تولید کامپوزیت های بتن سبز شامل الیاف پسماند پلاستیکی فلزی شده
چکیده
در میان راهحلهای موجود بالقوه برای یک محیط تمیزتر، یکی از انها به حداقل رساندن مصرف مصالح غیرقابل تجزیه زیستی و کاهش پسماند است. تولید و دفع پلاستیکهای پسماند اثرات شدیدی بر محیطزیست دارد. استفاده از مصالح پسماند جامد در ساختوساز پایدار به دلیل هزینه کمتر مصالح پسماند همراه با صرفهجویی در مکانهای دفن زباله، توجه زیادی را به خود جلب کردهاست. در این مقاله، امکان ارزیابی و استفاده از الیاف پسماند پلاستیکی فلزی شده (MPW)و خاکستر سوخت روغن نخل (POFA)در تولید کامپوزیت های بتنی با ارزیابی خواص مکانیکی و سرعت پالس اولتراسونیک مورد بررسی قرار گرفت. شش مخلوط بتنی حاوی الیاف پسماند پلاستیکی فلزی شده MPW به صورت متغیر از ۰ تا ۱.۲۵ % با طول ۲۰ میلی متر از سیمان پورتلند معمولی (OPC)ساخته شدند. شش مخلوط بتنی مختلف با میزان الیاف یکسان نیز ساخته شدند، که در آن ۲۰ % خاکستر سوخت روغن نخل POFA جایگزین سیمان پورتلند معمولی OPC شد. نتایج نشان میدهد که الیاف پسماند پلاستیکی فلزی شده MPW، به همراه خاکستر سوخت روغن نخل POFA کارایی بتنها را کاهش دادهاند. همچنین مشخص شدهاست که با اضافه کردن الیاف پسماند پلاستیکی فلزی شده MPW به مخلوطهای بتنی، مقاومت فشاری برای مخلوطهای سیمان پورتلند معمولی OPC و خاکستر سوخت روغن نخل POFA در سنین اولیه گیرش بتن کاهش مییابد. اگرچه در دوره عملآوری ۹۱ روزه، این مخلوطها حاوی خاکستر سوخت روغن نخل POFA بودند که مقاومت فشاری بالاتری از مخلوطهای دارای سیمان پورتلند معمولی OPC داشتند. مخلوط های دارای الیاف پسماند پلاستیکی فلزی شده MPW و خاکستر سوخت روغن نخل POFA همچنین مقاومت کششی و خمشی را افزایش دادند و در نتیجه باعث افزایش انعطافپذیری شدند.. این مطالعه نشان داد که الیاف پسماند پلاستیکی فلزی شده MPW پتانسیل استفاده در بتن پایدار با بهبود خواص مکانیکی را دارند.
4. نتیجه گیری
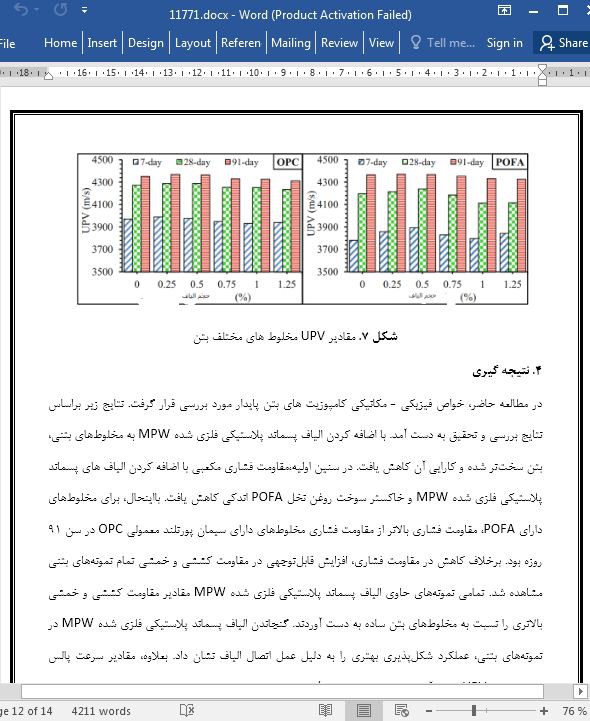
در مطالعه حاضر، خواص فیزیکی - مکانیکی کامپوزیت های بتن پایدار مورد بررسی قرار گرفت. نتایج زیر براساس نتایج بررسی و تحقیق به دست آمد. با اضافه کردن الیاف پسماند پلاستیکی فلزی شده MPW به مخلوطهای بتنی، بتن سختتر شده و کارایی آن کاهش یافت. در سنین اولیه،مقاومت فشاری مکعبی با اضافه کردن الیاف های پسماند پلاستیکی فلزی شده MPW و خاکستر سوخت روغن نخل POFA اندکی کاهش یافت. بااینحال، برای مخلوطهای دارای POFA، مقاومت فشاری بالاتر از مقاومت فشاری مخلوطهای دارای سیمان پورتلند معمولی OPC در سن ۹۱ روزه بود. برخلاف کاهش در مقاومت فشاری، افزایش قابلتوجهی در مقاومت کششی و خمشی تمام نمونههای بتنی مشاهده شد. تمامی نمونههای حاوی الیاف پسماند پلاستیکی فلزی شده MPW مقادیر مقاومت کششی و خمشی بالاتری را نسبت به مخلوطهای بتن ساده به دست آوردند. گنجاندن الیاف پسماند پلاستیکی فلزی شده MPW در نمونههای بتنی، عملکرد شکلپذیری بهتری را به دلیل عمل اتصال الیاف نشان داد. بعلاوه، مقادیر سرعت پالس اولتراسونیک UPV بدستآمده از ۳۷۰۰ تا ۴۴۰۰ m / s برای مخلوطهای حاوی الیاف های پسماند پلاستیکی فلزی شده MPW و خاکستر سوخت روغن نخل POFA در همه سنین به عنوان بتن با کیفیت خوب مشخص شدند. تولید بتن سازگار با محیطزیست با اضافه کردن الیاف های پسماند پلاستیکی فلزی شده MPW و خاکستر سوخت روغن نخل POFA پتانسیل بالایی برای صنعتی شدن با عملکرد رضایتبخش برای کاربردهای سازه ای و غیرسازه ای دارد.
Abstract
Amongst the potential solutions to a cleaner environment is to minimize the consumption of non-biodegradable materials and to reduce wastes. The generation and disposal of waste plastics cause severe impacts on the environment. The utilization of solid waste in the sustainable constructions has concerned much attention due to the lower cost of wastes along with saving a necessary place of landfills. In this paper, the feasibility of metalized plastic waste (MPW) fibers and palm oil fuel ash (POFA) in the production of concrete composites was investigated by assessing the mechanical properties and ultrasonic pulse velocity. Six concrete mixes containing MPW fibers varying from 0 to 1.25% with a length of 20 mm were made of ordinary Portland cement (OPC). A different six concrete mixtures with the same fiber content were made, where 20% POFA substituted OPC. The results show that MPW fibers, together with POFA reduced the workability of concretes. It has also been found that by adding MPW fibers to the concrete mixtures, the compressive strength decreased for both OPC and POFA mixes at the early ages. Though at the curing period of 91 days, the mixes contain POFA attained compressive strength higher than those of OPC mixes. The mixture of MPW fibers and POFA subsequently enhanced the tensile and flexural strengths, thereby increasing the ductility. The study revealed that the MPW fibers are potential to be used in sustainable concrete by improving the mechanical properties.
4. Conclusions
In the present study, the physico-mechanical properties of sustainable concrete composites were explored. The following results were concluded based on the examination and investigational results. By adding MPW fibers into concrete mixes, concrete was harsher, and the workability decreased. At the early ages, cube compressive strength diminished slightly with the adding of MPW fibers and POFA. However, for POFA mixes, the compressive strength was higher than that of OPC mixes at the age of 91 days. Unlike diminution in compressive strength, remarkable enhancements in both tensile and flexural strengths of all concrete specimens were noted. All specimens containing MPW fibers obtained higher tensile and flexural strength values than those of plain concrete mixes. The inclusion of MPW fibers in concrete specimens revealed better ductility performance due to the linking action of fibers. Furthermore, the obtained UPV values of 3700 to 4400 m/s for mixes containing MPW fibers and POFA at all ages were characterized as good quality concrete. The production of eco-friendly concrete by adding MPW fibers and POFA is highly potential to be industrialized with the satisfactory performance for both structural and non-structural applications.
چکیده
1.مقدمه
۲. مصالح و روش هایآزمایش
۳. نتایج و بحث
۳. ۱. کارایی
3.2 مقاومت فشاری
3.3 مقاومت کششی در برابر تقسیم(دو نیم) شدگی
3.4 مقاومت خمشی
3.5 سرعت پالس التراسونیک
4. نتیجه گیری
منابع
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and test methods
3. Results and discussion
3.1. Workability
3.2. Compressive strength
3.3. Splitting tensile strength
3.4. Flexural strength
3.5. Ultrasonic pulse velocity
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgements
References
- اصل مقاله انگلیسی با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه