق بررسی تجربی و تحلیل عددی رفتار فشار محوری در ستونهای مربعی شکل سرد با ضخامت دیوارهی بینهایت، نتیجهگیری زیر حاصل میگردد:
1) خواص مواد در ستونهای سرد مربعی که از طریق لولهی توخالی دایرهای شکل تولید میشوند، بهدلیل فرآیندهای سرد شدن بهصورت مشخص تغییر میکنند، خواص آنها نسبت به ستونهای سردی که توسط صفحات فولادی تولید میگردند، بیشتر یکنواخت میشود.
Abstract
This paper describes a study on the extreme thick-walled cold-formed square columns which are manufactured from circular to square shape, of which the width was 800 mm and the thickness was 22 mm. A systematic investigation of material behavior, residual stress distribution, and axial compression performance was performed numerically and experimentally. Results demonstrate thefollowing.1) The material properties of cold-formed columns manufactured by indirect method are clearly changed because of the cold-formed processes and are more uniform than those of cold-formed columns manufactured by direct method. 2)The extreme thick-walled cold-formed square columns work well under axial compression. 3) The residual stresses at the middle and corner parts of extreme thick-walled cold-formed square columnsareapproximately95 and 210 MPa, respectively.
1. Introduction
Cold-formed steel members are widely used in civil engineering because of their high strength-to-weight ratio; their thickness is generally limited to approximately3 mm because of the limitations of coldforming technology in the early stage. This thickness is much thinner than that of hot-rolled steel section. Nowadays, cold-formed sections with a wall-thickness greater than 6 mm, which are referred to as “thick-walled”, are more commonly manufactured and used in civil engineering [1]. They are commonly fabricated as closed shapes, such as circular or square hollow sections, and used increasingly in columns of high-rise buildings. The maximum size for the square hollow section is 800 mm wide by 22 mm thick; this type of section was used in the Tianjin Wanhui Square Project in China.
6. Conclusion
Through the experimental research and numerical analysis of the axial compression behavior of the extremely thick-walled cold-formed square columns, the following conclusions were obtained:
1) The material properties of square cold-formed columns manufactured from circular hollow tube change clearly due to the cold-formed processes; their properties are more uniform than that of cold-formed columns manufactured by steel plates.
چکیده
1- مقدمه
2- روش تجربی
2-1 طراحی نمونههای آزمایشی
2-2 ویژگی مکانیکی مواد
2-3 روشها و شرایط آزمایش
3- تحلیل نتایج آزمایشگاهی
4- شبیهسازی عددی
4-1 شبیهسازی عملکرد فشار محوری
4-2 شبیهسازی فرآیند شکلدهی
5- تحلیل پارامتر و فرمول محاسباتی ظرفیت فشار محوری
6- نتیجهگیری
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental scheme
2.1. Specimens design
2.2. Material mechanical property
2.3. Test conditions and procedures
3. Experimental results analysis
4. Numerical simulation
4.1. Axial compression performance simulation
4.2. Forming process simulation
5. Parameter analysis and calculation formula of axial compression capacity
6. Conclusion
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه