کنترل فرکانس بار مقاوم مبتنی بر بهینه سازی افراطی محدود به جمعیت
چکیده
این مقاله کنترل کننده مقاوم انتگرالی- تناسبی (PI) را همراه با پارامترهای آن پیشنهاد می دهد که توسط بهینه سازی افراطی با جمعیت محدود برای مساله کنترل فرکانس بار مربوط به چندین ناحیه متصل به یکدیگر طراحی شده است. در طی فرآیند بهینه سازی، شاخص عملکرد مقاوم به عنوان تابع تناسب مورد استفاده قرار می گیرد که تکنیک نابرابری های ماتریس خطی برای توصیف محدودیت ∞ H به کار گرفته می شود و الزامات عملکرد خطا همانند خطای زمان انتگرال به عنوان محدودیت دیگری به کار گرفته می شود. سه سیستم برق متصل به دو ناحیه به عنوان سیستم های تست برای نمایش اثربخشی کنترل کننده پیشنهادی با مقایسه با دیگر روش های کنترل PI و یک کنترل پیش بینی مدل بهینه شده مورد استفاده قرار می گیرند. علاوه بر این، به منظور بررسی عملکرد کنترل کننده پیشنهادی برای مساله LFC مربوط به سیستم با مقیاس بزرگ، یک سیستم برق متصل به سه ناحیه به عنوان سیستم تست دیگری مورد استفاده قرار می گیرند. نتایج جامع تجربی به طور کامل نشان می دهند که روش کنترل پیشنهادی در این مقاله عملکرد بهتری نسبت به استراتژی دیگر کنترلی در بیشتر سناریوهای در نظر گرفته شده تحت شرایط اغتشاش بار و عدم قطعیت پارامترها براساس شاخص های عملکرد کنترل و پاسخ سیستم دارد.
1. مقدمه
کنترل فرکانس بار (LFC) از اهمیت زیادی برای سیستم های برق (توان) یا شبکه های کوچک در حفظ فرکانس زمان بندی شده سیستم و تبادل توان بین مناطق در طی شرایط بار معمولی و غیر معمولی برخوردار است [1]. هدف کنترل LFC به حداقل رساندن انحراف فرکانسی و خطای جریان خالص خط – شبکه بین مناطق کنترلی است. به طور ویژه، LFC می بایست از پایدارسازی با در نظر گرفتن غیرخطی های سیستم، عدم قطعیت پارامترهای مدل و اختلال بار یا حمله تشدید اطمینان حاصل شود [1-4]، به طوری که می تواند در مهندس واقعی برق رخ دهد. در طی چند دهه اخیر، تلاش های قابل توجهی به توسعه استراتژی های کنترلی برای مساله LFC اختصاص یافته است به طوری که به دو دسته تفکیک می شوند. اولین دسته تکنیک های مختلف پیشرفته [4-14] را برای طراحی کنترل کننده های پیشرفته برای سیستم برق متصل یا شبکه های کوچک به کار می گیرد. به عنوان مثال، کنترل پیش بینی کننده مدل [6-9]، ∞H و تجزیه و تحلیل- μ [10]، منطق فازی [12,13] و تکنیک مدل کشویی [14] برای مساله LFC به کار گرفته شده است.
5. نتیجه گیری
در این مقاله کنترل کننده PI مقاوم همراه با پارامترهای بهینه شده آن توسط روش CPEO گنجانده شده توسط روش TCH پیشنهاد داده شده است تا محدودیتی به نام روش کنترل CPEO-LMI-PI را مدیریت کند، که در آن تکنیک LMI برای توصیف محدودیت های H∞ به کار گرفته می شود و شاخص ITAE محدودیت نیاز به عملکرد خطا را در نظر می گیرد که به عنوان محدودیت دیگری برای بهبود و کنترل عملکرد و تعامل با برخی عبارت های غیرخطی به کار گرفته می شود. به منظور ارزیابی رقابت قدرتمند، ما از چهار آزمایش و مقایسه با کنترل کننده های متفاوت استفاده می کنیم.
Abstract
This paper proposes a robust proportional-integral (PI) controller with its parameters designed by constrained population extremal optimization for load frequency control problem of multi-area interconnected. During the process of optimization, the robust performance index is used as fitness function, where linear matrix inequalities technique is employed to describe the H∞ constraint, and the taking error performance requirement such as integral time absolute error is incorporated as another constraint. Three different two-area interconnected power systems are used as test systems to demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed controller by comparing with other PI control methods and one optimized model predictive control. In addition, in order to investigate the performance of proposed controller for the LFC problem of large scale system, a three-area interconnected power system is used as another test system. The comprehensive experimental results fully demonstrate that the proposed control scheme in this paper performs better than other control strategies on the most considered scenarios under the conditions of load disturbance and parameters uncertainties in terms of system response and control performance indices.
1. Introduction
Load frequency control (LFC) is of great importance for power systems or microgrids to maintain the scheduled system frequency and power exchange between areas during normal and abnormal conditions [1]. The control objective of LFC is to minimize the frequency deviation and net tie-line flow error between control areas. More specifically, the LFC should be ensured stabilization considering system nonlinearities, model parameters uncertainties, and load disturbance or resonance attack [1–4], which may take place in realistic power engineering. Over the past decades, considerable efforts have been devoted to developing control strategies for LFC problem, which can be roughly separated into two categories. The first category employs various advanced techniques [4–14] to design advanced controllers for LFC of interconnected power system or microgrids. For example, model predictive control [6–9], H∞ and μ-synthesis [10], fuzzy logic [12,13] and sliding model technique [14] have been utilized for LFC issue.
5. Conclusion
In this paper, we have proposed a robust PI controller with its parameters optimized by CPEO embedded by TCH method to handle the constraint called CPEO-LMI-PI control scheme, wherein the LMI technique is applied to describe the H∞ constraints and ITAE taking error performance requirement constraint is employed as another constraint for improving the control performance and dealing with some nonlinear terms. To validate the strong competitiveness, we use four Experiments by comparing with different controllers.
چکیده
1. مقدمه
2. پیشینه فنی
2-1 تکنیک تکنیک کنترل H∞ مبتنی بر LMI
2-2 نمونه ای از مدل پویای سیستم
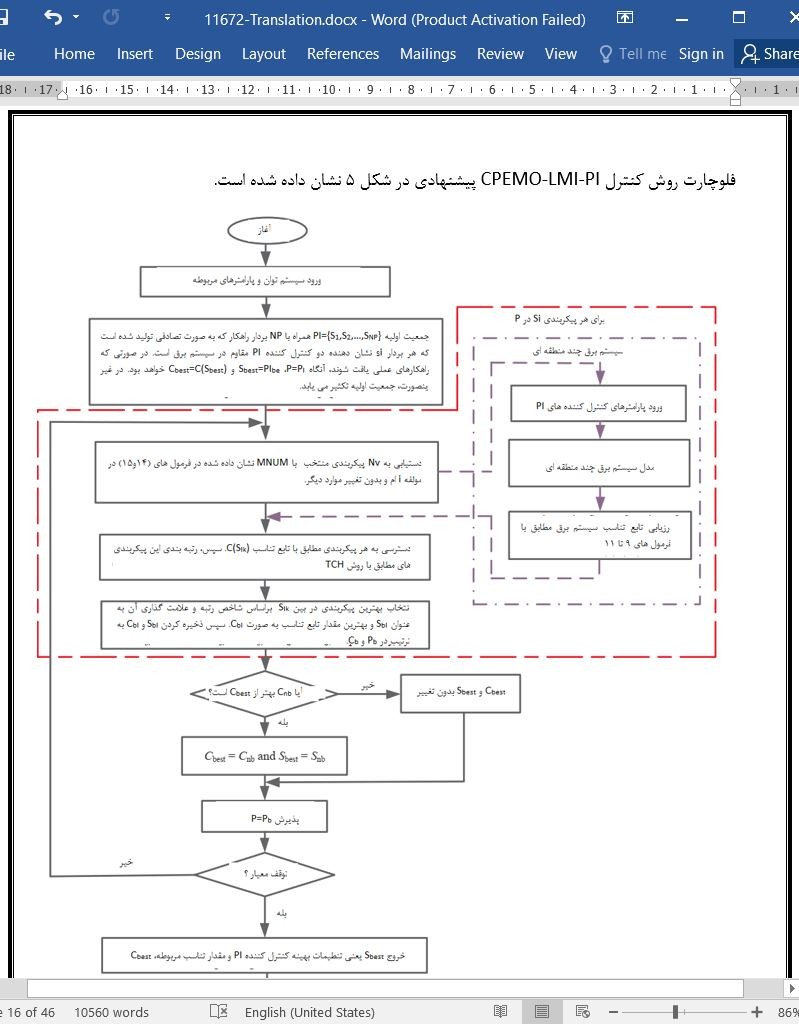
3. روش کنترل پیشنهادی
3-2 مکانیزم اصلی روش کنترل پیشنهادی
3-3 تحیل روش کنترل پیشنهادی
4. نتایج شبیه سازی
4-1 آزمایش 1
4-2 آزمایش 2
4-3: آزمایش 3
4-4 آزمایش 4
5. نتیجه گیری
منابع
Abstract
Nomenclature
1. Introduction
2. Technical background
2.1. LMI-based h∞ control technique
2.2. An example of system dynamic model
3. The proposed control scheme
3.1. Candidate objective function
3.2. Main mechanism of the proposed control scheme
3.3. Analysis of the proposed control scheme
4. Simulation results
4.1. Experiment I
4.2. Experiment II
4.3. Experiment III
4.4. Experiment IV
5. Conclusion
Appendix A.
References
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه