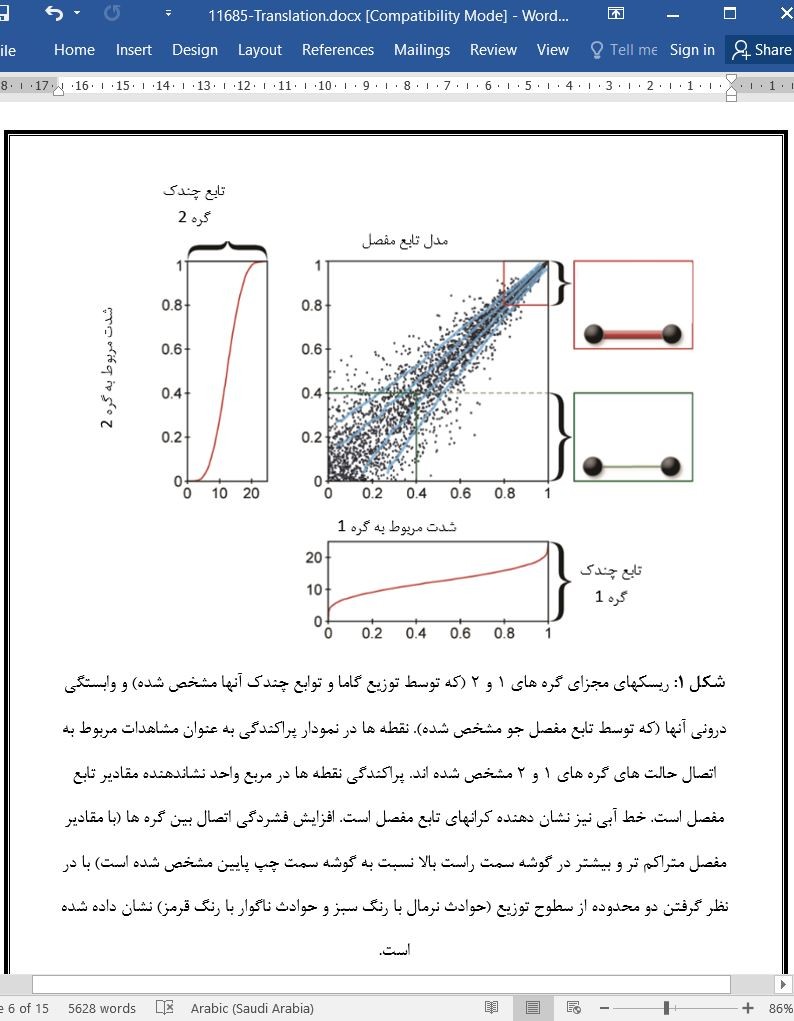
تحلیل ریسک و تحلیل ریسک سیستمی یکپارچه بر اساس توابع مفصل
خلاصه
تحقیق در زمینه ریسک سیستمی در جوامع تحقیقاتی در رشته های مختلف مورد توجه قرار گرفته است اما این تحقیقات نتوانسته اند رابطه قدرتمندی با تحقیقات مربوط به تحلیل ریسک سنتی و معتبر برقرار کنند. این مسئله به این علت است که تحقیقات مربوط به ریسک سیستماتیک، بیشتر روی ارتباط بین مولفه های موجود در یک سیستم تمرکز می کنند درحالیکه در تحقیقات مربوط به تحلیل ریسک تمرکز معمولا روی ریسک مجزای مربوط به هر مولفه مستقل است. بنابراین ما در این تحقیق، این مورد را بررسی کردیم که چطور می توان تحقیقات مربوط به ریسک سیستمی کنونی را از لحاظ مفهومی و همچنین تجربی به روشهای تحلیل ریسک سنتی مرتبط کرد. ما بر مبنای نظریه اسکلار که یک رابطه تک به تک بین توزیع چند متغیره و توابع مفصل در نظرگرفته، یک شکل جدید از مفهوم توابع مفصل را براساس دیدگاه شبکه ای پیشنهاد دادیم. این دیدگاه یک روش مطمئن را در مورد ریسک مجزای یکپارچه ( به شکل توزیع های احتمالی) و ریسک سیستمی (به شکل توابع مفصل که مولفه های مستقل موجود در چنین توزیع هایی را مشخص می کنند) در تمامی حوزه های تحقیقاتی ارائه می دهد. توابع مفصل می توانند حالت های گره ها را که مشخص کننده ریسک های مجزا هستند به طور پیوسته به صورت یک تابع تدریجی از شدت اتصال بین گره ها در حالت خودشان که مشخص کننده ریسک سیستمی هستند، مرتبط کنند. زمانیکه توابع مفصل برای توضیح چنین اتصال دقیقی بین گره ها مورد استفاده قرار می گیرد می تواند یک کمیت بسیار دقیق تر از ساختار شبکه ای سیستم ارائه دهد که به این ترتیب ارزیابی ریسک سیستمی را واقعی تر می کند و مخصوصا در هنگام بروز حوادث بسیار ناگوار (که احتمال وقوع کمتر اما اثر بسیار بیشتری دارند) که روی گره های سیستم تاثیر می گذارند؛ کاربرد بیشتری دارد. به این ترتیب، توابع مفصل می توانند در محاسبه میزان تغییرات در ریسک سیستمی مورد استفاده قرار گیرند و بنابراین کمک بزرگی برای مدیریت آنها باشند. ما در این مقاله مزایا و محدودیت های توابع مفصل را برای تحلیل ریسک یکپارچه از لحاظ مدلسازی، اندازه گیری و مدیریت مورد بررسی قرار دادیم.
1- مقدمه
ریسک سیستمی به سبب افزایش پیچیدگی جهان و همچنین افزایش داده های در دسترس توجه بسیار زیادی را در رشته های علمی – کاربردی و نظری به خود جلب کرده است.) (Page, 2015گزارش مربوط به خطرات جهانی اخیر که توسط مجمع جهانی اقتصاد ارائه شده، افزایش روز افزون آسیب پذیری در برابر خطرات سیستمی و درک محدود از مدیریت آن را در حال حاضر و در آینده نشان داده است. درحالیکه تحقیق روی ریسک سیستمی مسئله جدیدی نیست – به طور مثال این مسئله در حوزه زیست شناسی از سال 1970مطرح بوده است (2003 Scheffer and Carpenter,)– حوادث اخیر مخصوصا در زمینه بحرانهای مالی جهانی (08/2007)، توجه بخش عظیمی از محققان و کارورزان را تاحد بی سابقه ای به خود جلب کرده است. ( Boss et al. 2004; Thurner and Poledna 2013; Hochrainer-Stigler et al. 2018) یکی از مشخصات متمایز کننده ریسک سیستم تاکید آن روی ارتباط بین ریسکهای مجزاست و به همین علت ریسک شبکه ای نیز نامیده می شود.(Helbing, 2013) برخلاف ریسک سیستمی تمرکز ریسک مجزا روی مولفه های مستقل است. مهمتر اینکه در صورت تحقق یافتن ریسکهای مستقل تنها بخشی از سیستم دچار مشکل می شود در حالکیه در صورت تحقق ریسک سیستمی طبق تعریف آن سیستم از کار می افتد یا حداقل یک اختلال عظیم در عملکرد کل سیستم بوجود می آید.(Kovacevic et al. 2014)
Abstract
Systemic risk research is gaining traction across diverse disciplinary research communities, but has as yet not been strongly linked to traditional, well-established risk analysis research. This is due in part to the fact that systemic risk research focuses on the connection of elements within a system, while risk analysis research focuses more on individual risk to single elements. We therefore investigate how current systemic risk research can be related to traditional risk analysis approaches from a conceptual as well as an empirical point of view. Based on Sklar’s Theorem, which provides a one-to-one relationship between multivariate distributions and copulas, we suggest a reframing of the concept of copulas based on a network perspective. This provides a promising way forward for integrating individual risk (in the form of probability distributions) and systemic risk (in the form of copulas describing the dependencies among such distributions) across research domains. Copulas can link continuous node states, characterizing individual risks, with a gradual dependency of the coupling strength between nodes on their states, characterizing systemic risk. When copulas are used for describing such refined coupling between nodes, they can provide a more accurate quantification of a system’s network structure. This enables more realistic systemic risk assessments, and is especially useful when extreme events (that occur at low probabilities, but have high impacts) affect a system’s nodes. In this way, copulas can be informative in measuring and quantifying changes in systemic risk and therefore be helpful in its management. We discuss the advantages and limitations of copulas for integrative risk analyses from the perspectives of modeling, measurement, and management.
1 Introduction
Systemic risk is gaining increasing attention in theoretical and applied science disciplines due to the growing complexity of the world and the rise in data availability (Page 2015). The recent global risk report published by the World Economic Forum (WEF 2018) highlights the growing vulnerability to systemic risks and the limited understanding of its management, today and in the future. While research on systemic risk is not new—it has been discussed in ecology, for example, since the 1970s (Scheffer and Carpenter 2003)—recent events, in particular the global financial crisis of 2007/08, have increased interest on the part of researchers and practitioners to unprecedented levels (Boss et al. 2004; Thurner and Poledna 2013; Hochrainer-Stigler et al. 2018). A distinguishing feature of systemic risk is its emphasis on the connection between individual risks; it is therefore also called network risk (Helbing 2013). Contrary to systemic risk, individual risk focuses on single elements. Importantly, while the realization of individual risks may lead to a disaster in part of the system, the realization of systemic risk, by definition, leads to a breakdown, or at least a major dysfunction, of the whole system (Kovacevic et al. 2014).
خلاصه
1- مقدمه
2- استفاده از تابع مفصل برای مدلسازی ریسک سیستمی
3- استفاده از تابع مفصل برای محاسبه ریسک سیستمی
4- استفاده از توابع مفصل برای مطلع کردن مدیریت ریسک سیستمی
5.جمع بندی
منابع
Abstract
1 Introduction
2 Copulas to Model Systemic Risk
3 Copulas to Measure Systemic Risk
4 Copulas to Inform the Management of Systemic Risk
5 Conclusion
References
- اصل مقاله انگلیسی با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه