رفتار چرخه ای قاب های مهاربندی هم مرکز با مهار بندی های مرکب متشکل از ناودانی
چکیده
قاب های مهاربندی هم مرکز، سیستم های مقاوم نسبت به زلزله هستند که معمولا در ساختمان ها مورد استفاده قرار می گیرند. رفتار لرزه ای این نوع از سازه ها تحت تاثیر پیکربندی آن ها، ویژگی مهار بندی ها و اتصالات به صفحه اتصال می باشد. در این مقاله، نتایج سه آزمایش گزارش می شود که هدف انجام این آزمایش ها ارزیابی رفتار چرخه ای قاب های مهار بندی شده به صورت هم مرکز با مهار بندی های متشکل از کانال های دو تایی، بوده است. آسیب های محسوس در اتصالات تیر به ستون مشاهده شد. قسمت زیادی از تغییر شکل در صفحه مهار بندی ها باعث شکل گیری ترک هایی در جوش های اتصالات شده بود؛ اما آن ها باعث شکستگی نشدند. با وجود این که جابجایی های زیادی بر روی قاب ها ایجاد شده بود، هیچ کدام از مهار بندی ها دچار شکست نشده بودند. علاوه بر این، آزمایش ها نشان داد که اکثریت مقاومت فشردگی در حالت بعد از کمانش و بخش محسوسی از مقاومت کششی در اثر عمل قاب ها ایجاد شده بود. با انتخاب کردن فضا بندی های اتصالات به عنوان پارامتر اصلی و استفاده از ماژول المان محدود، یک مطالعه پارامتری انجام شد تا بتوان تاثیر این پارامتر را بر روی این نوع از قاب با دو ترکیب مختلف از اتصالات مهار بندی ها به صفحه اتصال، بررسی کرد. اما صفحه های اتصالات، که یک فضای خطی 2t را فراهم می کنند، اتکای کمتری بر روی فضا بندی های اتصالات دارند که این تفاوت در مقایسه با فاصله بیضوی 6t محسوس می باشد. به نظر می رسد که محدودیت ضریب رعنایی در هر بخش، که مرتبط با شرایط لرزه ای مورد استفاده در ساختمان می باشد، باید در مطالعه های آتی بیشتر بررسی شود.
1. مقدمه
قاب های مهار بندی هم مرکز یا CBF ها، به صورت رایج به عنوان سیستم های ساختاری مورد استفاده قرار می گیرند تا بار زلزله کاهش پیدا کند. مقاومت و سفتی بالا همراه با ملاحظات اقتصادی، باعث شده است که مهندس ها این سیستم های ساختاری را در مطالعه های خودشان به صورت گسترده ارزیابی کنند. رفتار لرزه ای این نوع از قاب ها تحت تاثیر پیکربندی آن ها می باشد؛ ویژگی های مهار بندی آن ها مانند ضریب رعنایی، حالت هندسی مقطع، فشردگی و جزییات مهار بندی ها در صفحه اتصالات، از جمله ویژگی های موثر می باشد. در گذشته، مطالعه های مختلفی بر روی این قاب ها انجام شده است که می توان آن ها را در سه دسته بندی مختلف قرار داد. در دسته بندی اول، رفتار لرزه ای CBF ها از نظر پیکربندی شان مورد بررسی قرار گرفته است، از جمله قاب های قطری، X و مهار بندی های کاسه نمدی و یا سوپر X. در دسته بندی دوم، جزییات اتصالات مهار بندی ها به صفحه اتصالات ، پارامتر اصلی مد نظر بوده است. دسته بندی سوم تحقیقات نیز بر روی تاثیر ویژگی های مقطع مهار بندی مانند حالت هندسی، ضریب رفنایی و نسبت عرض به ضخامت بر روی رفتار لرزه ای CBF ها بوده است. در ادامه بعضی از مشکلات تحقیقات که در دسته بندی دوم و سوم قرار می گیرد را به صورت خلاصه بررسی می کنیم.
Abstract
Concentrically braced frames are earthquake resistant systems commonly used in buildings. Seismic behavior of this type of structures is affected by their configurations, brace properties, and brace to gusset plate connections. In this paper, the results of three experiments conducted to investigate the cyclic behavior of concentrically braced frames with braces built-up of double channels are reported. Significant damage was observed in beam to column connections. Large out of plane deformation of braces caused some cracks in the connector welds; however they did not result in fracture. Although large drift was applied to the frames, no brace fracture was observed. Furthermore, experiments showed that the majority of compressive strength in post-buckling state and a noticeable portion of tensile strength originated from frame action. By choosing connector spacing as the main parameter and using finite element models, a parametric study was performed to investigate the effect of this parameter on this type of frames with two different details of brace to gusset plate connections. It is observed that reducing the connector spacing increases the inelastic strain demand in braces and decreases it in gusset plates. However, gusset plates, which accommodate 2t linear clearance, are less dependent on connector spacing, compared to those accommodating 6t elliptical clearance. It seems that the limitations of slenderness ratio of individual section, stipulated in current seismic provisions, need further study.
1. Introduction
Concentrically braced frames, CBFs, are frequently used as a structural system to resist earthquake loading. High strength and stiffness as well as economic consideration have attracted engineers to this structural system. Seismic behavior of this type of frames is affected by their configurations; brace properties such as slenderness, section geometry, compactness, and details of brace to gusset plate connections. In the past, different studies have been undertaken on this kind of frames, which can be classified in three distinct categories. In the first category, the seismic behavior of CBFs have been investigated with respect to their configurations, e.g. frames with diagonal, X, and chevron braces or those with super-X. In the second category, details of connection of brace to gusset plates have been the main parameters of interest. The third category of research has concentrated on the effects of properties of the brace section such as geometry, slenderness ratio, and width to thickness ratio on the seismic behavior of CBFs. In the following paragraphs, some of the researches falling in the second and third categories are reviewed briefly.
چکیده
1. مقدمه
2. برنامه های آزمایشی
2.1 نمونه شماره 1
2.2 نمونه شماره 2
2.3 نمونه شماره 3
2.4 ویژگی های مواد
3. نتایج تست، مشاهدات و مباحث
3.1 تست 1
3.2 تست 2
3.3 تست 3
3.4 مباحث در رابطه با مشاهدات آزمایشی
4. شبیه سازی عددی آزمایش
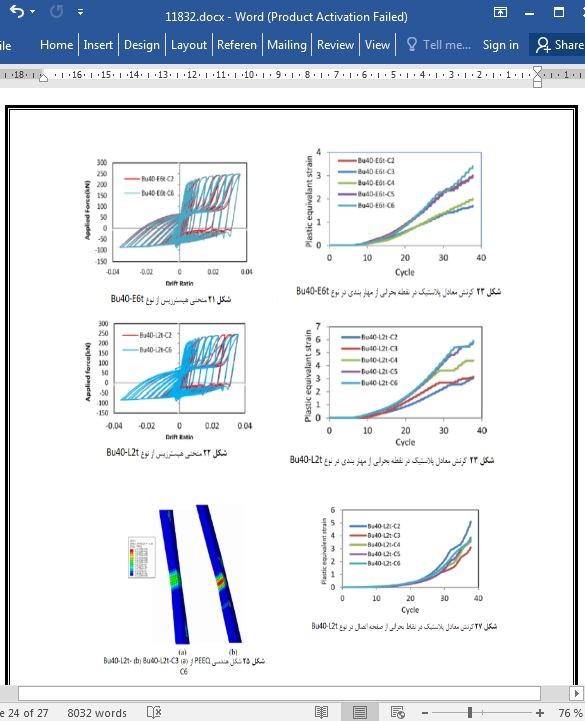
5. مطالعه های پارامتری
5.1 مشخصه مدل
5.2 اندازه گیری آسیب
6. نتایج عددی
7. خلاصه و جمع بندی
منابع
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Program
2.1. Specimen No. 1
2.2. Specimen No. 2
2.3. Specimen No. 3
2.4. Material properties
3. Test results, Observations and Discussion
3.1. Test 1
3.2. Test 2
3.3. Test 3
3.4. Discussion on experimental observations
4. Numerical Simulation of Experimental Models
5. Parametric Study
5.1. Model characteristics
5.2. Damage measure
6. Numerical Results
7. Summary and Conclusions
References
- اصل مقاله انگلیسی با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه