تعیین اثرات ارزیابی های محصول توسط مصرف کنندگان و اطمینان از قصد خرید مجدد
چکیده
این مطالعه ادبیات موجود در مورد اعتماد آنلاین را از طریق تکمیل مدل ارزیابی های محصول توسط مصرف کنندگان و مدل اتخاذ تکنولوژی در محیط های تجارت الکترونیکی ارتقاء می بخشد. در این مطالعه ما بررسی می کنیم که چگونه ارزش درک شده، درک اعتماد آنلاین میان خریداران آنلاین و تمایل آنها به خرید مجدد از همان وب سایت را تحت تاثیر قرار می دهد. این مطالعه یک مدل تحقیقاتی پیشنهاد کرده و از طریق آن اهمیت نسبی ارزش درک شده و اعتماد آنلاین به سودمندی درک شده در اثرگذاری بر قصد خرید مجدد مصرف کنندگان را مقایسه می کند. این مدل پیشنهادی با استفاده از داده های جمع آوری شده از مصرف کنندگان آنلاین تجارت الکترونیکی مورد آزمایش قرار گرفته است. نتایج نشان می دهند که اگرچه اجزای اعتماد و اتخاذ تجارت الکترونیکی در اثرگذاری بر قصد خرید مجدد بسیار حیاتی هستند، عوامل ارزیابی محصول نیز در تعیین قصد خرید مجدد اهمیت دارند. کیفیت درک شده، تحت تاثیر درک قیمت رقابتی و شهرت وب سایت است که به نوبه خود ارزش درک شده را تحت تاثیر قرار می دهد؛ و ارزش درک شده، شهرت وب سایت و ریسک درک شده، اعتماد آنلاین را تحت تاثیر قرار می دهد که این امر نیز به نوبه خود بر قصد خرید مجدد تاثیر می گذارد. نتایج همچنین نشان می دهند که اثر سودمندی درک شده بر قصد خرید مجدد خیلی قابل توجه نیست، در حالی که ارزش درک شده و اعتماد آنلاین، عوامل اصلی تعیین کننده قصد خرید مجدد هستند. همکاری های تئوری و مفاهیم عملی عمده، مورد بحث قرار گرفته اند.
1. مقدمه
وب سایت های تجارت الکترونیکی نه تنها ابزارهایی برای حمایت از یک معامله تجاری هستند، بلکه همچنین ابزارهایی هستند که کانال های شرکت ها با استفاده از آن ها با مصرف کنندگان خود در تعامل بوده و با آن ها ارتباط برقرار می کنند (Al-Natour, Benbasat, & Cenfetelli, 2011). با توجه به Gartner (2015)، انتظارات مصرف کنندگان آنلاین در چند سال اخیر در حال افزایش است. این افزایش در انتظارات مصرف کنندگان، پیچیدگی سیستم های آنلاینی را که کسب و کارها باید به کار بگیرند، افزایش داده است. کسب و کارهای آنلاین برای حفظ مصرف کنندگان خود، نیاز به تعریف مجدد استراتژی هایی برای برآورده کردن انتظارات مصرف کنندگان و به دست آوردن اعتماد آنها دارند. با توجه به اینکه جذب مشتریان جدید، زمان و تلاش بیشتری نسبت به حفظ مشتریان قدیمی نیاز دارد، کسب و حفظ وفاداری مصرف کننده در بازارهای تجارت الکترونیکی برای کسب و کارهای آنلاین بسیار سخت است (Harris and Goode, 2004; Hung, Cheng, & Chen, 2012; Zhang et al., 2011).
7. نتیجه گیری
این مطالعه ادبیات موجود در مورد اعتماد آنلاین را از طریق ادغام مدل ارزیابی های محصول و مدل اتخاذ تکنولوژی تقویت می کند. این مطالعه استدلال می کند که قصد خرید مجدد در زمینه تجارت الکترونیکی را می توان به واسطه ارزیابی روابط بین کیفیت درک شده، عناصر ارزش درک شده و اعتماد در تجارت الکترونیکی، بهتر درک کرد. یافته ها حاکی از آنند که تاثیر سودمندی درک شده بر قصد خرید مجدد، از طریق اثر ارزش درک شده، اعتماد آنلاین و ریسک درک شده تضعیف شده است. به طور خلاصه، این مطالعه به وضوح تبیین می کند که چگونه روابط بین خریدار و فروشنده آنلاین، می تواند با در نظر گرفتن درک کیفیت و همچنین ارزش محصول به منظور افزایش درک اعتماد خریداران آنلاین تقویت شود.
Abstract
This study enhances the existing literature on online trust by integrating the consumers’ product evaluations model and technology adoption model in e-commerce environments. In this study, we investigate how perceived value influences the perceptions of online trust among online buyers and their willingness to repurchase from the same website. This study proposes a research model that compares the relative importance of perceived value and online trust to perceived usefulness in influencing consumers’ repurchase intention. The proposed model is tested using data collected from online consumers of e-commerce. The findings show that although trust and e-commerce adoption components are critical in influencing repurchase intention, product evaluation factors are also important in determining repurchase intention. Perceived quality is influenced by the perceptions of competitive price and website reputation, which in turn influences perceived value; and perceived value, website reputation, and perceived risk influence online trust, which in turn influence repurchase intention. The findings also indicate that the effect of perceived usefulness on repurchase intention is not significant whereas perceived value and online trust are the major determinants of repurchase intention. Major theoretical contributions and practical implications are discussed.
1. Introduction
E-commerce websites are not only tools to support a business transaction, but also companies’ channels to interact and communicate with their consumers (Al-Natour, Benbasat, & Cenfetelli, 2011). According to Gartner (2015), online consumers’ expectations are continuing to increase in the last past years. These heightened consumer expectations have increased the complexity of online systems that businesses need to operate. In order to retain their consumers, online businesses need to redefine strategies to meet consumers’ expectations and win their trust. Considering that it costs more time and effort to acquire new consumers than to retain existing one, it is crucial for online businesses to gain and sustain consumer loyalty in e-commerce markets (Harris and Goode, 2004; Hung, Cheng, & Chen, 2012; Zhang et al., 2011).
7. Conclusions
This study augments the existing literature on online trust by integrating the product evaluations model and technology adoption model. This study argues that repurchase intention in the context of ecommerce can be better understood by assessing the relationships between perceived quality, perceived value elements, and trust in ecommerce. The findings indicate that the effect of perceived usefulness on repurchase intention is diminished by the effect of perceived value, online trust, and perceived risk. In sum, this study sheds light on how online buyer-seller relationships can be strengthened by considering the perceptions of product quality as well as product value to increase trust perceptions of online buyers.
چکیده
1. مقدمه
2. پیش زمینه نظری
2.1 اعتماد در تجارت الکترونیکی
2.2 مدل مفهومی برای ارزیابی های محصول
3. مدل تحقیق و فرضیات
3.1 ریسک و اعتماد درک شده
3.2 ریسک درک شده و قصد خرید مجدد
3.3. اعتماد و سودمندی درک شده
3.4. اعتماد و قصد خرید مجدد
3.5 سودمندی درک شده و قصد خرید مجدد
3.6. شهرت وب سایت و کیفیت درک شده
3.7 شهرت وب سایت و اعتماد
3.8. شهرت وب سایت و ارزش درک شده
3.9. قیمت رقابتی درک شده و کیفیت درک شده
3.10. قیمت رقابتی و ارزش درک شده
3.11. کیفیت درک شده و ارزش درک شده
3.12. ارزش درک شده و اعتماد
3.13. ارزش درک شده و قصد خرید مجدد
4. روش تحقیق
4.1. توسعه اندازه گیری
4.2. سیاست نظرسنجی
5. آنالیز داده ها و نتایج
5.1. آزمایش مدل اندازه گیری
5.2. مدل ساختاری
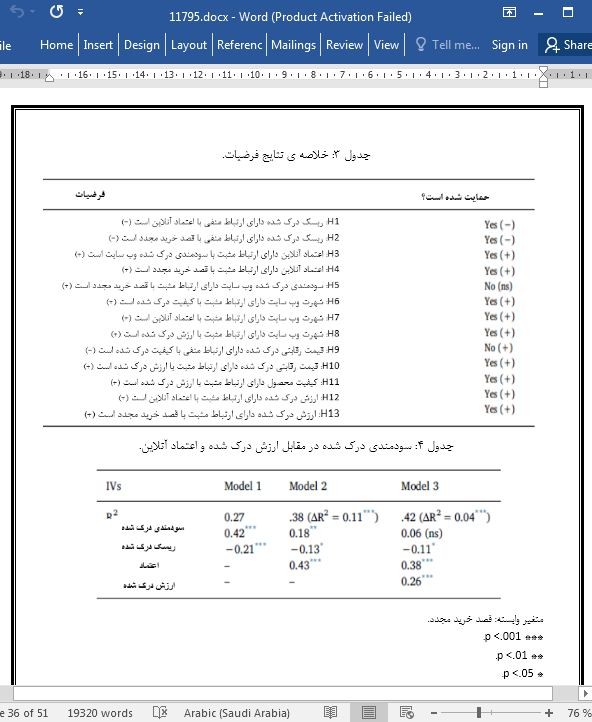
5.3. تأثیر سودمندی درک شده نسبت به ارزش درک شده و اعتماد آنلاین
6. بحث
6.1. مفاهیم تئوری و تحقیق
6.2. مفاهیم تمرین
6.3. محدودیت ها و پیشنهادات برای تحقیقات آینده
7. نتیجه گیری
منابع
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Theoretical background
2.1. Trust in e-commerce
2.2. Conceptual model for product evaluations
3. Research model and hypotheses
3.1. Perceived risk and trust
3.2. Perceived risk and repurchase intention
3.3. Trust and perceived usefulness
3.4. Trust and repurchase intention
3.5. Perceived usefulness and repurchase intention
3.6. Website reputation and perceived quality
3.7. Website reputation and trust
3.8. Website reputation and perceived value
3.9. Perceived competitive price and perceived quality
3.10. Perceived competitive price and perceived value
3.11. Perceived quality and perceived value
3.12. Perceived value and trust
3.13. Perceived value and repurchase intention
4. Research method
4.1. Measurement development
4.2. Survey administration
5. Data analysis and results
5.1. Testing the measurement model
5.2. The structural model
5.3. The effect of perceived usefulness relative to perceived value and online trust
6. Discussion
6.1. Implications for theory and research
6.2. Implications for practice
6.3. Limitations and suggestions for future research
7. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Appendix A. Empirical literature linking trust and adoption factors in e-commerce
Appendix B. Measurement items
Appendix C. Exploratory factor analysis results
Appendix D. PLS item factor loadings and cross loadings
Appendix E. Mediation test results (process model using SPSS)
Appendix F. Total effects (PLS)
References
- اصل مقاله انگلیسی با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه