شیوع، همبستگیهای اجتماعی - جمعیتی و دانشگاهی اختلال وسواسی جبری
چکیده
مقدمه: مطالعاتی که شیوع وسواس جبری را در منطقه عربستان سعودی نشان میدهد بسیار اندک است و بیشتر در نمونه جمعیتی دانشجویان پزشکی و پیراپزشکی وجود دارد. هدف از این مطالعه برآورد شیوع علائم وسواس اجباری در یک نمونه جامعه دانشجویان علوم پزشکی کاربردی بود. علاوه بر این، ارتباط بین علائم وسواسی جبری و متغیرهای اجتماعی-جمعیتی و چندین جنبه از زندگی دانشگاهی بررسی شد.
روشها: در این مطالعه مقطعی 404 دانشجوی دانشگاه متعلق به چهار بخش به کار گرفته شدند. ابزارهایی که در این مطالعه استفاده شد، شامل معیارهای ارزیابی وسواس جبری (OCI - R) ، DSM - IV برای تشخیص مقیاس درجه بندی شدت OCD و Y - BOCS بود. نتیجه اصلی اختلال وسواس جبری احتمالی است (امتیاز OCI - R> 21). دانشجویان با نمره بیشتر از 21 بیشتر از نظر وجود اختلال وسواس جبری با استفاده از معیارهای DSM - IV و Y - BOCS ارزیابی شدند.
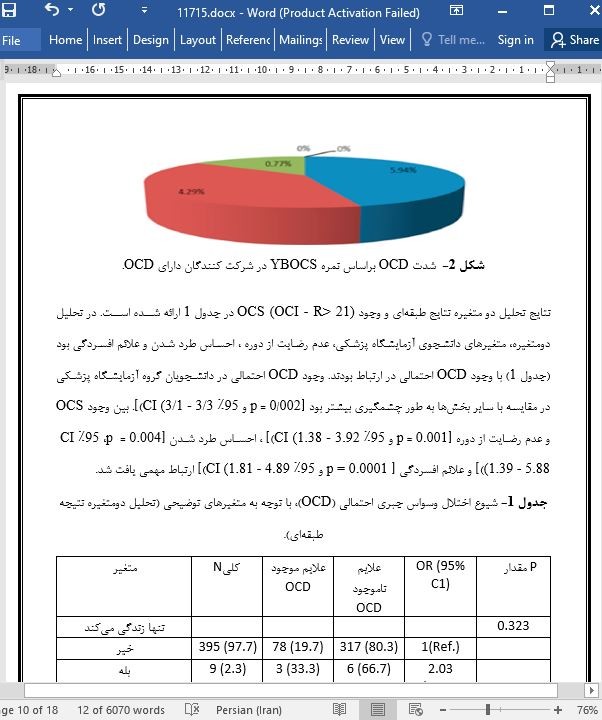
یافته ها: شیوع OCS با ابزار غربالگری OCI-R 20% بود [95% CI(19.902-20.098)]. شیوع واقعی OCD تأیید شده 5.06٪ بود [95% CI(4.39-6.12)]. وجود OCD احتمالی در دانشجویان گروه آزمایشگاه پزشکی بسیار زیاد بود [002/0 = p و95% CI(31.3-3.33) [. ارتباط مهمی بین حضور OCS و عدم رضایت از انتخاب دوره [001/0 = p ، 95٪ CI (1.38 - 3.92)] ، احساس طرد شدن [0.004 = p ، 95٪ CI (1.39 - 5.88]) و علائم افسردگی [0001/0 = p و CI (8/1 - 89/1)] وجود داشت. نمونه ما به زنان در سن دانشگاه محدود بود، بنابراین تفسیر شیوع قابل تعمیم نیست.
نتیجه گیری: وجود چنین اختلالی احتمالاً بر عملکرد تحصیلی ، کیفیت زندگی و روابط بین فردی تأثیر می گذارد ، شناسایی و درمان در زمان مناسب به بهبود عملکرد تحصیلی و کیفیت زندگی کمک می کند.
1- مقدمه
«وسواس به عنوان یک فکر ، تردید ، تصویر یا اصرار ناخوشایند ناخواسته تعریف می شود که به طور مکرر وارد ذهن می شود.» وسواس، اضطراب و خود ناهمخوان را تحریک میکند که به این معنی است که با عقاید فرد ناسازگار هستند. افراد اغلب تحمیلها را غیر منطقی و اغراق آمیز می دانند و سعی می کنند در برابر آنها مقاومت کنند. افکار وسواسی معمولاً شامل ترس از بیماری و آلودگی ، افکار تهاجمی ناخواسته ، دیگر افکار حرام مربوط به رابطه جنسی یا مذهبی و نیاز به تقارن یا دقت است. «اجبار رفتارهای تکراری یا اعمال ذهنی است که فرد احساس می کند در پاسخ به یک وسواس فکری انجام می شود. » آنها بیشتر غیر ارادی هستند و بندرت از آنها جلوگیری می شود (انجمن روانپزشکی آمریکا ، 1994). اجبار یک عمل آشکار است که توسط دیگران مشاهده می شود (مانند بررسی دری که قفل شده، تمیز کردن، مرتب کردن و جستجوی برای اطمینان مجدد) یا یک عمل ذهنی پنهانی که مشاهده نمی شود (مانند تکرار یک عبارت خاص در ذهن). اجبار، به طور کلی خنثی کردن پریشانی و اضطراب ناشی از وسواس است ( گودمن و دیگران ، 2014).
5- نتیجه گیری
شیوع محدود به نمونه زنان در سن دانشگاه با قابلیت تعمیم محدود است. OCD و OCD تحت بالینی، بیشتر در جامعه دانشجویان پزشکی و پیراپزشکی غیرمعمول نیست ، هر دو با همآیندی اختلالات قابل توجهی همراه است. بنابراین ، مهم است که هر دو در جامعه شناسایی شده و تحت درمان قرار بگیرند. وجود چنین اختلالی احتمالاً بر توانایی شناختی ، عملکرد تحصیلی ، کیفیت زندگی و روابط بین فردی تأثیر می گذارد. از این رو ، شناسایی و درمان در زمان مناسب به بهبود عملکرد تحصیلی و کیفیت زندگی کمک می کند.
Abstract
Introduction The studies suggesting the prevalence of Obsessive-compulsive disorder is scant in the region of Saudi Arabia and more so in a population sample of medical and paramedical students. The aim of this study was to estimate the prevalence of obsessive-compulsive symptoms in a community sample of students of applied medical sciences. Furthermore, an association between obsessive compulsive symptoms and various sociodemographic variables and several aspects of academic life were investigated.
Methods This cross-sectional study recruited 404 university students belonging to four departments. Tools used in the study included Obsessive compulsive inventory revised (OCI-R), DSM-IV criteria for diagnosis of OCD and Y-BOCS severity rating scale. The main outcome would be probable obsessive compulsive disorder (OCI-R score>21). The students with >21score were further evaluated for the presence of obsessive compulsive disorder using DSM-IV criteria and Y-BOCS.
Results The prevalence of OCS was 20% [95%CI (19.902–20.098)] with the OCI-R screening tool. Actual prevalence of confirmed OCD was 5.06% [95%CI (4.39–6.12)]. Presence of probable OCD was significantly high [p = 0.002 and 95%CI (1.31–3.53)] in students of laboratory medicine department. A significant association was found between presence of OCS and dissatisfaction with the course selection [p = 0.001, 95% CI (1.38–3.92)], feeling of rejection [p = 0.004, 95%CI (1.39–5.88)] and depressive symptoms [ p = 0.0001 and CI (1.81–4.89)]. Our sample was limited to college age women, therefore the interpretation of prevalence my not be generalizable.
Conclusion The presence of such a disorder is likely to effect academic performance, quality of life and interpersonal relationships hence, identification and treatment at the right time help improve academic performance and quality of life.
1. Introduction
“Obsession is defined as an unwanted intrusive thought, doubt, image, or urge that repeatedly enters the mind”. Obsessions are anxiety provoking and ego-dystonic which means they are incongruous with the person’s beliefs. The individual often regards the intrusions as illogical and exaggerated and tries to resist them. Obsessional thoughts typically include fears of illness and contamination, unwanted aggressive thoughts, other taboo thoughts involving sex or religion, and the need for symmetry or exactness. “Compulsions are repetitive behaviours or mental acts that a person feels driven to perform in response to an obsession”. They are mostly involuntary and are seldom resisted (American Psychiatric Association, 1994). A compulsion can be either an overt action observable by others (such as checking that a door is locked, cleaning, arranging and reassurance seeking) or a covert mental act that cannot be observed (such as repeating a certain phrase in the mind). Compulsions, generally serve to neutralize the distress and anxiety produced by obsessions (Goodman et al., 2014).
5. Conclusion
The prevalence is limited to the sample of college age women with limited generalizability. OCD and subclinical OCD are not uncommon in the community more so in medical and paramedical students, both being associated with significant comorbidity. Therefore, it is important that both are identified and treated in the community because of associated morbidity. The presence of such a disorder is likely to affect the cognitive capacity, academic performance, quality of life and interpersonal relationships. Hence, identification and treatment at the right time help improve academic performance and quality of life.
چکیده
1- مقدمه
2- مواد و روش ها
2-1- طراحی مطالعه
2-2- تنظیمات مطالعه
2-3- اندازه نمونه و راهبرد نمونه گیری
2-4- اندازه گیری (ابزار ارزیابی)
2-5- روش مطالعه
2-6- تحلیل آماری
3- نتیجه
4- بحث و گفتگو
4-1- شیوع OCD
4-2- شیوع OCD احتمالی و عوامل مرتبط با آن (نتیجه به شکل یک متغیر طبقه ای)
4-3- محدودیت ها
4-4- نقاط قوت
4-5- دستورالعمل های آینده
5- نتیجه گیری
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and methods
2.1. Study design
2.2. Study setting
2.3. Sample size and sampling strategy
2.4. Measurements (assessment instruments)
2.5. Study procedure
2.6. Statistical analysis
3. Result
4. Discussion
4.1. Prevalence of OCD
4.2. Prevalence of probable OCD and associated factors (outcome as a categorical variable)
4.3. Limitations
4.4. Strengths
4.5. Future directions
5. Conclusion
References
- اصل مقاله انگلیسی با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه