بهبودی موشهای مبتلا به سندرم تخمدان پلی کیستیک توسط کوئرستین با مقاومت به انسولین
چکیده
مقاومت به انسولین (IR)و ناباروری دو عارضه مهم سندرم تخمدان پلی کیستیک (PCOS) هستند که در نتیجۀ تغییر در بخشهای خاصی از سیستم تولید مثل و متابولیکی بوجود میآیند. هدف ما مشاهده تأثیر کوئرستین بر PCOS ناشی از دی هیدرو اپی آندروسترون (DHEA) و مقاومت به انسولین در موشها بود. همه حیوانات به پنج گروه تقسیم شدند و از DHEA برای ایجاد PCOS استفاده شد. وزن بدن و مورفولوژی تخمدانی در همه گروهها ثبت گردید. میزان قند خون و انسولین بطور ناشتا مورد بررسی قرار گرفت. از روش ارزیابی مدل هوموستاز مقاومت انسولین (HOMA-IR) برای تعیین سطح IR استفاده شد. بیان گیرنده استروژن (ER) و ژنهای حامل شمارۀ ۴ گلوکز در رحم توسط واکنش زنجیرهای پلیمراز در زمان واقعی مورد بررسی قرار گرفت. فعالیت هگزوکیناز کبد (HK) و گلوکوکیناز (GK) با استفاده از اسپکتروفتومتری تعیین شد. کوئرستین به طور قابل توجهی حالت IR را در موشهای PCOS بهبود بخشید. PCOS منجر به کاهش در GK کبد و افزایش در فعالیت ویژه HK در کبد شد، در جاییکه کوئرستین هم فعالیت GK و هم HK کبد را افزایش داد. دادههای ما کاهش قابل توجهی را در ERAS رحم و بیان GLUT4 در گروه PCOS نشان داد، که توسط کوئرستین افزایش یافته بود. یکی از اثرات قابل توجه کوئرستین، کاهش شدید PCOS-IR، و القای قابل توجه بیان ژن GLUT4 رحمی و ER بود؛ بنابراین، این میتواند درمان موثری برای PCOS و عوارض آن،IR و ناباروری باشد.
نتیجه گیری
در خاتمه، دادههای ما نشان میدهند که کوئرستین اثر محافظ و تقویت کنندهای در PCOS دارد و این نتایج یک موفقیت واقعی را در درمان PCOS در پیشگیری از دیابت و افزایش باروری نشان میدهند. مزیت قابل توجه استفاده از کوئرستین، کاهش شدید IR و القاء بیان GLUT4 و ERa بود که در مطالعات ژنی و همچنین افزایش فولیکول زایی در تخمدانها کاملاً آشکار بود. نتایج ما همچنین کاهش فعالیت GK و افزایش فعالیت HKرا در کبد نشان داد. اثر بهبودبخش کوئرستین، فعالیت ویژه این آنزیمها را در کبد بهبود بخشید.
Abstract
Insulin resistance (IR) and infertility are two major complications of polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), which are the results of changes in certain parts of the reproductive and metabolic systems. We aimed to observe the effect of quercetin on dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA)-induced PCOS and insulin resistance in rats. All animals were divided into five groups and DHEA was used to induce PCOS. Bodyweight and ovarian morphology of all groups were observed. Fasting blood glucose and insulin levels were analysed. The homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) method was used for IR level determination. The expression of oestrogen receptor a (ERa) and glucose transporter 4 (GLUT4) genesin the uterus was examined by real-time polymerase chain reaction. Liver hexokinase (HK) and glucokinase (GK) activity was determined using spectrophotometry. Quercetin significantly improved the IR state in PCOS rats. PCOS resulted in a decrease in liver GK and an increase in liver HK specific activity, whereas quercetin increased both liver HK and GK activity. Our data also showed a significant reduction in uterine ERa and GLUT4 expression in the PCOS group, which was increased by quercetin. A remarkable effect of quercetin was the intensive reduction of PCOS-IR and significant induction of uterine GLUT4 and ERa gene expression; it could thus be a possible effective treatment for PCOS and its complications, IR and infertility.
Conclusion
In conclusion, our data suggest that quercetin has a strengthening protective effect in PCOS and the results represent an actual success in PCOS therapy in both diabetes prevention and increasing fertility. A remarkable advantage of quercetin usage was the sharp reduction in IR and induction of GLUT4 and ERa expression, which was evident in gene studies, as well as the increase of folliculogenesis in the ovaries. Our results also showed a decrease in liver GK activity and an increase in HK activity. The ameliorative effect of quercetin improved the specific activity of these liver enzymes.
چکیده
مقدمه
موضوعات و روشها
جانوران
ارزیابی بروز IR
مورفولوژی تخمدانی در موشها
آزمایش مختص فعالیت GK و HK در کبد
تحلیلهای آماری
نتایج
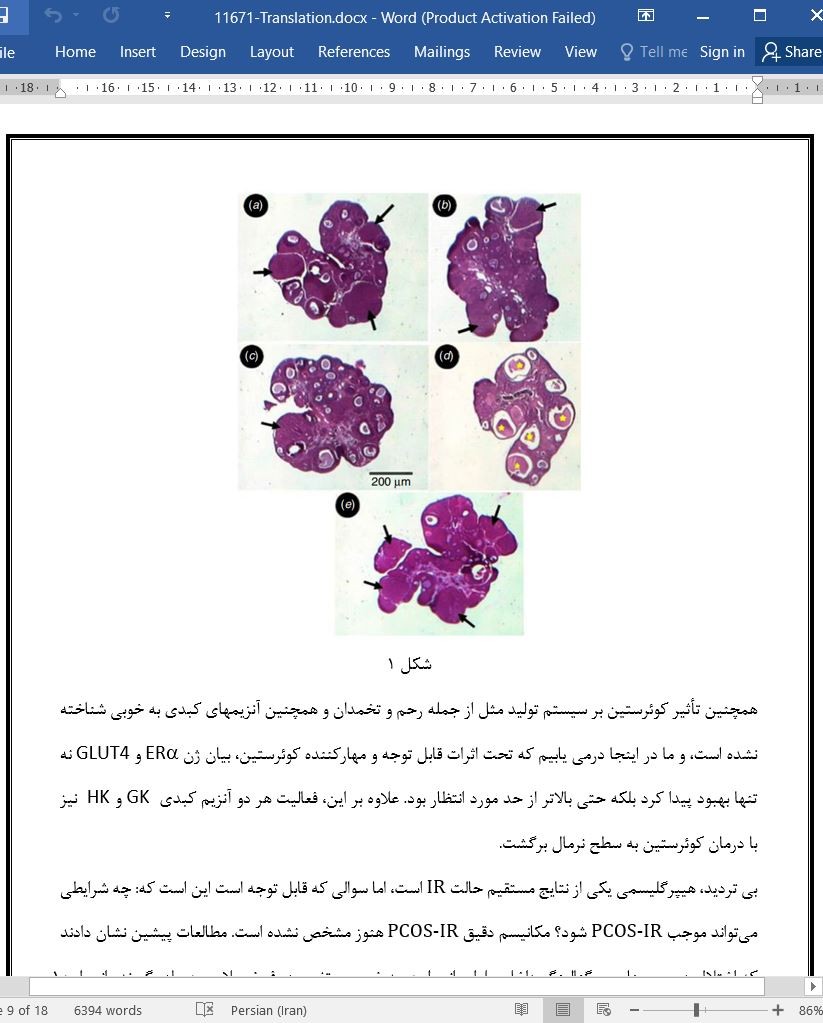
تأثیر PCOS و Q بر مورفولوژی تخمدانی
تأثیر PCOS و Q بر وزن بدن و میزان قند خون و انسولین ناشتا
فعالیت ویژه HK و GK در کبد
بیان ژنهای GLUT4 رحمی و Er
بحث
نتیجه گیری
منابع
Abstract
Introduction
Materials and methods
Animals
IR occurrence assessment
Rat ovarian morphology
Hepatic GK and HK specific activity assay
Endometrium RNA isolation and real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR)
Statistical analyses
Results
Effect of PCOS and Q on ovarian morphology
Effects of PCOS and Q on bodyweight and fasting insulin and glucose levels
Liver HK and GK specific activity
Expression of uterine GLUT4 and ERa genes
Discussion
Conclusion
References
- اصل مقاله انگلیسی با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه