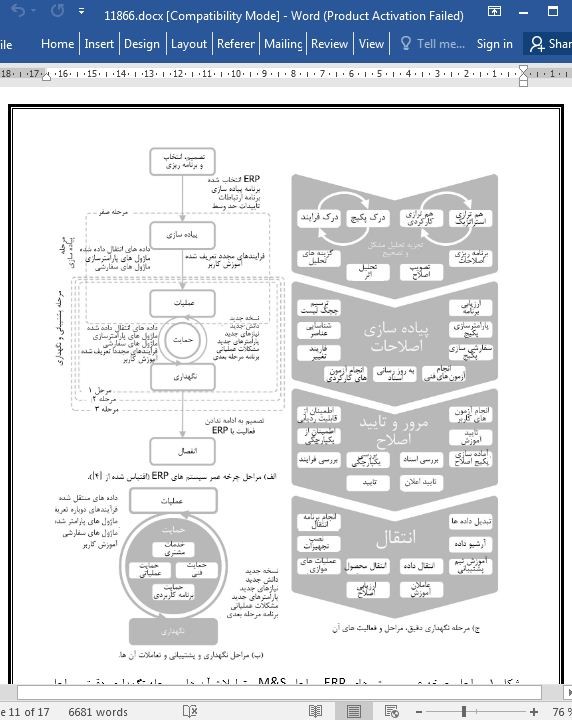
مدل نگهداری و پشتیبانی در چرخه عمر سیستم های ERP
چکیده
سازمان ها به اتخاذ سیستم های ERP ادامه می دهند. به نظر می رسد این راهی برای افزایش بهره وری و به دست آوردن مزایا نسبت به رقبا باشد. به طور سنتی، فازهای تصمیم گیری، انتخاب، برنامه ریزی و پیاده سازی، تمرکز چرخه عمر سیستم های ERP بودند. با این حال مشکلات اصلی چندین شکست در پیاده سازی، مربوط به عدم پشتیبانی مشتری و نگهداری کافی بود. این مقاله یک طرح پیشنهادی از یک مدل نگهداری و پشتیبانی (M&S) در چرخه عمر سیستم های ERP ارائه می دهد که شامل ۴ فعالیت پشتیبانی و ۴۱ فعالیت نگهداری جدا شده به ترتیب توسط ۴ مرحله است، شامل تجزیه و تحلیل مشکل و اصلاح، اجرای اصلاح، تجدید نظر و فاز پذیرش و انتقال. برخلاف سایر موارد، در این مدل پشتیبانی مستقل از نگهداری است که نقش آن را بین عملیات و نگهداری نشان می دهد. همچنین یک تحقیق عملی را ارائه می کند که در یک شرکت پیاده سازی ERP اجرا شده و در آن، یک ارزیابی از سطح بلوغ تمام فعالیت های 45 M&S انجام شد. تجزیه و تحلیل اقدامات موجود در این شرکت اجازه می دهد تا درک کنیم درک این اجرا از نقاط ضعف قابل توجهی برخوردار است و ۲۰ % از فرآیندهای آن (۹) اجرا نمی شوند یا به طور ضعیف اجرا می شوند و بنابراین فرصت های بزرگی برای بهبود ارائه می دهند. برخی از این اقدامات مورد بحث قرار گرفتند.
1. مقدمه
اتخاذ سیستم های ERP همچنان راهی برای سازمان ها جهت کسب مزایای رقابتی نسبت به رقبای خود است. احتمالا به همین دلیل ممکن است تایید شود که در اروپا نرخ پذیرش سیستم های ERP در حال افزایش است. در سال ۲۰۱۲، نرخ پذیرش در حدود ۲۲ درصد بود که در سال ۲۰۱۳ به ۲۶ درصد، در سال ۲۰۱۴ به ۳۱ درصد و در سال ۲۰۱۵ به ۳۶ درصد افزایش یافت. پذیرش رو به رشد ERP، چه سیستم های اختصاصی و چه سیستم های متن باز که در شرکت های بزرگ یا کوچک یا متوسط (SME ها) اجرا شده اند، همچنان سزاوار بررسی برای ارتباط آن ها است. از یک طرف پذیرش ERP در شرکت های بزرگ بیشتر است، از طرف دیگر نشان دهنده یک فرصت عالی برای SME ها است. در پرتغال، نسبت پذیرش ERP در سال ۲۰۱۴ نیز با اندازه شرکت کاهش یافت. شرکت های بزرگ دارای نرخ پذیرش ۹۰ %، شرکت های متوسط حدود ۶۰ % و شرکت های کوچک دارای نرخ پذیرش پایین تر، یعنی نزدیک به 35% بودند [1] ، [2].
Abstract
Organizations continue to adopt ERP systems. It seems to be a way to increase efficiency and gain advantages over competitors. Traditionally, decision, selection, planning, and implementation phases were the focus of ERP systems lifecycle. However, main problems of several implementation failures were related to lack of customer support and adequate maintenance. This paper presents a proposal of a maintenance and support (M&S) model within ERP systems lifecycle which includes 4 support activities and 41 maintenance activities separated by 4 phases, respectively, problem and modification analysis, implementation of modification, revision and acceptance phase and migration. Differently from others, at this model, the support is autonomous from maintenance, evidencing its role between operation and maintenance. It is also presented an action research performed in an ERP implementer company where an evaluation of maturity level of all 45 M&S activities were made. The analysis of existing M&S practices in this company allowed to understand this implementer has significant weaknesses with 20% of its processes (9) not or poorly implemented, and therefore, presenting great opportunities for improvement. Some of these practices were discussed.
1. Introduction
The adoption of ERP systems continues to be a way for organizations to gain competitive advantages over their competitors. Probably for this reason, it has been possible to verify that in the Europe there are increasing rates of adoption of ERP systems. In 2012, the adoption rate was around 22%, rising to 26% in 2013, 31% in 2014 and 36% in 2015. The growing adoption of ERP, whether proprietary or open source systems, implemented either in large or small or medium-sized companies (SMEs), continues to deserve investigation for their relevance. If, on the one hand, the ERP adoption is greater in large companies, on the other, it represents a great opportunity for SMEs. In Portugal, the ERP adoption ratio in 2014 also decreased with company size. Large companies had an adoption ratio of 90%, medium-sized companies around 60% and small companies registered an even lower adoption, close to 35% [1], [2].
چکیده
1. مقدمه
2. چرخه عمر ERP
3. نگهداری و پشتیبانی
4. پیشنهاد نگهداری و پشتیبانی سیستم های ERP
5. تحقیقات عملی در یک شرکت اجراکننده
6. نتیجه گیری
منابع
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. The ERP Life Cycle
3. Maintenance and Support
4. ERP Systems Maintenance and Support Model Proposal
5. Action Research in an implementer company
6. Conclusion
References
- اصل مقاله انگلیسی با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه