اثرات لرزه ای قائم بر شکنندگی لرزه ای سازه های زیر زمینی با فضای بزرگ
بیشینه ی شتاب زمین در راستای قایم بیشتر از بیشینه ی شتاب زمین در راستای افقی می باشد. برای ارزیابی شکنندگی لرزه ای مربوط به سازه های زیر زمینی با فضای بزرگ، مد نظر قرار دادن اثر لرزه ای قائم، ضروری می باشد. در این تحقیق رویکردی ارائه شده است که در ان با در نظر گرفتن اثر لرزه ای قائم، منحنی های شکنندگی مربوط به سازه های زیرزمینی با فضای بزرگ، را ایجاد می کند. در ظرفیت لرزه ای، متد تحلیل بار افزون (push over analys method) ساختار خاک زیرزمینی، در نظر می گیرد که برای بدست اوردن منحنی ظرفیت ستون مرکزی ، بارگزاری لرزه ای قائم، استفاده شود. لرزه های سطوح عملکردی از طریق مدل منحنی رفتاری رانش بار (load-drift backbone curve drift) ، اندازه گیری می شوند. در تقاضای لرزه ای (seismic demand)، لرزه های سطوح عملکردی را از طریق متد تحلیل دینامیکی افزایشی (IDA) و با تحریک شتاب عمودی و افقی، ارزیابی می کنیم و ویژگی های اثر متقابل ساختار خاک و زمین لرزه (ground motion) را نیز در نظر می گیریم. نتایج مربوط به تحلیل دینامیکی افزایشی (IDA) را، از لحاظ بیشینه شتاب زمین (peak ground acceleration) و بیشینه سرعت زمین (peak ground velocity) با یکدیگر مقایسه می نماییم. برای ایجاد منحنی های شکنندگی، شاخص عملکرد را ، با در نظر گرفتن عدم قطعیت مربوط به ان، در مقابل افزایش شدت زلزله ارزیابی می کنیم. نتایج نشان می دهند که اگر اثر لرزه ای قائم را برای ارزیابی شکنندگی سازه های زیرزمینی با فضای بزرگ بکار نگیریم، احتمال تجاوز اسیب های مربوط به سازه های زیرزمینی با فضای بزرگ کمتر از میزان نرمال براورد خواهد شد، که منجر به نتایج ارزیابی نامطلوب می شود.
1. معرفی
سازه های زیرزمینی با فضای بزرگ مانند متروها، خیابان های تجاری و پارکینگ ها، سازه های شهری می باشند که بصورت گسترده بکار گرفته می شوند. این ساختارها می توانند تحت لرزش زمین، متحمل اسیب های فراوانی شوند (1و2). خصوصا ساختارهایی که جاگذاری غیر مستحکمی بر روی زمین های سفت دارند، به سبب تغییر شکل زمین و افزایش شتاب و سرعت و زمین در هنگام نزدیک شدن به سطح زمین، حساسیتشان نسبت به اسیب، افزایش می یابد (3و4). علاوه بر این، برخی ساختارهای زیر زمینی با فضاهای بزرگ که کهنه ساخت می باشند، به سبب طراحی نامناسب در برابر زلزله ، با ریسک بالقوه ی بالاتری در رابطه با اسیب های لرزه ای مواجه می شوند. متعاقبا برای اطمینان از ایمنی لرزه ای سازه های زیر زمینی با فضای بزرگ،مخصوصا در نواحی مستعد زلزله، ارزیابی شکنندگی لرزه ای توسط محققان مختلف صورت می گیرد.
4. نتیجه گیری
رویکردی با در نظر گرفتن اثر لرزه ای قائم، برای ایجاد منحنی های شکنندگی در سازه های زیر زمینی با فضای بزرگ ، ارائه شده است. استانه ی سطوح عملکردی بر اساس متد تحلیل بار افزون ساختار خاک زیرزمینی، بدست می اید که توزیع اثر لرزه ای قائم را برای ظرفیت لرزه ای در نظر می گیرد. تقاضای لرزه ای سازه های زیر زمینی با فضای بزرگ از طریق متد تحلیل دینامیکی افزایشی (IDA) 3بعدی ارزیابی می شود و خاصیت غیر ارتجاعی خاک و مشخصه های زمین لرزه را محاسبه می کند. بر اساس نمونه سازه های زیر زمینی با فضای بزرگ انتخابی، این رویکرد برای ایجاد منحنی های شکنندگی لرزه ای در محل های مختلف و با محاسبه ی اثر متقابل ساختار خاک زیر زمینی، بکار گرفته می شود. منحنی های شکنندگی با توجه به اهمیت نقش محل و اثر لرزه ای قائم در اسیب پذیری سازه های زیر زمینی با فضای بزرگ، باهم مقایسه می شوند.
The measured vertical peak ground acceleration was larger than the horizontal peak ground acceleration. It is essential to consider the vertical seismic effect in seismic fragility evaluation of large-space underground structures. In this research, an approach is presented to construct fragility curves of large-space underground structures considering the vertical seismic effect. In seismic capacity, the soil-underground structure pushover analysis method which considers the vertical seismic loading is used to obtain the capacity curve of central columns. The thresholds of performance levels are quantified through a load-drift backbone curve model. In seismic demand, it is evaluated through incremental dynamic analysis (IDA) method under the excitation of horizontal and vertical acceleration, and the soil-structure-interaction and ground motion characteristics are also considered. The IDA results are compared in terms of peak ground acceleration and peak ground velocity. To construct the fragility curves, the evolutions of performance index versus the increasing earthquake intensity are performed, considering related uncertainties. The result indicates that if we ignore the vertical seismic effect to the fragility assessment of large-space underground structures, the exceedance probabilities of damage of large-space underground structures will be underestimated, which will result in an unfavorable assessment result.
1. Introduction
Large-space underground structures such as subway stations, commercial streets, and parking lots are wildly used urban construction measures. These structures can suffer severe damage under strong ground shaking [1, 2]. Especially for shallow embedded structures in soft soil, their susceptibility to damage can be increased, due to ground strain and velocity along with acceleration increase when approaching the ground surface [3, 4]. In addition, for some early built large-space underground structures, they are facing a high potential risk of seismic damage due to without properly considering seismic design. Consequently, to ensure the seismic safety of large-space underground structures, especially in seismic prone areas, the seismic fragility assessment is introduced to large-space underground structures by different researchers.
4. Conclusions
An approach is proposed to construct fragility curves for large-space underground structures considering the vertical seismic effect. Thresholds of performance levels are obtained based on the soil-underground structure pushover analysis method, which considers the contribution of vertical seismic effect to seismic capacity. The seismic demand of the large-space underground structure is evaluated through 3D incremental dynamic analyses, accounting for soil inelasticity and ground motion characteristics. Based on a selected typical large-space underground structure, this approach is applied to the derivation of seismic fragility curves of different sites, accounting for soil-underground structure interaction. The fragility curves are compared, highlighting the important role of site and the vertical seismic effect in the vulnerability of large-space underground structures.
1. معرفی
2. متودولوژی
2.1. بررسی متد ارائه شده برای استخراج منحنی شکنندگی
3.مطالعه موردی
3.1 مدل عددی
3.2 انتخاب حرکات ورودی
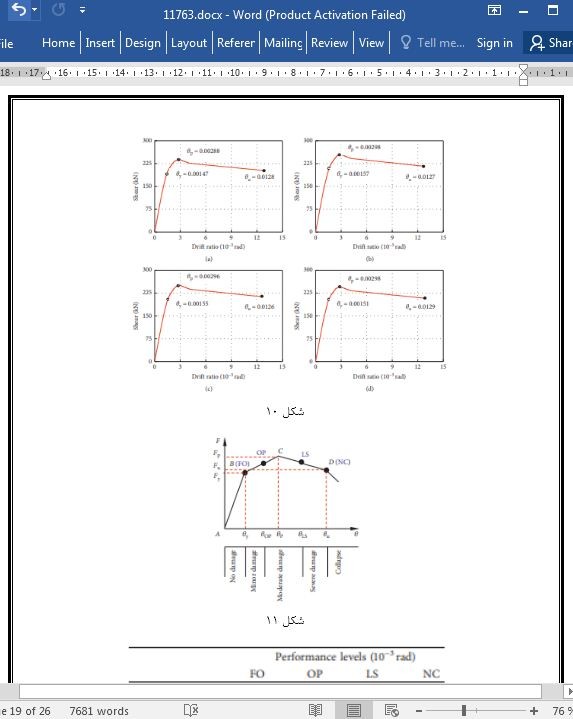
3.3 نتایج تجزیه و تحلیل بار افزون
3.4 آستانه ی سطوح عملکردی
3.5. نتایج تحلیل دینامیکی افزایشی
3.6. تحلیل شکنندگی
4. نتیجه گیری
منابع
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. Overview of the Proposed Method for Deriving Fragility Curve
2.2. Approach for Deriving Fragility Curves
3. Case Study
3.1. Numerical Models
3.2. Selection of Input Motions
3.3. Pushover Analysis Results.
3.4. Thresholds of Performance Levels
3.5. Incremental Dynamic Analysis Results
3.6. Fragility Analysis
4. Conclusions
References
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه