ویژگی های بهداشتی درک شده در صنعت هتلداری: حفظ مشتری در میان بحران کووید 19
چکیده
بیماری فراگیر کووید 19 بحرانی را در صنعت هتلداری در سراسر جهان ایجاد کرده است، اما تعداد کمی از مطالعات، روشی را برای حفظ مشتریان ارائه کرده اند. این مطالعه، مدیریت بهداشتی را به عنوان ابزاری برای کاهش آسیب های غیرمستقیم کووید 19 به صنعت هتلداری معرفی می کند. این مطالعه، ویژگی های بهداشتی درک شده را تعریف کرده و اثرات آن بر تصویر هتل، تبلیغات دهان به دهان و تمایل به بازدید مجدد را نشان می دهد. این مطالعه سه نوع ویژگی بهداشتی درک شده را با استفاده از روش های کیفی و کمی تعریف و تأیید می کند. همچنین از مدلسازی معادله ساختاری برای تأیید فرضیه ها بهره برده و نشان می دهد تأثیرات معناداری میان متغیرهای پیشنهادی وجود دارد. همچنین بینش معنادار و مهمی را در مورد تصویر هتل و رفتار مشتریان از طریق ویژگی های بهداشتی درک شده ارائه می دهد.
1. مقدمه
در دنیای امروز، میزان و طیف گسترش بیماری های عفونی با سرعت زیادی رو به افزایش است که دلیل آن توسعه حمل و نقل، رشد جمعیت، افزایش تعداد مسافران و جنبه های مشترک زندگی در کل جهان می باشد. بیماری کرونا ویروس (کووید 19) یک بیماری عفونی جدید است که به سرعت از شهری که برای اولین بار در دسامبر سال 2019 در آن یافت شد بود، یعنی ووهان چین به کل جهان انتقال یافت و توسط سازمان جهانی بهداشت به عنوان یک بیماری فراگیر در نظر گرفته شد. اثر کووید 19 بر روی اقتصاد و جامعه جهانی بسیار زیاد است. کووید 19 آسیب حادی بر صنعت هتلداری گذاشته است. برای مثال، گروه مهمانداری چند ملیتی فرانسه گزارش داد بیش از نیمی از موقعیت های برند هتلداری فعالیت خود در سراسر جهان را متوقف کرده اند و انتظار می رود این تعداد افزایش یابد (مدیریت هتلداری، 2020). علاوه بر این، انجمن اسکان و هتلداری امریکا (AHLA) گزارش داد از زمان آغاز بحران کووید 19، هتل ها در آمریکا بیش از 15 میلیارد دلار از دست داده اند و انتظار می رود نرخ اشغال اتاق ها در ماه های پیش رو 20% یا کمتر باشد شاید حتی در آینده این میزان وخیم تر نیز شود (AHLA، 2020). بنابراین، باید بررسی کنیم چطور صنعت گردشگری و هتلداری باید برای فجایع جدی مانند بیماری فراگیر کووید 19 آماده شوند (فالکنر، 2001).
6. نتیجه گیری
کووید 19 یک بیماری مسری جدیدی است که هیچ روش اثبات شده ای برای درمان یا پیشگیری از آن وجود ندارد. شیوع کووید 1 استفاده و بازدید از هتل ها را به میزان قابل توجهی کاهش داده است. لازم است بهداشت را بمنظور جلوگیری از بیماری مهمان و کارکنان هتل مدیریت کنیم. هرچند، هیچ تحقیقی در مورد بهداشت هتل در طی بیماری کوید 19 انجام نشده است. بنابراین، این مطالعه ویژگی های بهداشتی درک شده را بررسی کرده و اثر آنها بر تصویر هتل و رفتار مشتری را بررسی کرده است. این مطالعه اثر سه ویژگی را تعیین کرده است یعنی بهداشت محیط مورد استفاده مشتریان، بهداشت فردی کارکنان و بهداشت محیط کار. این تحلیل تجربی نشان می دهد ویژگی های بهداشتی درک شده بر تصویر هتل، تبلیغ دهان به دهان و تمایل به بازدید مجدد از هتل اثر می گذارد. همچنین، این مطالعه نقش های واسطه ای نسبی تصویر شناختی و تصویر عاطفی در چارچوب نظری پیشنهادی را تأیید می کند.
Abstract
The COVID-19 pandemic has caused a crisis in the hotel industry worldwide, but few studies have suggested methods to retain customers. This study proposes hygiene management as a means to minimize the indirect damage from COVID-19 to the hotel industry. It identifies perceived hygiene attributes and explores their influence on hotel image, word of mouth, and revisit intentions. This study identifies and validates three types of perceived hygiene attributes through qualitative and quantitative methods. It uses structural equation modeling to validate hypotheses and concludes that there are significant relationships of influence between the proposed variables. This study provides important and meaningful insights into hotel image and customer behavior through perceived hygiene attributes.
1. Introduction
In today’s globalized world, the rate and range of the spread of infectious diseases are rapidly accelerating due to developments in transportation, growing population, increasing number of travelers, and shared sphere of life of the entire world. Coronavirus disease (COVID19), a new infectious disease, has spread rapidly from its first discovery in Wuhan, China in December 2019 to the designation of COVID-19 as a pandemic by the World Health Organization (WHO). The unexpected outbreak and rapid spread of COVID-19 has shocked the world, and has had a major impact on the health and economic well-being of individuals, as well as corporate performance. The impact of COVID-19 on the global economy and society is rapidly intensifying. The damage from COVID-19 is acute in the hotel industry. For example, French multinational hospitality group Accor reported that more than half of its hotel brand locations had ceased to operate worldwide, and that this number was expected to grow (Hotel Management, 2020). In addition, the American Hotel and Lodging Association (AHLA) reported that hotels in the United States had lost more than $15 billion in room revenues since the beginning of the COVID-19 crisis, and expected occupancy rates of 20% or less in the coming months, with even further deterioration possible in the future (AHLA, 2020). Therefore, there is a need to investigate how the hotel and tourism industry must prepare for serious disaster situations such as the COVID-19 pandemic (Faulkner, 2001).
6. Conclusion
COVID-19 is a newly discovered infectious disease, with no proven methods of treatment or prevention. The prevalence of COVID-19 has significantly reduced the use and visits of hotels, which are utilized by large numbers of people. It is necessary to manage hygiene thoroughly to prevent infections of hotel guests and staff. However, there is no research on hotel hygiene amid the COVID-19 pandemic. Thus, this study explored perceived hygiene attributes and investigated their influence on hotel image and customer behavior. This study determined the influence of three attributes, namely, hygiene of customer-use spaces, personal hygiene of staff, and workspace hygiene. The empirical analysis found that the perceived hygiene attributes influenced hotel image, word of mouth, and revisit intention. Furthermore, this study confirmed the partial mediating roles of cognitive image and affective image in the proposed theoretical framework.
چکیده
1. مقدمه
2. مروری بر مقالات پیشین
2.1. بحران کووید 19
2.2. بهداشت هتل
2.3. تصاویر شناختی و عاطفی
2.4. تبلیغات دهان به دهان و تمایل به بازدید مجدد
2.5. روابط میان متغیرهای مورد مطالعه
2.6. مدل پژوهشی
3. روش ها
3.1. روش کیفی
3.2. ابزار اندازه گیری برای ساختارهای دیگر
3.3. جمع آوری اطلاعات و ویژگی های نمونه
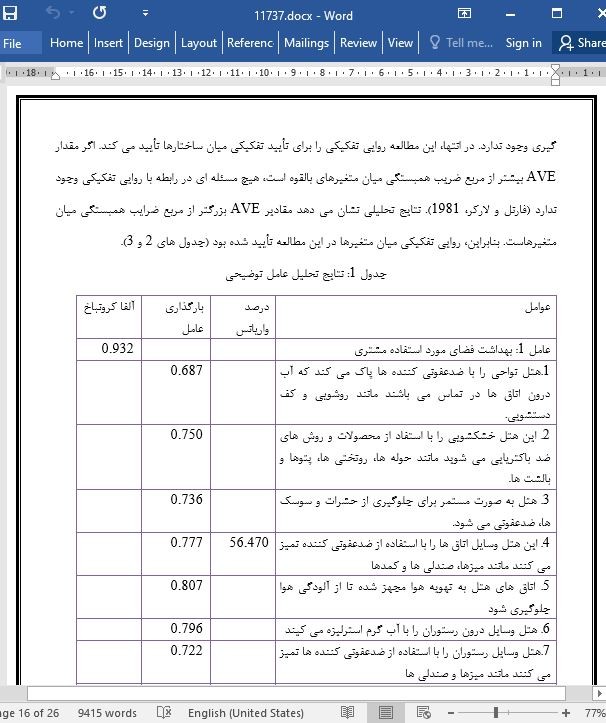
4. نتایج
4.1. روش های کمی
5. بحث
6. نتیجه گیری
منابع
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature review
2.1. The COVID-19 crisis
2.2. Hotel hygiene
2.3. Cognitive and affective image
2.4. Word of mouth and revisit intention
2.5. Relationships among study variables
2.6. Research model
3. Methods
3.1. Qualitative approach
3.2. Measurement tools for other constructs
3.3. Data collection and sample characteristics
4. Results
4.1. Quantitative procedures
5. Discussion
6. Conclusion
Funding
References
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه