ارزیابی عملکرد لرزه ای ساختمان های دیاگرید ( شبکه مورب) فولادی
چکیده
در این مطالعه، عملکرد لرزه ای سازه های ساختمانی فولادی متقارن محوری با شکل نقشه دایره ای ، بر اساس روش ATC-63 ارزیابی شده است. برای مدل های تحلیلی، ساختمان های سی و سه طبقه محدب ، مقعر و کدویی شکل عمودی با استفاده از سیستم های ساختاری شبکه مورب طراحی شد و عملکرد لرزه ای آن ها، با ساختمان های معمولی فولادی استوانه ای شکل، مقایسه شد. تحلیل های شکنندگی لرزه ای نیز با استفاده از بیست و دو جفت از گزارش های ثبت زلزله انجام شد تا بتوان احتمال شکست یک ساختمان در اثر شدت مشخصی از زلزله، تعیین شود. اعتبار ضریب اصلاح پاسخ مورد استفاده در طراحی های لرزه ای سازه های مدل نیز در این مطالعه ارزیابی شد. بر اساس نتایج تحلیل ها، ما به این جمع بندی رسیدیم که ضریب اصلاح پاسخ 0.3 مورد استفاده در طراحی سازه های مدل ، برای روش شناسی ATC-63 قابل قبول می باشد. همچنین مشاهده شد که حاشیه امنیت لرزه ای برای سطح خاصی از زلزله، متناسب با افزایش بی قاعدگی عمودی سازه، کاهش پیدا می کند.
1. مقدمه
اخیرا، پیچیدگی های هندسی و بی قاعدگی سازه های ساختمانی، به صورت گسترده افزایش پیدا کرده است و این موضوع به صورت محسوس بر روی عملکرد لرزه ای سازه ها تاثیر می گذارد. Al-Ali و Krawinkler (1998) ، رفتار لرزه ای سازه های ساختمانی با بی قاعدگی های عمودی را بررسی کرده اند و متوجه شدند که پاسخ لرزه ای سازه های ساختمانی، حساسیت بیشتری نسبت بی قاعدگی ها در سفتی و مقاومت ساختمان دارد و حساسیت اش نسبت به بی قاعدگی های جرمی، کمتر می باشد. Soni و Mistry (2006) نیز یک مرور بر روی مطالعه های مرتبط با رفتار لرزه ای سازه های بی قاعده از نظر ساختار عمودی را همراه با یافته های این مطالعه ها انجام دادند. Scott و همکارانش ( 2007) ، چالش های ساختاری را بررسی کردند که در ساختمان هایی با حالت های هندسی یا شکل های پیچیده ایجاد شده بود و بعضی از طراحی های اقتصادی و تکنیک های ساختاری در این ساختمان را بررسی کردند .
6. جمع بندی
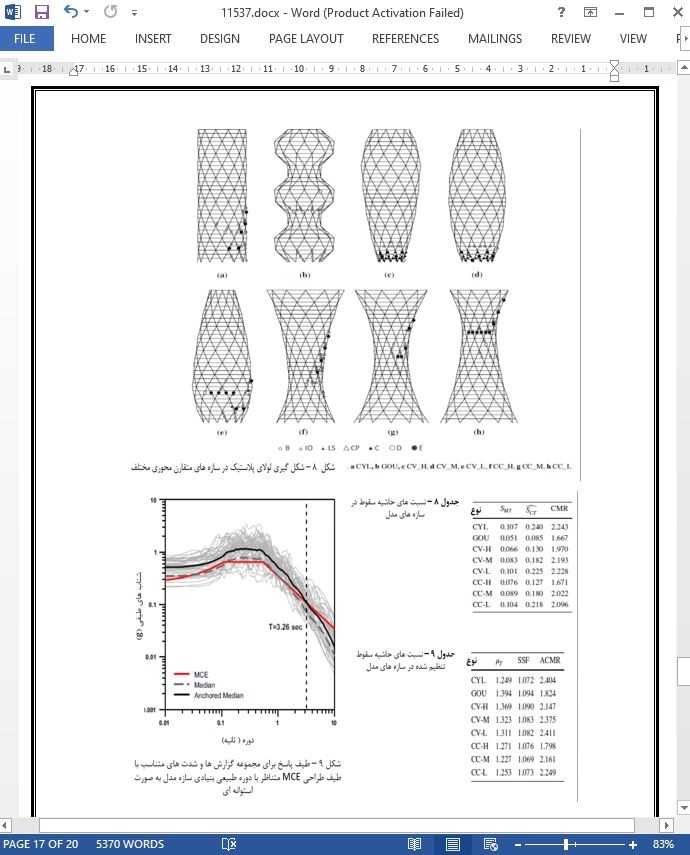
در این مطالعه، عملکرد لرزه ای ساختمان های شبکه مورب متقارن محوری با حالت های بی قاعدگی عمودی مختلف ، بر اساس روند پیشنهاد شده در ATC-63 ، ارزیابی شده است. تحلیل های شکنندگی لرزه ای با استفاده از گزارش های بیست و دو جفت زمین لرزه انجام شد تا بتوان احتمال شکنندگی برای شدت زمین لرزه مشخص، ارزیابی شود. مدل تحلیل به صورت سازه های سی و سه طبقه با ارزیابی های مختلف نیز طراحی شدند که دارای مساحت کف کلی مشابه با هم بودند و نسبت ابعادی سازه های مدل از 2.0 در سازه های مقعر با مرکز جرم پایین تا 6.2 در سازه های محدب با مرکز جرم بالا، متغیر بود.
Abstract
In this study the seismic performances of axi-symmetric steel building structures with circular plan shape were evaluated based on the ATC-63 approach. For analysis models, thirty-three-story vertically convex, concave, and gourd-type axisymmetric buildings were designed using diagrid structure system, and their seismic performances were compared with those of the cylinder type regular steel structure. Seismic fragility analyses were carried out using twenty-two pairs of earthquake records to obtain the probability of failure for a given earthquake intensity. The validity of the response modifcation factor used in the seismic design of the model structures was also investigated. Based on the analysis results it was concluded that the response modifcation factor of 3.0 used in the design of the model structures is acceptable for the ATC-63 methodology. It was also observed that the seismic safety margin for a specifc level of earthquake decreases as the vertical irregularity of the structure increases.
1 Introduction
Recently the geometric complexity and irregularity of building structures have been rapidly increasing, which signifcantly afects the seismic performance of the structures. Al-Ali and Krawinkler (1998) investigated the seismic behavior of building structures with vertical irregularities, and found that the seismic response of building structures is more sensitive to stifness and strength irregularities than to mass irregularities. Soni and Mistry (2006) carried out review of studies on the seismic behavior of vertically irregular structures along with their fndings. Scott et al. (2007) explored the structural challenges that are created by buildings with unique geometries or articulated forms, and discussed some of economic design and construction techniques.
6 Conclusions
In this study the seismic performances of axi-symmetric diagrid building structures with various vertical irregularities were evaluated based on the procedure recommended in the ATC-63. Seismic fragility analyses were carried out using twenty-two pairs of earthquake records to compare the probability of failure for a given earthquake intensity. The thirty-three story analysis model structures with diferent elevations were designed to have similar total foor areas, the aspect ratios of the model structures range from 2.0 in the case of the concave structure with low center of mass and to 6.2 in the case of convex structure with high center of mass.
چکیده
1. مقدمه
2. ارزیابی عملکرد لرزه ای بر اساس روش ارائه شده در ATC‑63
3. طراحی و مدل سازی تحلیل سازه های مدل
4. ارزیابی عملکرد لرزه ای سازه های مدل
4.1 نتایج تحلیل ایستای غیر خطی
4.2 اعتبار ضریب اصلاح پاسخ
5. تحلیل شکنندگی
6. جمع بندی
Abstract
1 Introduction
2 Seismic Performance Evaluation Procedure of ATC 63
3 Design and Analysis Modeling of Model Structures
4 Seismic Performance Evaluation of Model Structures
4.1 Nonlinear Static Analysis Results
4.2 Validity of the Response Modifcation Factor
5 Fragility Analysis
6 Conclusions
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه