مدل های پوشش دهنده و تکنیک های بهینه سازی برای موقعیت یابی و برنامه ریزی تجهیزات پاسخ دهی اورژانس
چکیده
متاسفانه با تبدیل شدن اورژانس به بخشی از زندگی ما، برنامه ریزی موثر و اختصاص امکانات برای پاسخ دهی اورژانس برای بررسی موثر مشکلات مردم نیازمند یک عامل ضروری گشته است. مشکلات اختصاص خدمات پزشکی اورژانس (EMS )به بررسی موقعیت یابی امکانات EMS در میان گزینه های بالقوه برای ارائه خدمات موثر در مناطق متعدد با توزیع مکانی مختلف می پردازد.این مسئله به دلیل وجود پیچیدگی درونی این مشکلات یک مسئله پیچیده می باشد. این تحقیق به بررسی مدل های پوشش دهنده و تکنیک های بهینه سازی برای موقعیت یابی و برنامه ریزی تجهیزات از چند دهه گذشته می پردازد، در حالی که پیشرفت های کنونی را تاکید خود قرار می دهند. ما چندین مدل پوشش دهنده و توسعه آنها از مدل های ساده تا پیچیده از جمله مسئله پوشش مجموعه موقعیت (LSCP ) – مسئله پوشش حداکثری موقعیت (MCLP ) – مدل استاندارد دوبله (DSM ) – مسئله حداکثر پوشش موقعیت (MEXCLP ) و مسئله حداکثر موقعیت مکانی ( MALP ) دربر می گیرد. به علاوه، پیشرفتهای اخیر در زمینه مدل های نوبت دهی – مدل های اختصاص دینامیک – مدل های پوشش تدریجی و مدل های پوشش دهنده مشارکتی نیز در این تحقیق مطرح شده است.تکنیک های بهینه سازی مربوط برای حل این مدل ها از جمله الگوریتم های اکتشافی – شبیه سازی و روش های دقیق بصورت خلاصه بیان شده اند.
4. نتیجه گیری و بحث
متاسفانه با تبدیل شدن اورژانس به بخشی از زندگی ما، برنامه ریزی موثر و اختصاص امکانات برای پاسخ دهی اورژانس برای بررسی موثر مشکلات مردم نیازمند یک عامل ضروری گشته است. این تحقیق به بررسی مدل های پوشش دهنده و تکنیک های بهینه سازی برای موقعیت یابی و برنامه ریزی تجهیزات از چشم انداز مدل های ریاضی و تحقیقات اجرایی می پردازد. تحقیقات اولیه در مورد مدل های پوششی توسط مسئله پوشش محموعه موقعیت ها (LSCP ) و مسئله حداکثر پوشش موقعیت (MCLP) نشان داده شده اند.LSCP یک مدل پوششی الزامی است که در آن تمام نقاط تقاضا حداقل یک بار پوشش داده می شود در حالی که MCLP تلاش می کند تا پوشش را به حداکثر برساند و منابع محدود ارائه کند. هر دو روش LSCP و MCLP دارای یک مقطه ضعف مشترک هستند که در آن منطقه پوشش دیگر تحت پوشش قرار نمی دهد. در این موقعیت، چندین مفهوم مربوط به پوشش متعدد برای بررسی تقاضای متعدد در چندین موقعیت معرفی شد که برای مثال می توان به مئل استاندارد دوبله (DSM) اشاره کرد که برای بررسی این موقعیت از طریق اختصاص آمبولانس در میان مناطق برای پوشش کامل در استاندارد فاصله طولانی تر معرفی شده اند.یک گرایش دیگر تحقیقی که برای غلبه بر این مشکل مطرح شده است مربوط به مدلسازی احتمال مشغول بودن است شامل مدل های حداکثر پوشش های مورد انتظار (MEXCLP) و مسئله موقعیت یابی حداکثر موجودی ( MALP) می شود. تحقیقات دیگر از مدل های صف بندی جذر مکعب برای تایید فرضیه های قوی در مدل های قبلی احتمالی و انجام تحلیل دقیق سیستم استفاده شوند. مدل های دینامیک برای اختصاص آمبولانس در زمان واقعی و برای ارائه پوشش بهتر تقاضا ارائه شده اند. به علاوه، فرضیه مطرح شده در مورد اینکه فقط نزدیکترین آمبولانس تعیین می کند که آیا نقطه تقاضا پوشش داده شود یا خیر توسط مدل های پوشش دهنده مشارکتی بررسی می شوند.
Abstract
With emergencies being, unfortunately, part of our lives, it is crucial to efficiently plan and allocate emergency response facilities that deliver effective and timely relief to people most in need. Emergency Medical Services (EMS) allocation problems deal with locating EMS facilities among potential sites to provide efficient and effective services over a wide area with spatially distributed demands. It is often problematic due to the intrinsic complexity of these problems. This paper reviews covering models and optimization techniques for emergency response facility location and planning in the literature from the past few decades, while emphasizing recent developments. We introduce several typical covering models and their extensions ordered from simple to complex, including Location Set Covering Problem (LSCP), Maximal Covering Location Problem (MCLP), Double Standard Model (DSM), Maximum Expected Covering Location Problem (MEXCLP), and Maximum Availability Location Problem (MALP) models. In addition, recent developments on hypercube queuing models, dynamic allocation models, gradual covering models, and cooperative covering models are also presented in this paper. The corresponding optimization techniques to solve these models, including heuristic algorithms, simulation, and exact methods, are summarized.
4 Conclusion and discussion
With emergencies unfortunately being part of our lives, it is crucial to efficiently plan and allocate emergency response facilities to deliver effective and timely relief to people most in need. This paper reviewed covering models and optimization techniques for emergency response facility location and planning, from the perspective of mathematical models and operations research. The earlier studies of the covering models are represented by the Location Set Covering Problem (LSCP) and the Maximal Coverage Location Problem (MCLP). The LSCP is a mandatory covering model in which all the demand points are covered at least once, while the MCLP attempts to maximize coverage, given limited resources. Both the LSCP and MCLP have a common drawback in that once an EMS facility is dispatched to serve an emergency call, other demands in its coverage area are not covered by it any more. In this context, multiple coverage concept was introduced to handle excess demands in some locations, such as the recent Double standard Model (DSM) that was proposed to remedy this situation by allocating facilities among potential sites to provide full coverage within a longer distance standard, and to maximize coverage within a shorter distance standard. Another strand of research designed to overcome this drawback is to explicitly model the busy probabilities and reliabilities of facilities. The most frequently used probabilistic models are the Maximum Expected Covering Location Problem (MEXCLP) and the Maximum Availability Location Problem (MALP). Further research developed hypercube queuing models to relax the strong assumptions in previous probabilistic models and obtain a more accurate analysis of the system. Dynamic models were proposed to allocate facilities in real time and provide better coverage for demands. Recently, the commonly used “all or nothing” assumption about the coverage of demands is relaxed by gradual covering models that model the gradual decline of coverage along with the increase of distance by mathematical functions. In addition, the individual assumption that only the nearest facility determines whether a demand point is covered or not is relaxed by cooperative covering models.
چکیده
1.مقدمه
2. مدل های پوشش دهنده برای برنامه ریزی و موقعیت یابی تجهیزات اورژانس
2.1 مسئله پوشش مجموعه موقعیت
2.2 مسئله حداکثر پوشش موقعیت
2.3 مدل استاندارد دوبله DSM
2.4 مسئله حداکثر میزان پوشش مورد انتظار (MEXCLP)
2.5 مدل صف بندی جذر مکعب
2.6 مسئله موقعیت یابی حداکثر موجودی (MALP)
2.7 مدل های موقعیت یابی و اختصاص دینامیک
2.8 مدل پوشش تدریجی
2.9 مدل پوشش مشارکتی
3.تکنیک های بهینه سازی
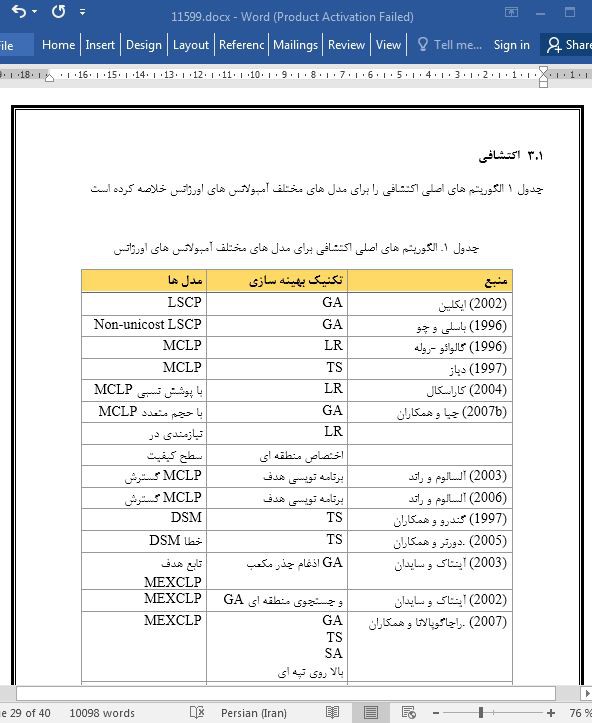
3.1 اکتشافی
3.2 شبیه سازی
3.3. روش های دقیق
4. نتیجه گیری و بحث
منابع
Abstract
1 Introduction
2 Covering models for emergency facility location and planning
2.1 Location set covering problem
2.2 Maximal covering location problem
2.3 Double standard model (DSM)
2.4 Maximum expected covering location problem (MEXCLP)
2.5 Hypercube queuing model
2.6 Maximum availability location problem (MALP)
2.7 Dynamic allocation and relocation models
2.8 Gradual coverage model
2.9 Cooperative coverage model
3 Optimization techniques
3.1 Heuristics
3.2 Simulation
3.3 Exact methods
4 Conclusion and discussion
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه