بررسی و تحلیل پروژه های بلاکچین در مدیریت زنجیره تامین
چکیده
زنجیره های تامین به طور فزاینده ای پیچیده شده اند که این امر تضمین شفافیت در کل زنجیره تامین را دشوار می سازد. در این زمینه، رویکردهای اولیه مطرح شده، ویژگی های تغییرناپذیر، غیرمتمرکز و امن فناوری بلاکچین را برای افزایش شفافیت، امنیت، اصالت و قابلیت حسابرسی دارایی ها در زنجیره های تامین اتخاذ می نمایند. مقاله حاضر با بررسی مقالات اخیر، فناوری بلاکچین و مدیریت زنجیره تامین را با هم ترکیب نموده و آن ها را با توجه به پیچیدگی که باید در بلاکچین ترسیم گردند دسته بندی می کند. در نتیجه، افزایش شفافیت زنجیره تامین به عنوان هدف اصلی پروژه های اخیر بلاکچین در مدیریت زنجیره تامین مشخص شده است. لذا، اکثر مقالات اخیر با زنجیره های تامین و محصولات ساده سر و کار دارند. رویکردهای معدودی با بخش های پیچیده ای سر و کار دارند که تنها نواحی تابعه زنجیره های تامین را ترسیم می نمایند. در حال حاضر، هیچ نمونه ای وجود ندارد که هدف آن افزایش شفافیت زنجیره های تامین تولید پیچیده باشد که نگاشت فرآیندهای مونتاژ پیچیده، قابلیت حسابرسی کارآمد همه دارایی ها، و پباده سازی اصلاحات پویا را ممکن می سازد.
۱. مقدمه
شرکت ها باید با منافع رو به رشد مشتریان، دولت ها، و سازمان های غیردولتی در داشتن شفافیت بیشتر برند، سازندگان و تولید کنندگان در سراسر زنجیره تامین رو به رو شوند [۱، ۲]. در نتیجه، مسائل پایداری اجتماعی و زیست محیطی برای تولید کنندگان به طور فزاینده ای مهم شده اند تا شهرت بی نقص برند آنان حفظ گردد [۳]. علاوه بر ریسک درگیری ناخواسته در مساءل پایداری اجتماعی و زیست محیطی، فقدان شفافیت زنجیره تامین نیز احتمال معرفی مولفه های ساختگی را به زنجیره تامین افزایش می دهد. به عنوان مثال، جعل بخش های الکترونیکی، ریسک های بالقوه ای مانند ایمنی و از دست دادن سود شرکت ها موجب شده و شهرت تولیدکنندگان و توزیع کنندگان را بدنام می نماید [6-4]. به گفته ماچادو و همکاران [7]، کنترل و اعتماد در زنجیره تامین پس از یکپارچه سازی خریداران و تامین کنندگان به منظور اجتناب از شیوه های مضر، جنبه های اولیه اجباری محسوب می شوند. با این حال، دستیابی به شفافیت کامل و تشخیص مولفه های ساختگی بسیار پیچیده بوده و امری پرهزینه است [4، ۷، 8]. چن و همکاران [2] اظهار داشتند که ایجاد پایگاه داده های عمومی کاملاً نظارت شده برای تبادل اطلاعات درباره هویت تامین کنندگان و سوابق تبعیت از قوانین در نهایت مسائل شفافیت و پایداری زنجیره های تامین جهانی را حل می کند. برای غلبه بر این چالش های شفافیت در زنجیره های تامین، تحقیقات اخیر و پروژه های صنعتی به بررسی استفاده از فناوری بلاکچین در این حوزه خاص پرداختند [12-9].
۴. نتیجه گیری
از فناوری بلاکچین در مدیریت زنجیره تامین صنایع مختلف استفاده می شود. در نتیجه، هدف اصلی پروژه های اخیر بلاکچین افزایش شفافیت زنجیره تامین است. الزامات ساده تر از نظر پیچیدگی محصول، برای مثال در زنجیره های تامین مواد غذایی، را می توان به طور کامل در بلاکچین ترسیم نمود. زنجیره های تامین مواد غذایی، بخش عمده ای از پروژه های بلاکچین مربوط به زنجیره تامین را در بر می گیرند. در زنجیره های تامینی که با بخش های پیچیده سر و کار دارند، هیچ راه حلی وجود ندارد که هدف آن افزایش شفافیت باشد که امکان نگاشت فرآیندهای همگذاری، قابلیت حسابرسی کارآمد همه دارایی ها، و اجرای اصلاحات پویا را فراهم می کند. مواد خام، اجزای واسطه، محصولات نهایی، و وقایع تبدیل همگی ویژگی های بسیار متفاوتی دارند و لاجرم همچنان با یکدیگر در یک نقطه خاص از زنجیره های تامین تولیدی پیچیده تعامل داشته یا در هم ادغام می شوند. هیچ یک از مقاله علمی تحلیل نشده حاوی رویکردی نیست که زنجیره های تامین پیچیده را از مواد خام گرفته تا محصولات نهایی همراه با رویدادهای تبدیل در بر گیرد.
Abstract
Supply chains have become increasingly complex, making it difficult to ensure transparency throughout the whole supply chain. In this context, first approaches came up, adopting the immutable, decentralised, and secure characteristics of the blockchain technology to increase the transparency, security, authenticity, and auditability of assets in supply chains. This paper investigates recent publications combining the blockchain technology and supply chain management and classifies them regarding the complexity to be mapped on the blockchain. As a result, the increase of supply chain transparency is identified as the main objective of recent blockchain projects in supply chain management. Thereby, most of the recent publications deal with simple supply chains and products. The few approaches dealing with complex parts only map sub-areas of supply chains. Currently no example exists which has the aim of increasing the transparency of complex manufacturing supply chains, and which enables the mapping of complex assembly processes, an efficient auditability of all assets, and an implementation of dynamic adjustments.
1. Introduction
Companies have to deal with the growing interests of customers, governments, and non-governmental organizations in having a greater transparency of brands, manufacturers, and producers throughout the supply chain [1, 2]. As a result, social and environmental sustainability issues have become increasingly important for manufacturers in order to maintain the flawless reputation of their brand [3]. In addition to the risk of being unintentionally involved in social and environmental sustainability issues, a lack of supply chain transparency also increases the probability of counterfeit components being introduced into a supply chain. For example, the counterfeiting of electronic parts causes potential risks including safety and loss of profits to companies, as well as maligning the reputation of manufacturers and distributors [4–6]. According to Machado et. al. [7], control and trust in the supply chain are mandatory initial aspects when integrating buyers and suppliers in order to avoid harmful practices. However, achieving full transparency and detecting counterfeit components is extremely complex and can be a costly undertaking [4, 7, 8]. Chen et. al. [2] suggested that the development of a strictly monitored public database to exchange information about suppliers’ identities and compliance records could eventually solve the transparency and sustainability problems of globalised supply chains. To overcome these transparency challenges in supply chains, recent research and industrial projects investigate the utilisation of the blockchain technology in this particular field [9–12].
4. Conclusion
The blockchain technology is used in supply chain management of various industries. Thereby, the main objective of recent blockchain projects is to increase the supply chain transparency. The simpler requirements in terms of product complexity, for example in food supply chains, can already be completely mapped on the blockchain. Food supply chains take a major part of supply chain related blockchain projects. In supply chains dealing with complex parts no solution exists which has the aim of increasing the transparency and which enables the mapping of assembly processes, an efficient auditability of all assets, and an implementation of dynamic adjustments. Raw materials, intermediate components, final products, and transformation events all have very different properties and still inevitably interact or merge with each other at a certain point in complex manufacturing supply chains. None of the analyzed scientific publications deals with an approach covering complex supply chains from raw materials to final products with transformation events included.
چکیده
۱. مقدمه
۲. روش شناسی
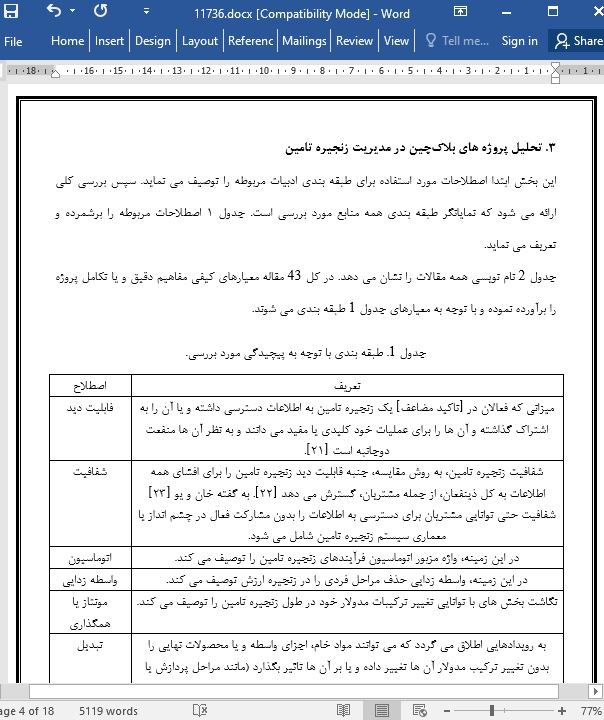
۳. تحلیل پروژه های بلاکچین در مدیریت زنجیره تامین
3.1. طبقه بندی با توجه به پیچیدگی مورد بررسی
3.2. تجزیه و تحلیل رویکردهای نگاشت بلاکچین
۴. نتیجه گیری
رفرنس
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
3. Analysis of blockchain projects in supply chain management
3.1. Classification regarding the investigated complexity
3.2. Analysis of blockchain mapping approaches
4. Conclusion
References
- اصل مقاله انگلیسی با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه