مروری بر چالش های جابجایی پسماند کووید-19 و مکانیزم مدیریت آن
چکیده
کووید-19 ویروس کرونای جدید نام مشهوری تبدیل شده است. شیوع جهانی کووید-19 به یک پاندمی در اوایل 2020 تبدیل شده و بر زندگی میلیون ها نفر در سراسر تاثیر گذاشته است. این پاندمی به شدت در حال گسترش بوده و اثرات آن بر سلامت انسان و محیط زیست روز به روز تشدید می شود. پسماند زیست پزشکی که روزانه به دلیل کووید-19 تولید می شود از جمله مشکلات عمده بهداشت محیطی است و مدیریت بحرانی آن به یک چالش جهانی تبدیل شده است. میزان پسماندهای آلوده کووید-19 که در سراسر جهان هر روزه تولید می شود و مدیریت صحیح آن برای قطع انتقال بیماری بسیار ضروری است. مدیریت ایمن و پایدار پسماندهای آلوده زیست پزشکی (BMW)، مسئولیت اجتماعی و قانونی همه افراد در طی این دوره بحرانی از انتقال بیماری می باشد. مدیریت نادرست این پسماند می تواند منجر به اثرات دنباله دار پیش بینی نشده بر سلامت انسان و محیط زیست شود. کارکنان بهداشت، کارگران شهرداری، کهنه جمعکن ها و سایر افرادی که مستقیم یا غیرمستقیم در نبرد کووید-19 درگیر هستند، در معرض خطر بالایی قرار داشته و باید در هنگام ادای مسئولیت خود با مکانیزم کارآمد و موثر دفع زباله، مراقب باشند.
1. مقدمه
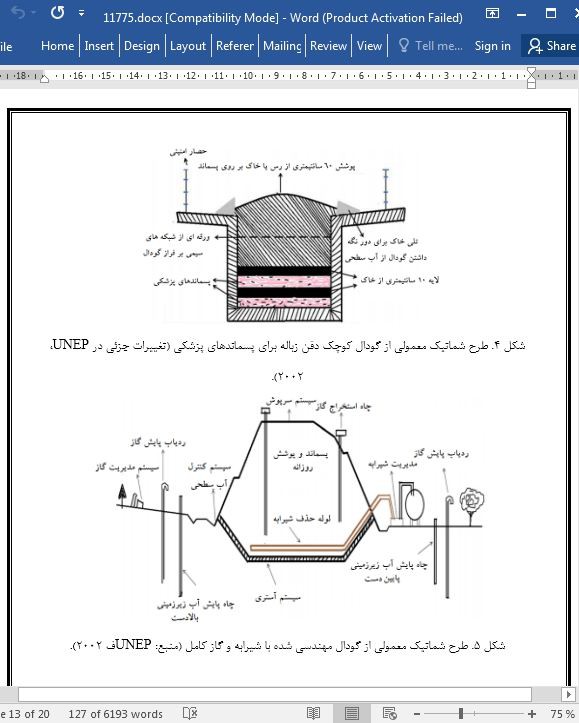
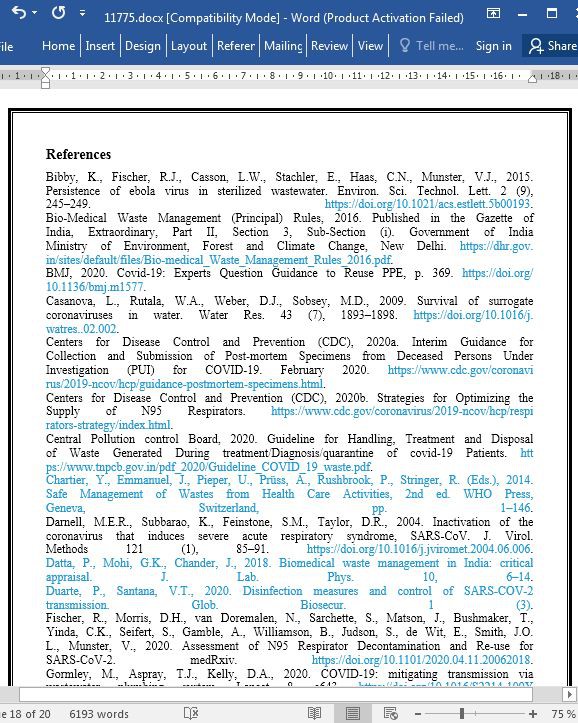
با توجه به دفع و یا جابجایی نامناسب پسماندهای آلوده، ممکن است عوامل بیماریزای ویروسی به کادر درمان و کارکنان بازیافت انتقال یابد. مشخص شده که با توجه به دفع نامناسب پسماندهای پزشکی تا 30 دزصد هپاتیت B، 1 الی 3 درصد هپاتیت C و 0.3 درصد HIV از بیماران به کادر درمان منتقل می گردد (سینگ و همکاران، 2020). بنابراین در راستای حفظ بهداشت جامعه در میان گسترش ویروس کرونا، دفع پسماندهای پزشکی از اهمیت ویژه ای برخوردار است. این بیماری نه تنها زندگی ارزشمند میلیون ها انسان را از بین برده بلکه چالش هایی را برای مدیریت پسماند تولید شده از بیمارستان، شهرداری، و خانه آلوده به کووید-19 پدید آورده است. اغلب مردم دنیا در رنج به سر برده و بسیاری از موسسات و صنایع تعطیل شده، مردم کار را از دست داده اند. با توجه به شیوع این بیماری، مقادیری پسماندهای پزشکی مانند ماسک، دستکش، روپوش، روزانه تولید می شوند. طبق گزارشات مورنینگ پست جنوب چین، در طی این پاندمی در ووهان میزان پسماند تولیدی روزانه از 40 تن به 240 تن افزایش یافت. در طی پاندی کووید-19، تولید پسماند پزشکی در کشورهای مختلف افزایش بسیاری یافته است (جدول ۱).
۶. نتیجه گیری
پسماند کووید اگر به درستی مدیریت نشود می تواند باعث گسترش آلودگی در جامعه شود. در مطالعه حاضر، منابع مختلف تولید پسماند کووید-19، ضدعفونی احتمالی و استراتژی دفع آن به صورت مفصل مورد بحث قرار گرفته که می تواند به مهندسان، متخصصان محیط زیست، کادر درمان و مقامات شهرداری محلی کمک کند تا پسماند خطرناک پاندمی فعلی را برنامه ریزی و مدیریت کنند. علاوه بر برنامه های آموزشی و آگاهی اجتماعی، اجرای دقیق شناسایی، تفکیک، ضدعفونی، حمل و نقل و شیوه دفع ایمن عوامل کلیدی مدیریت موثر و ایمن کووید-19 محسوب می شوند. از آنجایی که پسماند جامعه به چالش لجستیکی و عملی تبدیل شده در نتیجه مشارکت عمومی همراه با سیاست های مناسب مدیریت خُرد برای جمع آوری پسماند جامعه باید اتخاذ شود.
Abstract
COVID-19, the novel corona virus has become a household name. The global COVID-19 outbreak, become a pandemic in early 2020, and spurred millions of life across the world. The pandemic is spreading extremely and its impacts upon human health and environment intensifying day-by-day. Biomedical waste generated daily due to COVID-19 are about the major environmental health concern and its critical management becomes a global challenge. Tones of COVID-19 contaminated wastes are generated every day worldwide and its sound management is very essential to break the disease transmission. The safe and sustainable management of COVID-19 contaminated biomedical waste (BMW) is a social and legal responsibility of all people during this critical period of disease transmission. Unsound management of this waste could cause unforeseen “knock-on” effects on human health and the environment. Health workers, municipal workers, rag-pickers and other persons who are involved directly or indirectly in the COVID -19 war are at high risk and needs to be careful while discharging their responsibility with an efficient and effective waste disposal mechanism.
1. Introduction
Viral pathogens can be transmitted to healthcare and recycling workers due to the improper disposal or handling of contaminated waste. It has been found that due to improper disposal of medical waste up to 30 % of hepatitis B, 1–3 % of hepatitis C, and 0.3 % of HIV rates have been communicated from patients to healthcare workers (Singh et al., 2020). Therefore in a bid to maintain community sanitation amid corona virus spread, disposal of biomedical waste is of utter importance. The disease not only killing millions valuable life but also brought challenges for the management of the waste generated from hospital, municipal, and house contaminated with COVID-19. Most of the people round the globe are suffering and many institutions and industries are locked, people lost their jobs as well. Due to this outbreak, tones of medical wastes such as masks, gloves, gowns are generated daily. According to the South China Morning Post reports, during the pandemic at Wuhan the quantity of medical waste produced daily was increased from 40-ton to 240 tons. During this COVID-19 pandemic, production of medical waste has greatly increased in different country (Table 1).
6. Conclusion
COVID-waste may cause to the community spread if not handled properly. In the present study, various sources of COVID-19 waste generation, its possible disinfection and disposal strategy have been discussed in details which can assist the engineers, environmentalist, healthcare personnel and local municipal authorities to plan and manage the present pandemic hazardous waste. Besides training programs and social awareness, strict execution of identification, segregation, disinfection, transportation and safe disposal practice are the key factors for effective and safe management of COVID-19 waste. As community waste becomes logistical and practical challenge hence public participation along with proper micro-management policies for collection of community waste should be adopted.
چکیده
1. مقدمه
2. مدیریت پسماندهای آلوده کووید-19
2.1. جمع آوری
۲.۲. تفکیک و نگهداری مناسب
3.3. حمل و نقل
2.4. تصفیه و دفع
3. نحوه برخورد و دفن اجساد مردگان کووید-19
4. آلودگی و مدیریت آب در حین پاندمی کووید-19
5. کمبود PPE و استفاده منطقی، استفاده مجدد و بازیابی آن
۶. نتیجه گیری
منابع
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Management of COVID-19 contaminated waste
2.1. Collection
2.2. Proper separation and storage
2.3. Transportation
2.4. Treatment and disposal
3. Treatment and disposal of COVID-19 dead bodies
4. Water contamination and management during COVID-19 pandemic
5. Scarcity of PPE and its rational use, reuse and recycling
6. Conclusion
References
- اصل مقاله انگلیسی با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه