مشارکت مشتری در جامعه برند تجارت الکترونیک
چکیده
هدف: هدف این مطالعه، ترسیم چارچوب مفهومی برای مشارکت مشتری در زمینه ی رسانه ی اجتماعی برای بازارهای نوظهور است. سه مدل از مشارکت مشتری شناسایی شده و برای رسیدن به بهترین مدل برای زمینه های خاص مورد آزمون قرار گرفتند. چارچوب های مفهومی جایگزین شامل ساختارهای مشارکت فعال، اعتماد جامعه و تعهد جامعه در رابطه با مشارکت مشتری است.
طرح/متدولوژی/رویکرد: داده های مورد نظر با استفاده از ارسال پرسشنامه از طریق ایمیل به پاسخ دهندگان جمع اوری شد. مدل سازی معادلات ساختاری برای رسیدن به بهترین مدل مورد استفاده قرار گرفت در حالی که رابطه ی بین ساختارها مورد آزمون قرار گرفت.
یافته ها: مطالعه ی مورد نظر با روش مقایسه ی تجربی چارچوب های مفهومی، چارچوب مشارکت مشتری را ارائه می دهد که تناسب بهتریت در زمینه ی رسانه ی اجتماعی برای بازارهای نوظهور دارد. این مطالعه هم چنین مشارکت فعال، اعتماد جامعه و تعهد جامعه را به عنوان سوابق و عوامل مشارکت مشتری ترسیم می کند. مشارکت فعال به عنوان سابقه و عامل فعال برای مشارکت مشتری بر مبنای ارزیابی تطبیقی چارچوب ها شناسایی می شود.
محدودیت ها/پیامدهای پژوهش: در حالی که توافق زیادی در مورد ماهیت مشارکت مشتری وجود ندارد، این مطالعه بینشی هایی را برای بازاریابان از نظر مدیریت مشارکت مشتری با جوامع طرفداران برند آن ها ارائه می دهد. این مطالعه، نقش و اهمیت ترغیب مشارکت فعال در زمینه ی جامعه ی برند را شناسایی می کند. هم چنین، اعتماد جامعه و تعهد جامعه را به عنوان عوامل و سوابقی برای مشارکت مشتری شناسایی کرده و بیان می کند که تعهد، نقش ویژه ای در چارچوب دارد.
منشا/ارزش: هیچ گونه توافق و اجماعی در بین محققان در مورد شبکه ی علمی پیرامون مشارکت مشتری وجود ندارد. علاوه براین، مطالعات بسیار اندکی بر این ساختار در زمینه ی بازارهای نوظهور تمرکز کرده اند. این مطالعه تلاش می کند تا با آزمون چارچوب های جایگزین از جمله مشارکت مشتری در زمینه ی رسانه ی اجتماعی برای بازارهای نوظهور، این شکاف را کمتر کند.
مقدمه
مشارکت مشتری یکی از بزرگترین کلمات کلیدی بازاریابی قرن بیست و یکم در بین افراد علمی و شاغلین حرفه ای است. این واژه در ادبیات بازاریابی پیرامون سال 2006 شناسایی و مشخص شد (برودی 2011) و از آن پس، تمرکز پژوهش پیرامون این ساختار به شدت افزایش یافت. دسارت در سال 2016 مشارکت مشتری را ارائه داد در حالی که آن را با مفاهیم قدیمی تر مانند مشارکت برند یا کیفیت رابطه مقایسه می کرد که در آن"مشارکت" دیدگاه اصلاح شده ای از روابط را ارائه می دهد که به شدت تعاملی و اجتماعی هستند. هنینگ و تورو در سال 2010 شناسایی کردند که روابط مدرن مشتری، نتیجه ی عوامل اجتماعی، تعاملی و موقعیتی است. این ویژگی ها، برخورد و مطالعه ی تجربی روابط مدرن مشتری را افزایش می دهند.
نتیجه گیری:
مطالعه ی کنونی با مقایسه ی چارچوب هایی که توصیف هایی بهتری از سوابق و پیامدهای تعامل مشتری ارائه می دهند، ادبیات تعامل و مشارکت مشتری را گسترش می دهد. این مطالعه شواهد تجربی از نظر شناسایی اعتماد و تعهد به عنوان سوابقی برای ساختار تعامل مشتری در زمینه ی رسانه ی اجتماعی برای بازارهای نوظهور را فراهم می سازد. هم چنین یکی از مطالعات محدودی است که تمایز بین دو بعد از مشارکت رسانه ی اجتماعی-فعال و غیرفعال- را ارائه می دهد، در حالی که مشارکت فعال را به عنوان سابقه ای برای تعامل مشتری در نظر می گیرد. تعامل مشتری در زمینه ی رسانه ی اجتماعی، اولویتی را در بین انجمن های علمی کسب کرده است و محققان مختلف تاثیر آن از نظر تاثیرگذاری بر تعامل مشتری با برند را شناسایی می کنند. این پژوهش پاسخی به درخواست مطالعات متمرکز بر تعامل مشتری در زمینه های مختلف است. در حالی که پژوهش در این حیطه شاهد روند صعودی است، بسیاری از ابعاد زمینه ای وجود دارند که هنوز کشف نشده اند. با نقش فزاینده ی بازارهای نوظهور در نقشه ی برند جهانی، این مطالعه بینش هایی را در مورد مدیریت تعامل مشتری در رسانه ی اجتماعی برای بازارهای نوظهور ارائه می دهد. مطالعه ی مورد نظر با مقایسه ی تجربی به شبکه ی علمی برای تعامل مشتری در زمینه ی جوامع برند تجارت الکترونیک در رسانه ی اجتماعی می رسد.
Abstract
Purpose – The purpose of this study is to outline a conceptual framework for customer engagement in the context of social media for emerging markets. Three competing models of customer engagement were identified and tested to arrive at the best suited model for the given contexts. The alternative conceptual frameworks involve the constructs of active participation, community trust and community commitment in relation to customer engagement.
Design/methodology/approach – Data were collected using questionnaires sent via e-mail to respondents. Structural equation modelling was then used to arrive at the best suited model, while also empirically testing for the relationships among the constructs.
Findings – The study, by way of an empirical comparison of alternative conceptual frameworks, presents a customer engagement framework best suiting the social media context for emerging markets. The study also outlines active participation, community trust and community commitment to be acting as antecedents to customer engagement. Further active participation is identified as a necessary antecedent to customer engagement based on the comparative assessment of the frameworks.
Research limitations/implications – While there is not much consensus on the nature of customer engagement, the study offers insights to marketers in terms of managing customer engagement with their brand communities. The study identifies the role and importance of inducing active participation in a brand community context. Further, it also identifies community trust and community commitment to be occurring as antecedents to customer engagement, with commitment implying for a more pronounced role in the framework.
Originality/value – There is no consensus among researchers regarding the nomological network surrounding customer engagement. Further, very few of these studies have focussed on this construct in the context of emerging markets. This study thus attempts to close the above gap, by testing for alternative conceptual frameworks involving customer engagement, in the context of social media for emerging markets.
Introduction
Customer engagement is one of the biggest marketing buzzword of the twenty-first century among both academicians and practitioners alike. The term was recognized in marketing literature around 2006 (Brodie et al., 2011), and since then the research focus around the construct has grown formidably. Dessart et al. (2016) presented customer engagement while contrasting it to the older established concepts, such as, brand involvement or relationship quality, in that engagement “offers a modified view of relationships” which are highly interactive and social. On a similar note, Henning-Thurau et al. (2010) too identified that the modern-day customer relationships are the result of social, interactive and empowering situational elements. These engagement features enhance the empirical treatment of modern customer relationships (Dessart et al., 2016).
Conclusion
The present study advances the customer engagement literature by comparing alternative frameworks that best describe the antecedents and consequences to customer engagement. The study provides empirical evidence in terms of identifying both trust and commitment as antecedents to the construct of customer engagement, in the context of social media for emerging markets. It is also one of the few studies offering a distinction between the two dimensions of social media participation – active and passive; while presenting active participation as an antecedent to customer engagement. Customer engagement within the social media context is gaining precedence among the academic fraternity, with various researchers (Bowden et al., 2017) identifying for a spill over effect it exerts in terms of influencing consumer’s engagement with the brand (p. 891). This research is an answer to call for studies focussing on customer engagement in various contexts. While research in this area is witnessing an upward trend, there are many contextual dimensions that are still unexplored. With emerging markets playing an increasing role in the world brand map, this study offers insights on managing customer engagement on social media for emerging markets. The study by way of an empirical comparison arrives at a nomological network for customer engagement, in the context of e-commerce brand communities on social media.
چکیده
مقدمه
هدف مطالعه
مروری بر ادبیات
رسانه ی اجتماعی و جوامع طرفدار برند
مشارکت و تعامل مشتری با جامعه
اعتماد جامعه
تعهد جامعه
مشارکت فعال
چارچوب مفهومی مشارکت و تعامل مشتری
چارچوب مفهومی و توسعه ی فرضیات
سابقه و زمینه ی مطالعه
موقعیت و تنظیمات پژوهش
توسعه ی پرسشنامه
جمع آوری داده ها
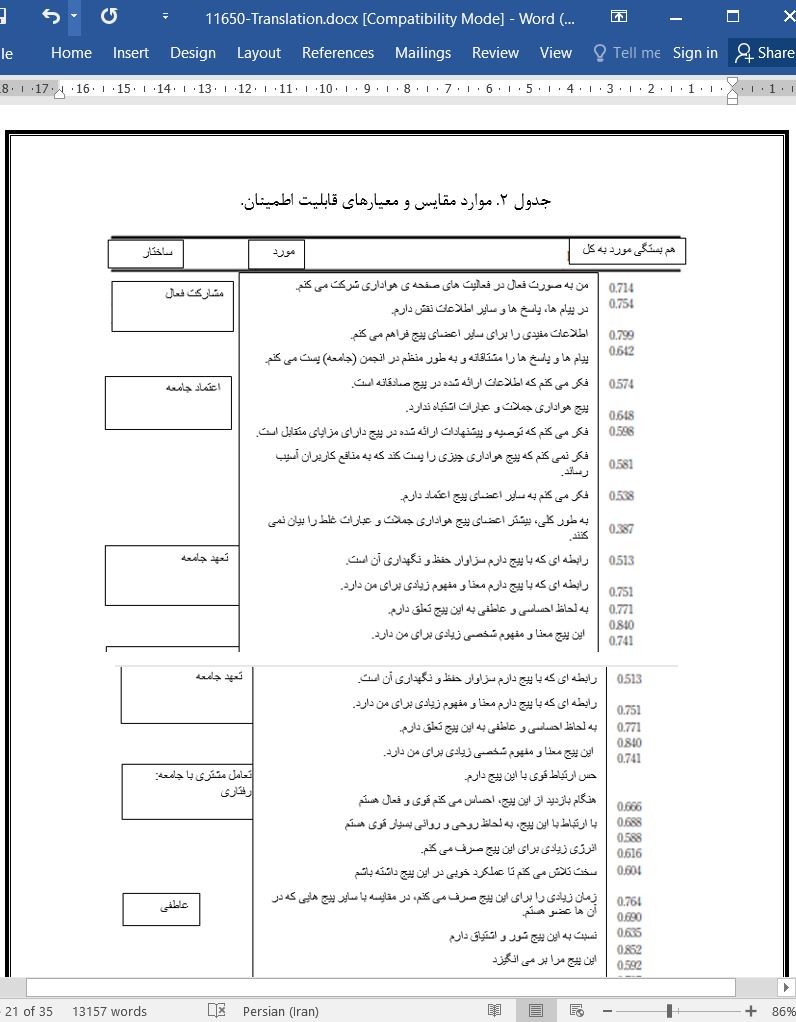
اعتبار و قابلیت اطمینان (پایایی و روایی)
ابزارها و تکنیک های به کار برده شده
نتایج مطالعه
بحث و پیامدهای مدیریتی
مشارکت فعال منجر به تعامل و مشارکت مشتری می شود
اعتماد جامعه و تعهد جامعه به عنوان نتایجی برای مشارکت فعال
چارچوب مفهومی مشارکت و تعامل مشتری
نقش اعتماد-تعهد در چارچوب مشارکت و تعامل مشتری
اهمیت تعهد جامعه
نتیجه گیری
پژوهش آینده
منابع
Abstract
Introduction
Purpose of study
Review of literature
Social media and Brand communities
Customer engagement with the community
Community trust
Community commitment
Active participation
Conceptual framework of customer engagement
Conceptual framework and Hypotheses development
Methods
Background of the study
Research setting
Questionnaire development
Data collection
Validity and reliability
Tools and techniques used
Results of the study
Discussion and managerial implications
Active participation leads to customer engagement
Community trust and community commitment as outcomes to active participation
Conceptual framework of customer engagement
Role of Trust-Commitment in customer engagement framework
The importance of community commitment
Conclusion
Future research
References
- اصل مقاله انگلیسی با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه