تحلیل استراتژیک منحنی ارزش: تشخیص و بهبود ارزش پیشنهادی مشتری
چکیده
مدیران اغلب در تلاشند تا دریابند چرا شرکتشان عملکرد پایینتری نسبت به رقبای خود دارد. این مقاله نشان میدهد که چگونه مدیران و مشاوران میتوانند از ابزار استراتژی موجود، بوم استراتژی Kim و Mauborgne ، برای بررسی دقیق علت ناکارآمدی شرکتشان استفاده کنند، به این دلیل که شرکت (1) ارائه ارزش پیشنهادی نادرست را به درستی اجرا میکند یا (2) نمیتواند به درستی ارزش درست پیشنهادی مشتری را ارائه دهد. زمانیکه مسائل مربوط به ارزش پیشنهادی شرکت و امور مربوط به ارائه خدمات آن به درستی تشخیص داده شود، استفاده از ابزار تحلیل منحنی ارزش مشتری میتواند مؤثر باشد. این مقاله با توضیح اینکه چگونه نویسندگان از این ابزار در بررسی استراتژی خود برای کمک و مشاوره به یک مشتری با موفقیت استفاده میکنند، به پایان میرسد.
1. طراحی ارزشهای پیشنهادی برنده
ارزش پیشنهادی مشتری یک توصیف مختصر از ارزشی است که شرکت عرضه مداوم آن را به مشتریان وعده میدهد. طراحی ارزش پیشنهادی مشتری با تحلیل نیازهای مشتریان، پیشنهادات رقبا و نقاط قوت شرکت آغاز میشود. زمانی که شرکتی بخش جاویژه و جذاب مشتری را هدف قرار میدهد، بنابراین مدیران آن با انتخاب ویژگیهایی که به بهترین شکل ممکن نیاز مشتریان مورد نظر را برآورده میکنند، پیشنهادی را مطرح میکنند. ویژگیهای یک پیشنهاد میتواند با رفع نیازهای عملکردی مشتری مانند کیفیت محصول یا زمان تحویل آن مرتبط باشد یا اینکه میتواند در جهت برآورده ساختن نیازهای عاطفی مشتری مانند میل به اعتبار یا مشارکت سوق داده شود. تصمیم نهایی در مورد ویژگیهایی که باید در پیشنهاد شامل شود، بر این اساس است که چگونه شرکت میتواند به طور سودمندی نیازهای مشتریان مورد نظر خود را به گونهای متفاوت از رقبای خود برآورده سازد.
5. مزیتها و محدودیتهای تحلیل استراتژیک منحنی ارزش
برای مدیران دشوار است که بدانند که آیا از ارزش پیشنهادی درست و فرایند مناسبی برای ارائه ارزش پیشنهادی خود برخوردارند یا خیر. مثالهایی مانند Blockbuster، Blackberry و Nokiaبر پیامدهایی تاکید دارند که در صورت عدم تشخیص مسائل مربوط به ارزش پیشنهادی مشتریان شرکت و رسیدگی به آنها توسط مدیران ایجاد میشوند. ابزار تحلیل استراتژیک منحنی ارزش که در این مقاله معرفی شد، روشی ساده است که مدیران میتوانند از آن در ارزیابی و بهبود ارزش پیشنهادی مشتری و فرایندهای تحویل آن استفاده کنند.
Abstract
Managers often struggle to determine why their firm is underperforming relative to its rivals. This article outlines how managers and consultants can use an existing strategy tool, Kim and Mauborgne's strategy canvas, to robustly test whether their firm is underperforming because it is (1) properly executing the wrong value proposition's delivery or (2) failing to properly execute the right customer value proposition's delivery. Once the issues with the firm's value proposition and its delivery activities are correctly diagnosed, the strategic value curve analysis tool assists in developing recommendations to improve the firm's profitability. The article concludes by describing how the authors successfully used the tool to help a consulting client complete a review of its strategy.
1. Designing winning value propositions
A customer value proposition is a succinct description of the value the firm promises to consistently deliver to its customers. Developing a customer value proposition starts with an analysis of customers’ needs, competitors’ offerings, and the firm’s strengths. Once the firm has selected an attractive customer niche segment to target, its managers then design an offering by selecting the attributes that best meet the needs of the targeted customers. An offering’s attributes can be directed at meeting the customers’ functional needs, such as product quality or delivery time, or they can be directed at meeting the customers’ emotional needs, such as their desire for prestige or inclusion. The final decision on what attributes to include in the offering is based on how well the firm can profitably meet the needs of its target customers differently than its competitors.
5. Advantages and limitations of strategic value curve analysis
It is difficult for managers to know whether they have the right value proposition and the right process to deliver the value proposition. Examples such as Blockbuster, Blackberry, and Nokia underscore the repercussions if managers do not quickly identify and address problems with the firm’s customer value proposition. The strategic value curve analysis tool outlined in the article is a straightforward method that managers can use to evaluate and improve their customer value propositions and delivery processes.
چکیده
1. طراحی ارزشهای پیشنهادی برنده
2. بوم استراتژی
3. تحلیل استراتژیک منحنی ارزش برای تشخیص و اصلاح مسائل ارزش پیشنهادی مشتری
3.1. منحنی ارزش # 1: ارزش پیشنهادی که شرکت به مشتریان خود وعده میدهد
3.2. منحنی ارزش # 2: ارزشی که شرکت در حال حاضر به مشتریان خود ارائه میدهد
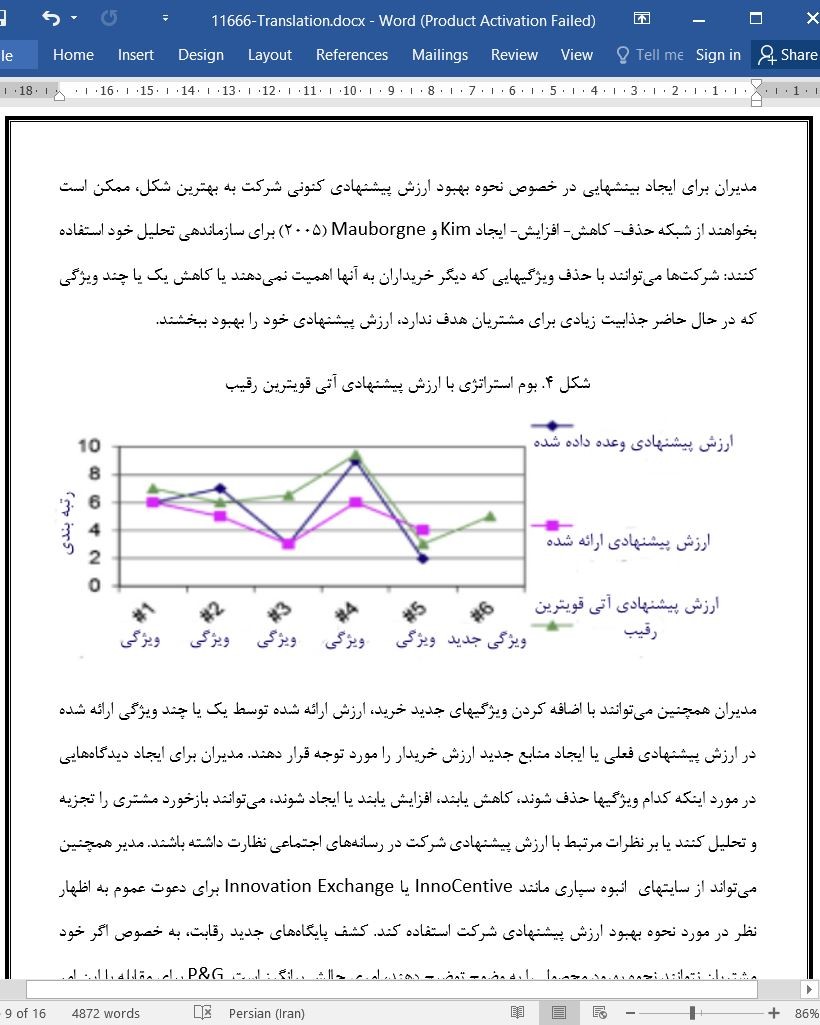
3.3. منحنی ارزش # 3: ارزش پیشنهادی آتی قویترین رقیب شرکت
4. تحلیل استراتژیک و عملی منحنی ارزش : باشگاه برون شهری و گلف کلمبیا
4.1. منحنی ارزش # 1: هیئت مدیره CGCC ارزش پیشنهادی وعده داده شده به اعضای خود را مطرح میکند
4.2. منحنی ارزش #2: ارزشی که بطور معمول به اعضای CGCC ارائه میشود
4.3. منحنی ارزش#3: ارزش پیشنهادی آتی قویترین رقیب
5. مزیتها و محدودیتهای تحلیل استراتژیک منحنی ارزش
منابع
Abstract
1. Designing winning value propositions
2. The strategy canvas
3. Strategic value curve analysis to diagnose and repair customer value proposition issues
3.1. Value Curve #1: The value proposition the firm promises to its customers
3.2. Value Curve #2: The value the firm currently delivers to its customers
3.3. Value Curve #3: The future value proposition of the firm’s strongest competitor
4. Strategic value curve analysis in practice: Columbian Golf and Country Club
4.1. Value Curve #1: The CGCC board draws the value proposition promised to its members
4.2. Value Curve #2: The value normally delivered to CGCC’s members
4.3. Value Curve #3: Strongest rival’s future value proposition
5. Advantages and limitations of strategic value curve analysis
References
- اصل مقاله انگلیسی با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه