بررسی تاثیر ارزش تجربی روی احساسات، دلبستگی خود-پیوندی و وفادری به برند
چکیده
این مطالعه به بررسی نحوه تاثیر ارزش تجربی ادراک شده توسط مشتریان رستورانهای خانوادگی کرهای روی احساسات مربوط به مصرف، دلبستگی خود پیوندی به برند رستوران، و در نهایت، وفاداری به برند میپردازد. با مرور جامع تحقیقات، این مطالعه مدلی را ارائه داده و براورد میکند که روابط میان چهار بُعد ارزش تجربی (یعنی، جو، گریزگرایی، بازده سرمایهگذاری مشتری، و تعالی خدمت)، و متغیرهای نهفته احساسات مثبت و منفی، دلسبتگی خود-پیوندی و وفاداری به برند را تعیین میکند. تجزیه و تحلیل با مدلبندی معادلات ساختاری با دادههای جمعآوری شده از مشتریان رستورانهای خانوادگی در کره جنوبی انجام شد. نتایج نشان میدهند که ابعاد ارزش تجربی دارای تاثیر روی احساسات مثبت و منفی هستند. متغیرهای احساسات، همراه با دلسبتگی خود-پیوندی، نیز واسطهگر روابط بین ارزش ادراک شده تجربه نهارخوری و وفاداری به برند هستند.
پیشگفتار
مفهوم ارزش تجربی به «ادراکات مشتری از ارزش ناشی از تجربه مصرف اشاره دارد (جین، لاین و گو، 2013، ص 68). در حالی که اثرات ارزش تجربی در زمینههای مختلف خردهفروش در نظر گرفته شدهاند (کنگ، هوانگ، ژانگ و هسو، 2007؛ متویک، مالهورتا، و ریگدان، 2001، 2002)، علاقه به این پدیده به تازگی در زمینه رفتار نهارخوری گسترش یافته است (جین و همکاران، 2013؛ وو و لیانگ، 2009). رستوران محلی است که افراد در آن نه تنها غذا میخورند بلکه تعامل نیز دارند، سرگرم میشوند، روز خاصی را با خانواده یا دوستان نزدیک خود جشن میگیرند، یا استرحت کرده و از زندگی روزمره خود لذت میبرند. همه این تجارب مربوط به رستوران، مفهوم ارزش تجربی را برای مطالعه کل تجربه نهارخوری در یک محیط مصرف رستوران، مناسب میسازند (جین و همکاران، 2013؛ اوه، لی، کیم و شین، 2015). ادعا شده است که ارزش تجربی، ناشی از ادراکات از جو رستوران، گریز از زندگی روتین، کیفیت خدمات و ارزیابی کلی از این موضوع است که آیا این تجربه ارزش صرف وقت و پول را دارد یا نه. این ابعاد ارزش، که اغلب به عنوان جو/زیباییشناختی، گریزگرایی، برتری خدمات، و بازده سرمایهگذاری مشتری شناخته میشوند، برای ایجاد و حفظ روابط مثبت (به عنوان مثال، رضایت و اعتماد) با مشتریان رستران ضروری هستند، که این منجر به سطح بالایی از وفاداری رفتاری میشود (جین و همکاران، 2013؛ کنگ و همکاران، 2007؛ وو ولیانگ، 2009).
ABSTRACT
This study examines how experiential value as perceived by customers of Korean family restaurants influences consumption emotions, self-connective attachment to the restaurant brand, and, ultimately, brand loyalty. Having conducted a comprehensive literature review, the study proposes and estimates a model that specifies the interrelationships among four dimensions of experiential value (i.e., atmosphere, escapism, customer return on investment, and service excellence), and latent variables of positive and negative emotions, self-connective attachment, and brand loyalty. Analysis with structural equation modeling was conducted with data collected from customers of family restaurants in South Korea. The results show that dimensions of experiential value influence either positive or negative emotions. The emotion variables, together with self-connective attachment, also mediate the relationships between perceived value of dining experience and brand loyalty.
Introduction
The concept of experiential value refers to “a customer’s perceptions of value arising from the consumption experience” (Jin, Line, & Goh, 2013, p. 680). While the influences of experiential value have been considered in various retail contexts (Keng, Huang, Zhang, & Hsu, 2007; Mathwick, Malhotra, & Rigdon, 2001, 2002), interest in this phenomenon has recently been extended to the context of dining behavior (Jin et al., 2013; Wu & Liang, 2009). A restaurant is a place where people not only eat but interact socially, where they are entertained, celebrate a special day with family or close friends, or relax and refresh from their daily life. All these restaurant experiences make experiential value concept very relevant to study the total dining experience in a restaurant consumption setting (Jin et al., 2013; Oh, Lee, Kim, & Shin, 2015). It has been suggested that the experiential value is derived from perceptions of restaurant ambience, escape from routine, quality of service, and overall evaluation of whether the experience is worth time and money spent. These dimensions of value, often termed as atmosphere/aesthetics, escapism, service excellence, and customer return on investment, are essential to building and maintaining positive relationships (e.g., satisfaction and trust) with restaurant customers, which result in a high level of behavioral loyalty (Jin et al., 2013; Keng et al., 2007; Wu & Liang, 2009).
چکیده
پیشگفتار
مرور تحقیقات و توسعه فرضیه
پیشزمینه سنتی
ارزش تجربی
دلبستگی خود-پیوندی
عواطف
وفاداری به برند
روش
نمونه و جمعآوری دادهها
معیارها
نتایج تجربی
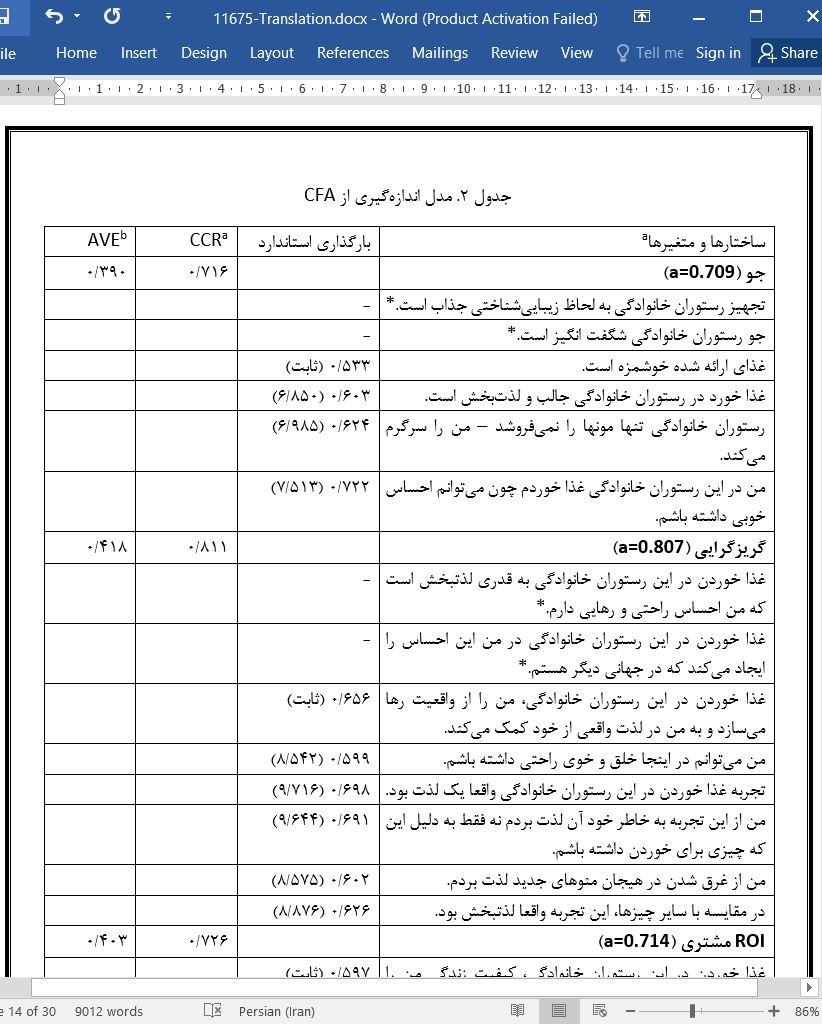
مدل اندازهگیری
مدل ساختاری و آزمایش فرضیات
بحث و پیامدها
محدودیت و تحقیقات آینده
منابع
ABSTRACT
Introduction
Literature review and hypothesis development
Theoretical background
Experiential value
Self-connective attachment
Emotion
Brand loyalty
Method
Sample and data collection
Measures
Empirical results
Measurement model
Structural model and test of hypotheses
Discussion and implications
Limitation and further research
References
- اصل مقاله انگلیسی با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه