نظارت امنیتی تطبیقی برای نسل بعدی روترها
چکیده
در اینترنت امروزی، روترهای مدرن برای پشتیبانی از قابلیت انعطاف پذیری، عملیات پروتکل و برنامه های کاربردی پرتراکم، متکی بر سیستم های ارسال بسته همه منظوره ی چند هسته ای بسیار کارآمد هستند. این سیستم های پردازشی قابل برنامه ریزی هستند و در مسیر داده چنین روترهایی جایگزین ASIC های سنتی که درای منطق ثابت بوند، شده اند. از این رو، بسیاری از آسیب پذیری ها و اشکال ها که سیستم ها را در معرض حملات و خرابی ها قرار می دهد، در نتیجه همین قابلیت برنامه پذیری به وجود می آید. به طورخاص، تشخیص اینکه آیا یک هسته پردازشی به درستی کار نمی کند، یا دچار یک خرابی ناشی از خطاها و حملات شده است، کار دشواری است. در این مقاله، ما با ارائه یک رویکرد جدید برای بررسی صحت عملکرد پردازنده شبکه، این مسأله را بررسی می کنیم. ما یک زیرسیستم نظارتی امن، تحمل پذیر خطا و قابل اطمینان را پیشنهاد می کنیم که به طور موازی با هسته پردازشی روتر کار می کند و به شناسایی حملاتی که رفتار پردازشی پردازنده را تغییر می دهند؛ کمک میکند. ما از طریق آزمایش ثابت می کنیم که سیستم ما توانایی شناسایی فعالیتهای مخرب و بازگرداندن امن عملیات روتر به حالتی دیگر اما با عملکرد یکسان را دارد. همچنین به طور تجربی نشان می دهیم که رویکرد ما در مقایسه با سایر روشهای موجود کارایی بهتری دارد.
1 معرفی
اندازه، تنوع و پیچیدگی شبکه های مدرن رو به افزایش است و منجر به توسعه پروتکل ها و الگوهای ارتباطی جدید مانند شبکه های دارای قابلیت آدرس دهی محتوایی می شود، که نیاز است به منظور بهبود عملکرد شبکه مورد استفاده قرار گیرند. این کار برای پاسخگویی به چنین نیازمندیهایی مستلزم استفاده از پردازنده های قابل برنامه ریزی است. خوشبختانه پیشرفتها در کارایی پردازنده های چند هسته ای همه منظوره، با ایجاد امکان توسعه روترهای مبتنی بر سیستم های بر تراشه (SoC) چند پردازنده ای توکار با درجه توازی بالا (MPSoCs) ، این خلأ را پر کرده اند. اکنون ارائه دهندگان شبکه و اپراتورها می توانند با استفاده از اجزای قابل برنامه ریزی در مسیر داده ها به سطح جدیدی از انعطاف پذیری دست یابند [1].
6. نتیجه گیری
استفاده از روترهای مجهز به موتورهای پردازش چند منظوره و اجرای پردازش بسته مبتنی بر نرم افزار، در اینترنت افزایش زیادی یافته است. استفاده از پردازش مبتنی بر نرم افزار در سطح داده شبکه، هدفی برای حمله های جدید و حمله های قطع سرویس است. این مسأله می تواند تأثیر قابل توجهی بر امنیت عمومی شبکه داشته باشد. ما طرح یک مکانیسم امنیتی تطبیقی برای پردازنده های بسته جدید را ارائه می دهیم. پیاده سازی یک نمونه اولیه از یک سیستم نظارت امن را ارائه می دهیم که می تواند برای شناسایی حملات هدف قرار دادن سطح داده شبکه استفاده شود. این سیستم نظارت، تحمل پذیر خطا و قابل اعتماد است و از مزایای تنوع نرم افزار بهره برده است که عملکرد هسته پردازشی را با رفتار متناظر مورد انتظار برای آن که در تحلیل آفلاین کد باینری پردازش بسته به دست آمده مقایسه می کند. سیستم نظارت شامل رفتارهای مختلف مربوط به اجراهای های مختلف کد باینری است که قرار است پردازش شود. این سیستم به طور مداوم اجرای پردازنده را بررسی می کند و اگر یک انحراف از مسیر اجرای رفتاری شناسایی شود، مکانیزم بازیابی را راه اندازی می کند. سیستم نظارت ما سریع است چرا که با یک نوع حافظه جدید، حافظه TCAM ، پیاده سازی می شود که جستجوی سریع و تطبیق را در دو سیکل ساعت انجام می دهد. همچنین این یک سیستم نظارت امن است که یک درهم سازی SHA-256 را پیاده سازی می کند تا یکپارچگی کد باینری بارگذاری شده را تضمین کند. پیاده سازی نمونه اولیه سیستم نظارت ما نشان می دهد که سیستم ما یک رویکرد موثر در حفاظت از زیرساخت های شبکه در اینترنت آینده با منابع اضافی ناچیز و سرعت بسیار خوب است.
Abstract
In today’s Internet, modern routers rely on high-performance reliable general-purpose multi-core packet processing systems in order to support the flexibility and the plethora of protocol operations and applications. These processing systems are programmable and have replaced the traditional-fixed logic ASICs in the data path of such routers. Hence, lots of vulnerabilities and faults are introduced as the result of such programmability making the systems susceptible to attacks and failures. Particularly, it is a difficult task to detect whether a processing core behaves correctly, or it has a failure resulting from errors or attacks. In this paper, we address this problem by proposing a novel approach to verify the correct operation of the network processor. We propose a secure, faulttolerant, and reliable monitoring subsystem which functions in parallel with the processing core of the router and aids in the detection of attacks changing the processing behavior of the processor. We prove experimentally that our system has the ability to detect the malicious activity and securely restore the router’s operation to a different, but functionally equivalent, state. We also show experimentally that our approach has a better efficiency when compared with other existing work.
1 Introduction
The size, diversity, and complexity of modern networks continue to increase resulting in the development of new protocol and communication paradigms, such as content-addressable networks, that need to be deployed in order to improve the network operation. This entails the use of programmable network processors to meet such demands. Fortunately, the advances in the performance of general-purpose multi-core processors fulfilled this necessity by enabling the development of routers which are based on highly parallel, embedded multiprocessor systems-on-chip (MPSoCs) as an integral component. Network vendors and operators can now achieve a new level of flexibility due to the use of programmable components in the data path [1].
6 Conclusion
The use of routers equipped with general-purpose processing engines and executing software-based packet processing is becoming more prevalent in the Internet. Using software-based processing in the data plane of the network presents a target for novel intrusion and denial-of-service attacks. This can have a significant impact on the overall security of the network. In our work, we present the design of an adaptive security mechanism for modern packet processors. We present a prototype implementation of a secure monitoring system which can be used in order to detect the attacks targeting the data plane of the network. This monitoring system is fault tolerant and reliable taking advantage of software design diversity comparing the operation of the processing cores to its corresponding expected behavior obtained by the offline analysis of the packet processing binary. The monitoring system will include different behaviors corresponding to different executions of the binary to be processed. The system continuously checks the execution of the processor and triggers a recovery mechanism if a deviation from the behavioral execution path is detected. The monitoring system we present is fast because it implements a new type of memory, the TCAM memory, performing fast searching and matching within two clock cycles. It is also a secure monitoring system implementing a SHA-256 hash which ensures the integrity of the binary code loaded. The prototype implementation of our monitoring system shows that our system is an effective approach in protecting the networking infrastructure in the future Internet with a negligible additional resource utilization and a very good speed.
چکیده
1 معرفی
2 مرور ادبیات
1.2 کارهای مرتبط
3 مدل امنیتی چارچوب
4 طراحی نظارت
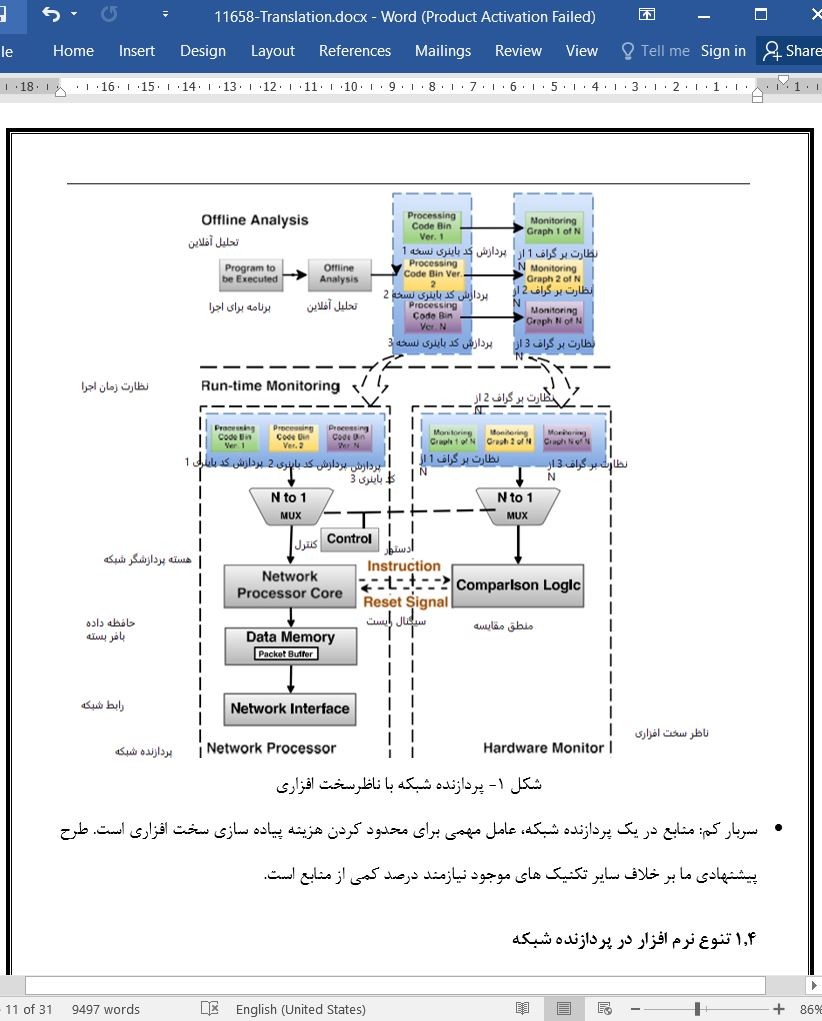
1.4 تنوع نرم افزار در پردازنده شبکه
2.4 تولید گراف نظارت
3.4 نظارت بلادرنگ
4.4 مکانیزم بازیابی
5.4 حافظه قابل آدرس پذیر از طریق محتوا (CAM)
6.4 معماری جامع گراف نظارت
4.7 عملکرد ناظر
5 ارزیابی
1.5 سناریوی تشخیص حمله
2.5 سناریوی مکانیزم بررسی صحت
3.5 استفاده از منابع
4.5 مقایسه تجربی با تکنیک های پیشرفته فعلی
6. نتیجه گیری
منابع
Abstract
1 Introduction
2 Literature review
2.1 Related work
3 Framework security model
4 Monitor design
4.1 Software diversity in network processor
4.2 Monitoring graph generation
4.3 Real-time monitoring
4.4 Recovery mechanism
4.5 Content-addressable memory (CAM)
4.6 Compact monitoring graph architecture
4.7 Monitor operation
5 Evaluation
5.1 Attack detection scenario
5.2 Integrity checking mechanism scenario
5.3 Resource utilization
5.4 Experimental comparison with state of the art techniques
6 Conclusion
References
- اصل مقاله انگلیسی با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه