مدل سازی و بررسی استقامت شبکه های حمل و نقل ریلی با استفاده از شبکه های پتری زماندار
سیستم های حمل و نقل عمومی روز به روز اهمیت بيشتري مي يابند. این سیستم ها باید پاسخگوي تقاضاي فزاينده برای جابه جايي جمعیت و ازدحام ترافیکي باشند. شبکه های حمل و نقل ریلي می توانند به عنوان سیستم های رویداد گسسته (DES) با محدودیت هاي زماني در نظر گرفته شوند. عامل زمان یک پارامتر حیاتی است، زیرا شامل دادههايي است که باید به منظور جلوگيري از همپوشانی، تاخیر و برخورد بین قطارها لحاظ شوند. شبكههاي پتري زماندار به عنوان ابزارهاي قدرتمند مدل سازی و تجزیه و تحلیل برای سیستم های حمل و نقل ريلي شناخته شده اند. اختلالات زمانی در این سیستم ها شامل زیرساخت های ريلي، مدیریت ترافیک و اختلالات (آب و هوا، موانع در مسير، تخريب، جنبش اجتماعی، و غیره) است. پيشرفتهاي ارائه شده در این مقاله به مدل سازی و بررسی استقامت سیستم های حمل و نقل ريلي به منظور ارزیابی ثبات و کارایی این شبکه ها اختصاص داده شده اند. در این مقاله دو استراتژی قدرتمند کنترل در جهت اختلالات زماني ارائه شده است. اولین استراتژي شامل جبران این اختلال به محض مشاهده آن به منظور جلوگیری از نقض محدودیت ها است. دومین استراتژي، اين امكان را فراهم ميسازد تا با کنترل، یک تاخیر زمانی یکسان با این اختلال به منظور اجتناب از نابودي علائم در سطوح تحولات هماهنگ با مدل شبكه پتری زماندار ايجاد شود.
1. مقدمه
در سیستم های حمل و نقل ريلي، اختلالات زمانی قابل پیش بینی یا جلوگیری نيستند. تحقیق ما بر رفع و جبران این اختلالات با استفاده از تکنیک های کنترل استقامت متمركز است.
استقامت به عنوان توانایی سیستم برای حفظ قابليت ها در مواجهه با برخي تغییرات مورد انتظار و یا غیر منتظره تعریف شده است. این استقامت به ويژگيهاي مختلفي تعبير شده است. استقامت غیرفعال مبني بر تغییرات موجود در فواصل زمانی معتبر است. برای حفظ قابليت مورد نیاز هیچ اصلاح حلقه کنترلي وجود ندارد. از سوی دیگر، استقامت فعال از اختلالات زمان مشاهده شده برای تغییر حلقه کنترل به منظور برآوردن اين قابليت ها استفاده مي نمايد.
5. نتیجه گيري
مدلسازی و بررسي استراتژی کنترل استقامت در مواجهه با اختلالات که در سیستم حمل و نقل ريلي ساختار اصلي این مقاله را تشكيل ميدهد. شبکه های پتری زماندار برای مدل سازی استفاده شده اند. برخي تعاریف به منظور به ساختن یک تئوری در مورد مسئله استقامت ذكر شده اند.
دو روش برای کنترل استقامت ارائه شده است. اولین روش شامل جبران اختلال به محض مشاهده آن به منظور جلوگیری از نقض محدودیت در سطح انتقال همزمان مدل شبكه پتري زمان دار می باشد. دومین استراتژی امكان تولید یک وقفه زمانی یکسان با اختلال را توسط کنترل، در مسیر موازی انتشار اختلال فراهم ميسازد. نشان داده شده است که ایجاد استراتژی امكان جلوگیری از وقايع پيشبيني شده فاجعه آميز و اجتناب از نقض محدودیت های زمانی را به منظور تضمین ثبات و ایمنی ترافیک راه آهن را فراهم ميسازد.
Te importance of public transport systems continues to grow.Tese systems must respond to an increasing demand for population mobility and trafc disturbances. Rail transport networks can be considered as Discrete Event Systems (DES) with time constraints. Te time factor is a critical parameter, since it includes dates to be respected in order to avoid overlaps, delays, and collisions between trains. P-time Petri Nets have been recognized as powerful modeling and analysis tools for railway transport systems. Temporal disturbances in these systems include railway infrastructure, trafc management, and disturbances (weather, obstacles on the tracks, malice, social movement, etc.). Te developments presented in this paper are devoted to the modeling and the study of the robustness of the railway transport systems in order to evaluate the stability and the efciency of these networks. In this study two robust control strategies towards time disturbances are presented. Te frst one consists of compensating the disturbance as soon as it is observed in order to avoid constraints violation. Te second one allows generating, by the control, a temporal lag identical to the disturbance in order to avoid the death of marks on the levels of synchronization transitions of the P-time Petri net model.
1. Introduction
In railway transport systems, a temporal disturbance cannot be predicted or prevented. Our research focuses on the elimination and compensation of these disturbances by an application of robustness control techniques.
The robustness is defned as the ability of the system to preserve the specifcations facing some expected or unexpected variations. Te robustness is interpreted into diferent specializations. Te passive robustness is based upon variations included in validity time intervals. Tere is no control loop modifcation to preserve the required specifcations. On the other hand, active robustness uses observed time disturbances to modify the control loop in order to satisfy these specifcations.
5. Conclusion
The modeling and the study of the robust control strategy facing disturbances in railway transport system constitute the main contributions of this paper. P-time Petri nets are used for modeling. Some defnitions are quoted in order to build a theory dealing with robustness problem.
Two approaches for the robust control are presented. Te frst one consists of compensating the disturbance as soon as it is observed in order to avoid constraints violation on the levels of synchronization transitions of P-time PN model. Te second strategy allows generating by the control, a temporal lag identical to the disturbance, on the parallel path of the propagation of the disturbance. It is shown that the established strategy allows averting catastrophic scenarios and avoiding the violation of time constraints in order to guarantee the stability and safety of railway trafc.
1. مقدمه
2. متون تحقيقاتي مربوطه
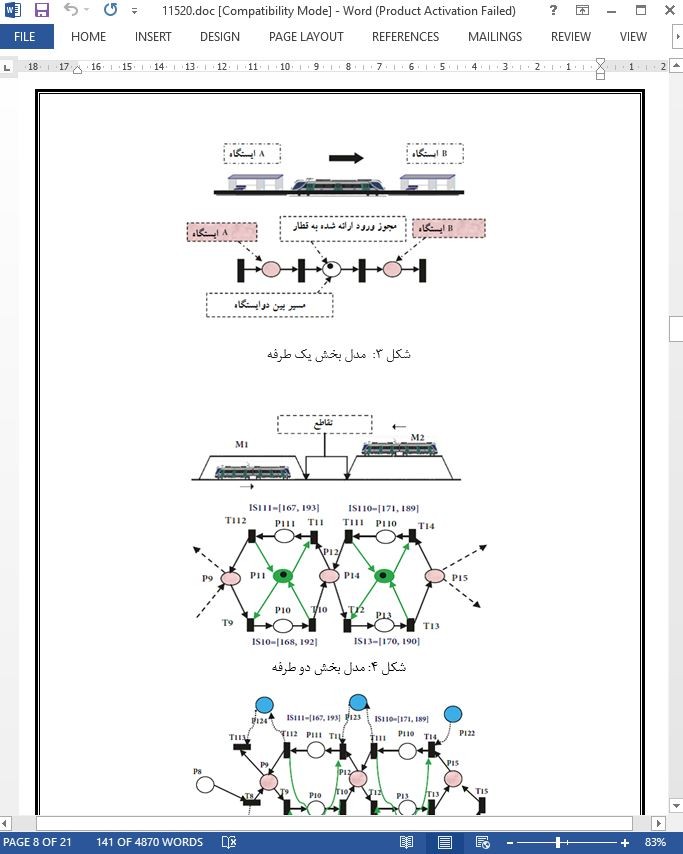
3. مطالعه موردی: شبکه حمل و نقل ریلی
3. 1. نمایشی از شبکه خطوط ریلی
3. 2. مدلسازی شبکه حمل و نقل ریلی
4. استقامت در مواجهه با اختلالات زمان
4. 1. تعاريف اصلي
4. 2. رویکرد استقامت
5. نتیجه گيري
1. Introduction
2. Relevant Literature
3. Case Study: Railway Transport Network
3.1. Presentation of Railway Network
3.2. Modeling of Railway Transport Network
4. Robustness Facing Time Disturbances
4.1. Basic Defnitions
4.2. Robustness Approach
5. Conclusion
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه