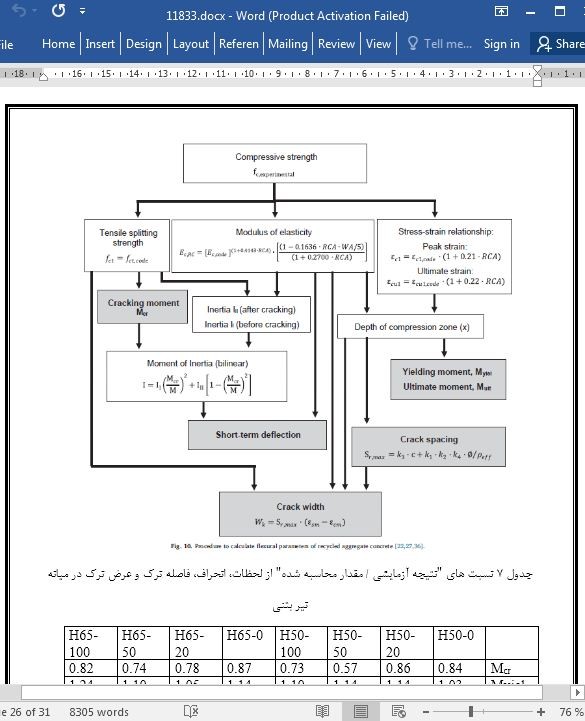
عملکرد خمشی تیرهای بتنی تقویت شده ساخته شده با مصالح درشت بتن بازیافتی
چکیده
این مطالعه به عملکرد خمشی بتن بازیافتی که در حضور بارهای زیاد تا مرز خرابی پیش می رود، می پردازد. برای این هدف، هشت تیر بتنی تقویت شده با مصالح درشت بازیافتی با استفاده از دو نسبت متفاوت آب به سیمان (0.50 و 0.65) و چهار درصد جایگزینی (0 درصد، 20 درصد، 50 درصد و 100 درصد) ساخته شدند. در ابتدا، خصوصیات اولیه بتن (استحکام مکانیکی و ضریب قابلیت ارتجاعی) مشخص شدند و سپس نمونه های تیر با استفاده از یک تست خمش چهار نقطه ای در 28 روز تا خرابی بارگذاری شدند. در نتیجه، لحظات خمشی، انحراف، کشش و انحنا در سطوح مختلف بار (ترک خوردگی، سرویس، جاری شدن و شرایط نهایی) و همچنین الگوی ترک به دست آمدند.
براساس این نتایج، قابل ذکر است که سرویس، جاری شدن و شرایط نهایی بتن بازیافتی، در کل، روندی مشابه با بتن معمولی دارند. با این حال، رفتار ترک خوردگی تفاوت بین بتن بازیافتی و معمولی را نشان می دهد. در آخر، عبارات مبتنی بر کد برای محاسبه لحظات خمشی و انحرافات خمشی زیر بار، با توجه به محتوای مختلف مصالح درشت بازیافتی استفاده شدند.
1. مقدمه
برای افزایش پایداری بتن، تلاش هایی انجام شده اند تا برخی از مشکلات زیست محیطی در ارتباط با زباله های بتنی برطرف شوند. در راستای این کار، تحقیقات متعددی برای آنالیز عملکرد سازه بتن بازیافتی انجام شده اند ]1-13[. با این حال، استفاده از آن در ساختمان های واقعی و برنامه های کاربردی مهندسی عمران به مطالعات در مقیاس کامل تری نیاز دارد، تا واکنش تغییر شکل در برابر بار بتن بازیافتی ارزیابی شود که منجر به توافقی خوب در طراحی سازه می شود.
6. نتیجه گیری
در این کار، عملکرد خمشی بتن های بازیافتی تعیین شده است. بر اساس این نتایج می توان نتیجه گیری های زیر را بیان کرد:
• با افزایش درصد جایگزینی، لحظه ترک خوردگی کاهش می یابد. این کاهش با استحکام کششی پایین بتن های بازیافتی سازگار است، که باعث ترک خوردگی بیشتر و زودتر از بتن معمولی می شود.
• در زمان سرویس دهی، لحظه ها و انحرافات خمشی کمی تحت تأثیر محتوای مصالح درشت بازیافتی قرار می گیرند که دلیل آن تأثیر کم خصوصیات مواد بر پاسخ سازه است زمانی که اعضای سازه برای ارائه یک رفتار شکل پذیر طراحی شده اند.
Abstract
This work deals with the flexural performance of recycled concrete subjected to increasing loads up to failure. For this purpose, eight reinforced concrete beams were made with recycled coarse aggregates using two different water to cement ratios (0.50 and 0.65) and four replacement percentages (0%, 20%, 50% and 100%). Firstly, the basic concrete properties were determined (mechanical strengths and modulus of elasticity) and then, beam specimens were loaded up to failure using a four-point bending test at 28 days. As a result, bending moments, deflections, strains and curvatures were obtained at different load levels (cracking, service, yielding and ultimate state conditions), and also, the crack pattern.
On the basis of these results, it can be noted that service, yielding and ultimate state of recycled concrete exhibits, in general, a similar trend to that of conventional concrete. However, the cracking behaviour shows differences between recycled and conventional concrete. Finally, code-based expressions were used to calculate bending moments and deflections under flexural load, taking into account the different content of recycled coarse aggregate.
1. Introduction
In order to promote the sustainability of concrete, efforts have been made to address some of the environmental problems associated with concrete waste. In line with this, numerous researches have been conducted to analyse the structural performance of recycled concrete [1–13]. However, its use in real building and civil engineering applications requires more full scale studies, to assess the load-deformation response of recycled concrete that leads to good agreement on structural design.
6. Conclusions
In this work, the flexural performance of recycled concretes has been determined. On the basis of these results the following conclusions can be drawn:
• The cracking moment decreases as the replacement percentage increases. This reduction is consistent with the lower tensile splitting strength of recycled concretes, which leads to a greater and earlier cracking than with conventional concrete.
• At serviceability, bending moments and deflections are slightly affected by the content of recycled coarse aggregate due to the low influence of material properties on structural response when structural members are designed to present a ductile behaviour.
چکیده
1. مقدمه
2. اهداف و روش
اختصارات
3. برنامه آزمایشی
3-1 مخلوط های مواد و بتنی
2-3 نمونه های آزمایش
3-3 روش تست و ابزار دقیق
3-4 خصوصیات بتن
4- نتایج و بحث
4-1 نتایج
4-2 الگوی ترک
4-3 آنالیز مقطعی
5. پیش بینی کد
6. نتیجه گیری
منابع
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Objectives and methodology
3. Experimental program
3.1. Materials and concrete mixtures
3.2. Test specimens
3.3. Test procedure and instrumentation
3.4. Concrete properties
4. Results and discussion
4.1. Results
4.2. Crack pattern
4.3. Cross section analysis
5. Code predictions
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه