تاثیر اشتراک هیات مدیره بر عملکرد شرکت
چکیده
با توجه به اهمیت استراتژیک منابع و خدماتی که مدیران مشترک به یک شرکت می آورند، هدف مطالعه حاضر بررسی تاثیر اشتراک هیات مدیره بر عملکرد مالی در صنعت رستورانداری بر اساس نظریه وابستگی به منابع است. ضمناً، به عنوان هدف اولیه، مطالعه حاضر تنوع جغرافیایی را به عنوان عامل اقتضائی محوری که نقش تعدیل کننده ای در رابطه بین عملکرد شرکت – اشتراک هیات مدیره دارد، در نظر می گیرد. مطالعه حاضر نه تنها اثر تاثیر اصلی مثبت اشتراک هیات مدیره بر عملکرد مالی بلکه اثر تعدیل کننده مثبت تنوع جغرافیایی بر رابطه بین اشتراک هیات مدیره و عملکرد شرکت را نشان داد. این یافته ها با ارائه بُعد منحصر به فردی مبنی بر اینکه تنوع جغرافیایی یک عامل برجسته تعدیل کننده تاثیر اشتراک هیات مدیره بر عملکرد شرکت در صنعت رستورانداری است بر غنای ادبیات حاکمیت شرکتی می افزاید. نتایج مزبور پیامدهایی برای مدیران و سهامداران شرکت های رستورانداری در هنگام انتخاب مدیران به عنوان نماینده سهامداران به همراه دارد.
۱. مقدمه
در عصر شرکت های مدرن، هیات مدیره به شدت در تصمیمات استراتژیک و نتایج سازمانی شرکت دخالت دارد (فینکلشتاین و مونی، ۲۰۰۳). اگر چه مدیران عامل و سایر مدیران اجرایی به طور کلی مهم ترین نقش را در فرآیند تصمیم گیری استراتژیک ایفا می کنند (همبریک و میسون، ۱۹۸۴) اما هیات مدیره، به عنوان تیمی منتخب به نمایندگی از سهامداران، از قدرت ضمنی برای اعمال بر دامنه وسیعی از انتخاب های استراتژیک برخوردار است. بر این اساس، هیات مدیره از طریق نظارت بر مدیران ارشد و فراهم ساختن منابع مناسب برای شرکت در راستای دستیابی به مزیت رقابتی بر عملکرد شرکت تاثیر می گذارد (فینکلشتاین و همکاران، ۲۰۰۹؛ هیلمن و دالزیل، ۲۰۰۳). به دلیل نقش محوری هیات مدیره، شرکت ها باید با تمرکز بر سرمایه و منابعی که مدیران منتخب جدید برای شرکت به ارمغان می آورند، صلاحیت های متعدد نامزدها را در هنگام گردهمایی هیات مدیره لحاظ نمایند (ناهاپیت و گوشال، 1998؛ کلمن، 1988؛ اوی و همکاران، ۲۰۱۵).
بیانیه تاثیرگذاری
انتظار می رود که مطالعه حاضر با ارائه رهنمودهایی برای دست اندرکاران و سهامداران شرکت های رستورانداری آمریکا در هنگام انتخاب هیات مدیره، به اقتصاد آمریکا کمک نماید. به طور خاص و بر اساس نتایج مطالعه حاضر، با افزایش تعداد مدیران مشترک در شرکت های رستورانداری، عملکرد مالی بهتر مورد انتظار خواهد بود. ضمناً، منافع اقتصادی حاصل از اشتراک هیات مدیره با پیاده سازی فعال تنوع جغرافیایی از سوی شرکت های رستورانداری، افزایش می یابد.
Abstract
Given the strategic importance of resources and service that interlocking directors bring to a firm, this study aims to examine the influence of board interlocks on financial performance in the restaurant industry based on the resource dependence theory. Further, as the primary purpose, this study incorporates geographic diversification as a pivotal contingent factor, playing a moderating role on the board interlocks-firm performance relationship. This study found not only a positive main effect of board interlocks on financial performance, but also a positive moderating effect of geographic diversification on the relationship between board interlocks and firm performance. These findings contribute to the corporate governance literature by providing a unique dimension that geographic diversification is a salient factor adjusting the effect of board interlocks on firm performance in the restaurant industry. The results further offer implications for managers and shareholders of restaurant firms when electing directors as representatives of shareholders.
1. Introduction
In the modern corporate era, a board of directors heavily involves in strategic decision-making and organizational outcomes of firms (Finkelstein & Mooney, 2003). Although CEOs and other top executives have generally played the most significant role in a strategic decision-making process (Hambrick & Mason, 1984), the board of directors, as a team elected to represent shareholders, has exerted implicit power over a wide range of strategic choices. Accordingly, boards affect firm performance by monitoring top executives and providing appropriate resources a firm needs to obtain a competitive advantage (Finkelstein et al., 2009; Hillman & Dalziel, 2003). Due to the pivotal role of a board, firms need to consider multiple qualifications of candidates when assembling the board, focusing particularly on what capital and resources newly elected directors are expected to bring to the firm (Nahapiet & Ghoshal, 1998; Coleman, 1988; Ooi et al., 2015).
Impact statement
This study expects to contribute to the US economy by providing guidelines for practitioners and shareholders of US restaurant firms when selecting a board of directors. Specifically, as restaurant firms increase a proportion of interlocking directors, based on the results of this study, they may expect better financial performance. Further, the economic benefits from board interlocks may be magnified while restaurant firms actively implement geographic diversification.
چکیده
۱. مقدمه
2. بررسی ادبیات و تدوین فرضیات
2.1. رابطه بین اشتراک هیات مدیره و عملکرد شرکت
2.2. اثر اشتراک هیات مدیره بر عملکرد شرکت در صنعت رستورانداری
2.3. تاثیر تعدیل کننده تنوع جغرافیایی
۳. روش ها
3.1. داده ها
3.2. مدل ها و روش های برآورد
3.3. معیار عملکرد شرکت
۳.۴. معیار اشتراک هیات مدیره
3.5. سایر متغیرهای توضیحی
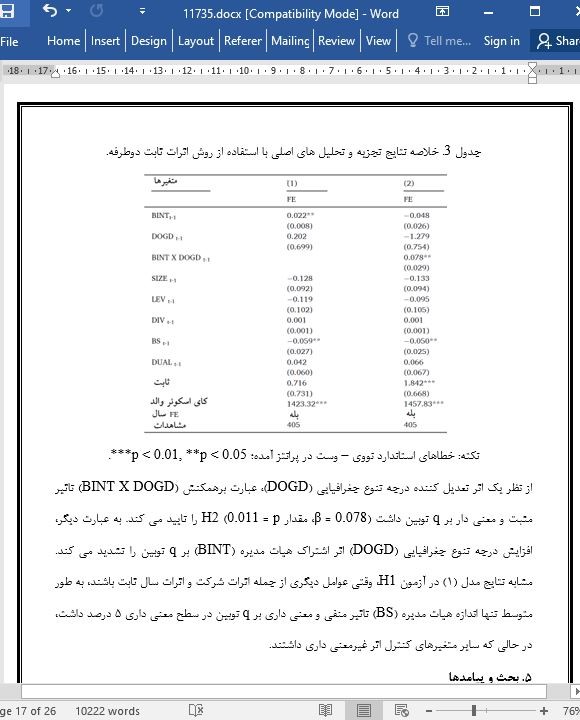
۴. تجزیه و تحلیل و نتایج
4.1. آمار توصیفی
4.2. تجزیه و تحلیل های اصلی و آزمون فرضیه ها
۵. بحث و پیامدها
بیانیه تاثیرگذاری
رفرنس
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature review and hypotheses development
2.1. The relationship between board interlocks and firm performance
2.2. The effect of board interlocks on firm performance in the restaurant industry
2.3. The moderating effect of geographic diversification
3. Methods
3.1. Data
3.2. Models and estimation methods
3.3. Firm performance measure
3.4. Board interlocks measure
3.5. Other explanatory variables
4. Analyses and results
4.1. Descriptive statistics
4.2. Main analyses and hypotheses testing
5. Discussions and implications
Impact statement
CRediT author statement
Declaration of competing interest
References
- اصل مقاله انگلیسی با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه