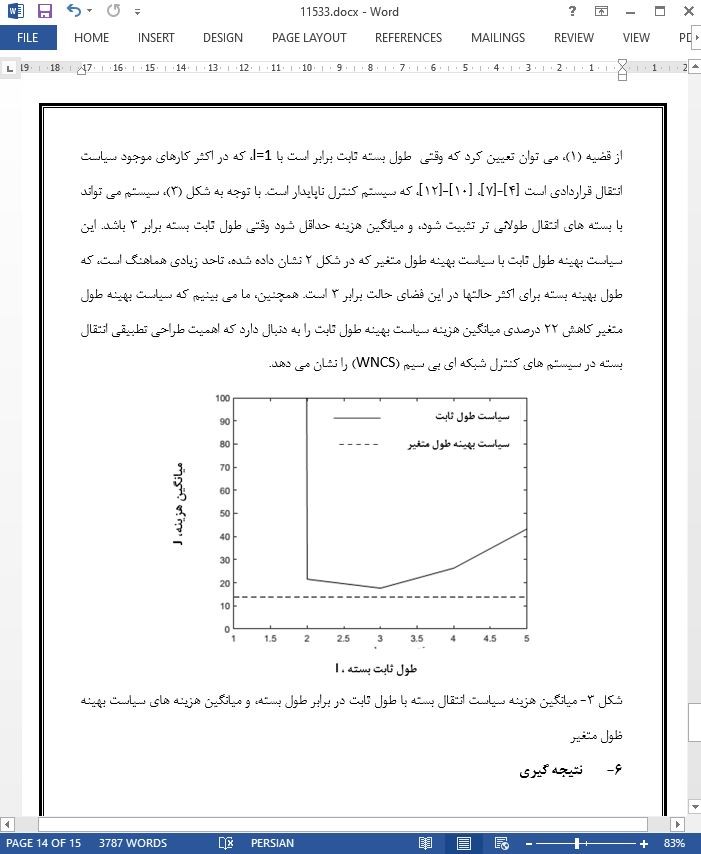
کنترل بازخورد بی سیم با طول بسته متغیر برای اینترنت اشیا صنعتی
چکیده
این مقاله یک سیستم کنترل شبکه ای بی سیم (WNCS) را در نظر می گیرد، که یک کنترل کننده بسته های حامل اطلاعات کنترل را از طریق یک کانال بی سیم به یک فعال کننده (محرک) می فرستد تا فرایند فیزیکی را برای کاربردها و برنامه های کنترل صنعتی کنترل کند. در اکثر کارهای موجود در زمینه سیستم کنترل شبکه ای بی سیم (WNCS)، طول بسته برای انتقال ثابت است. با این حال، باتوجه به نظریه کدگذاری کانال، اگر یک پیام به صورت یک رمز طولانی تر کدگذاری شود، قابلیت اطمینان آن به ازای تاخیر طولانی تر بهبود خواهد یافت. تاخیر و قابلیت اطمینان بر عملکرد کنترل خیلی تاثیر دارند. این طور مبادله اساسی تاخیر- قابلیت اطمینان به ندرت در سیستم کنترل شبکه ای بی سیم (WNCS) درنظر گرفته می شود. در این مقاله، ما یک سیستم کنترل شبکه ای بی سیم (WNCS)را پیشنهاد می دهیم، که در آن کنترل کننده به طور تطبیقی طول بسته را برای کنترل براساس وضعیت فعلی فرایند فیزیکی تغییر می دهد. ما یک مسئله تصمیم گیری را فرمول بندی کرده و سیاست بهینه انتقال بسته با طول متغیر را برای حداقل کردن میانگین هزینه طولانی مدت سیستم های کنترل شبکه ای بی سیم (WNCS) پیدا می کنیم. ما برحسب قابلیت های اطمینان انتقال با طول های بسته متفاوت و پارامتر سیستم کنترل، یک شرط لازم و کافی برای وجود سیاست بهینه به دست می آوریم.
1- معرفی
اینترنت اشیا صنعتی (IIOT) به عنوان گسترش اینترنت اشیا مصرف کننده در کاربردهای صنعتی مورد استفاده قرار می گیرد. یکی از مهمترین کاربردهای اینترنت اشیا صنعتی (IIOT) کنترل صنعتی [1] با سناریوهای کاربر می باشد که از خودکار سازی فرایند تا کاربردهای عامل حیاتی تر رده بندی می شوند، مانند اتوماسیون کارخانه و کنترل سیستم قدرت [2]. سیستم های کنترل شبکه ای بی سیم (WNCS) از کنترل کننده های توزیع شده فضایی، سنسورها و محرک ها تشکیل می شوند که از طریق کانالهای بی سیم، و فرایندهای فیزیکی کنترل شده ارتباط برقرار می کنند. به خاطر افزایش انعطاف پذیری و کاهش هزینه های گسترش و نگهداری، سیستم کنترل شبکه ای بی سیم (WNCS) تبدیل به یک تکنولوژی زیرساختی اساسی و مهم برای کاربردهای کنترل عامل حیاتی شده است [3]. در [4]، سیاست کنترل بهینه و حالت پایداری و ثبات سیستم کنترل شبکه ای بی سیم (WNCS) بررسی شدند. در [5]، زمان بندی انتقال بهینه چندین سیستم کنترل برای منابع ارتباطی مشترک مورد مطالعه قرار گرفت. در [6]، مشکل زمان بندی انتقال فروسو و فراسو یک سیستم کنترل شبکه ای بی سیم (WNCS) با یک کنترل کننده یک طرفه درنظر گرفته شدند. در [7]، یک سیستم کنترل شبکه ای بی سیم (WNCS) پیشامد محور برای کاهش هزینه ارتباطات پیشنهاد شد. در [8] و [9]، سیستم های کنترل شبکه ای بی سیم (WNCS) با شبکه های بی سیم کم مصرف و چند مرحله ای با عملکرد بالا به ترتیب بررسی شدند.
6- نتیجه گیری
در این مقاله، ما سیاست انتقال بسته با طول متغیر را پیشنهاد داده و بهینه کرده ایم. ما شرایط ثبات و پایداری سیستم کنترل را برای سیاست های طول ثابت و متغیر به دست آورده ایم. نتایج عددی ما برتری روش پیشنهادی انتقال بسته با طول متغیر را در سیستم های کنترل بی سیم نشان می دهند.
Abstract
This letter considers a wireless networked control system (WNCS), where a controller sends packets carrying control information to an actuator through a wireless channel to control a physical process for industrial-control applications. In most of the existing work on WNCSs, the packet length for transmission is fixed. However, from the channel-encoding theory, if a message is encoded into a longer codeword, its reliability is improved at the expense of longer delay. Both delay and reliability have great impact on the control performance. Such a fundamental delay-reliability tradeoff has rarely been considered in WNCSs. In this letter, we propose a novel WNCS, where the controller adaptively changes the packet length for control based on the current status of the physical process. We formulate a decision-making problem and find the optimal variable-length packet-transmission policy for minimizing the long-term average cost of the WNCSs. We derive a necessary and sufficient condition on the existence of the optimal policy in terms of the transmission reliabilities with different packet lengths and the control system parameter.
I. INTRODUCTION
The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) can be treated as an extension of the consumer IoT in industrial applications. One of the most important applications for IIoT is industrial control [1] with user scenarios ranging from building and process automation to more mission-critical applications, such as factory automation and power system control [2]. Wireless networked control systems (WNCSs) are composed of spatially distributed controllers, sensors and actuators communicating through wireless channels, and physical processes to be controlled. Due to the enhanced flexibility and the reduced deployment and maintenance costs, WNCS is becoming a fundamental infrastructure technology for mission-critical control applications [3]. In [4], the optimal control policy and the stability condition of a WNCS were investigated. In [5], the optimal transmission scheduling of multiple control systems over shared communication resources were studied. In [6], the uplink and downlink transmission scheduling problem of a WNCS with a half-duplex controller were considered. In [7], an event-triggered WNCS was proposed to reduce the communication cost. In [8] and [9], WNCSs with low-power and high-performance multi-hop wireless networks were investigated, respectively.
VI. CONCLUSIONS
In this paper, we have proposed and optimized the variablelength packet transmission policy. We have also derived the control-system stability conditions for both the fixedlength and variable-length policies. Our numerical results have demonstrated the superior of the proposed variable-length packet transmission method in wireless control systems.
چکیده
1- معرفی
2- مدل سیستم
A. عملیات طرف کنترل کننده
B. عملیات طرف محرک
3- کنترل بسته های دارای طول متغیر
A. فرمول بندی مسئله
B. راه حل نیمه مارکوف (semi-MDP)
C. مسائل اجرای عملی سیاست طول متغیر
4- شرایط پایداری و ثبات سیستم کنترل
A. سیاست انتقال بسته با طول ثابت
B. سیاست انتقال بسته با طول متغیر
5- نتایج عددی
6- نتیجه گیری
Abstract
I. INTRODUCTION
II. SYSTEM MODEL
A. Controller-Side Operation
B. Actuator-Side Operation
III. CONTROL WITH VARIABLE-LENGTH PACKETS
A. Problem Formulation
B. Semi-MDP Solution
C. Practical Implementation Issues of Variable-Length Policy
IV. STABILITY CONDITION OF THE CONTROL SYSTEM
A. Fixed-Length Packet Transmission Policy
B. Variable-Length Packet Transmission Polic
V. NUMERICAL RESULT
VI. CONCLUSIONS
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه