پیش بینی تعداد مسافران سیستم حمل و نقل عمومی
چکیده
این مقاله پژوهشی، چارچوبی را برای ارائه و تحلیل کارآمد ابعاد مکانی و زمانی داده های پانلی ارائه می کند. این چارچوب از طریق ارائه ی داده ها به صورت ماتریس تصویری مکانی-زمانی میسر می شود و به مطالعه ی موردی درخصوص پیش بینی تعداد مسافران سیستم حمل و نقل عمومی اعمال می شود. عملکرد نسبی زیرمجموعه ی تکنیک های یادگیری ماشین بررسی می شود و بر شبکه های عصبی پیچشی و حافظه ی کوتاه مدت ماندگار تمرکز می شود. علاوه بر شبکه های عصبی پیچشی-حافظه ی کوتاه مدت ماندگار متوالی ، شبکه های عصبی پیچشی-حافظه ی کوتاه مدت ماندگار موازی ، شبکه های عصبی پیچشی-حافظه ی کوتاه مدت ماندگار متوالی افزوده نیز بررسی می شوند. تمام مدل ها برمبنای اثرات ثابت رگرسیون کمترین مربع معمولی آزمایش شدند. داده های مربوط به سابقه ی تعداد مسافران در چارچوبی در یک پروژه ارائه شده اند که بر اثری که خط متروی جدید بر تعداد مسافران داشت، تمرکز می کرد. نتایج نشان می دهد که پیش بینی های انجام شده توسط مدل شبکه های عصبی پیچشی-حافظه ی کوتاه مدت ماندگار، بهترین عملکرد را داشت و این یافته حاکی از آن است که چارچوب پیشنهادی را می توان در اپلیکیشن هایی به کار برد که مستلزم مدلسازی دقیق تقاضا برای سیستم حمل و نقل عمومی هستند. فرآیند افزایش توصیفی شبکه های عصبی پیچشی-حافظه ی کوتاه مدت ماندگار متوالی را می توان برای معرفی متغیرهای برونزا در این مدل استفاده کرد. این متغیرها موجب می شوند که این مدل در محیط های زندگی واقعی قابلیت تبیین و پابرجایی بیشتری داشته باشد.
1. مقدمه
1.1. بیان مسئله و پیش زمینه
در بستر سیستم حمل و نقل عمومی، پیش بینی تعداد مسافران برای عملیات های کسب و کار ضروری است. داشتن اطلاعات درخصوص تقاضای مسافرت، به شرکت های سیستم حمل و نقل عمومی اجازه می دهد تا سیستم حمل و نقل را کارآمدتر سازند و بهبود سطح خدمات برای مشتریان و حذف هزینه های غیرضروری کمک شود (13، 1). در اختیار داشتن مدلی کارآمد درخصوص نحوه ی تغییر تقاضای سیستم حمل و نقل عمومی، برای برنامه ریزی آینده ضروری است و مسیرهای جدید، برنامه های کارآمدتر و بهینه سازی عملیات های حمل و نقل (برای مثال، تعداد اتوبوس های خطوط خاص) را معرفی می کند (3، 5).
6. بحث
به نظر می رسد که شبکه های عصبی پیچشی-حافظه ی کوتاه مدت ماندگار متوالی، بهترین مدل از نظر عملکرد در مجموعه ی آزمون هستند. با این حال، امتیاز آن کاملاً به امتیاز مدل شبکه های عصبی پیچشی-حافظه ی کوتاه مدت ماندگار افزوده ی پیشنهادی نزدیک است. علاوه براین، از منظر سرعت همگرایی، مدل شبکه های عصبی پیچشی-حافظه ی کوتاه مدت ماندگار متوالی، از نظر زمان ها (دوره های) لازم برای همخوانی با مجموعه ی آموزش سریعترین مدل هستند.
Abstract
This research paper provides a framework for the efficient representation and analysis of both spatial and temporal dimensions of panel data. This is achieved by representing the data as spatio-temporal image-matrix, and applied to a case study on forecasting public transport ridership. The relative performance of a subset of machine learning techniques is examined, focusing on Convo-lutional Neural Networks (CNN) and Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) neural networks. Furthermore Sequential CNN-LSTM, Parallel CNN-LSTM, Augmented Sequential CNN-LSTM are explored. All models are benchmarked against a Fixed Effects Ordinary Least Squares regression. Historical ridership data has been provided in the framework of a project focusing on the impact that the opening of a new metro line had on ridership. Results show that the forecasts produced by the Sequential CNN-LSTM model performed best and suggest that the proposed framework could be utilised in applications requiring accurate modelling of demand for public transport. The described augmentation process of Sequential CNN-LSTM could be used to introduce exogenous variables into the model, potentially making the model more explainable and robust in real-life settings.
1. Introduction
1.1. Problem statement and background
In the context of public transport, forecasting ridership is essential for business operations. Knowing the demand for travel allows public transport companies to make the transportation system more efficient, and helps to proactively improve the level of service for their customers and eliminate unnecessary costs [13, 1]. Having an effective model of how demand for public transport changes over time is important for future planning, introducing new routes, more efficient schedules, and optimising transportation operations (e.g. frequency of buses on a certain line) [3, 5].
6. Discussion
It appears that Sequential CNN-LSTM is the best model in terms of performance on the test set. Its score, however, is quite close to that of the suggested Augmented CNN-LSTM model. Moreover, in terms of convergence speed, the Sequential CNN-LSTM model is the fastest in terms of passes (epochs) required to fit the training set.
چکیده
1. مقدمه
1.1. بیان مسئله و پیش زمینه
1.2. حیطه پوشش پژوهش و پرسش پژوهش
2. مرور پیشینه تحقیقاتی مربوطه
2.1. شبکه های عصبی پیچشی
2.2. شبکه های عصبی حافظه کوتاه مدت ماندگار و شبکه های عصبی ترکیبی
3. داده ها
4. روش پژوهش
4.1. توصیف «ورودی تصویر» برای شبکه های عصبی پیچشی
4.2. تولید مثال و ترکیب مجموعه های آموزش، اعتبارسنجی و آزمون
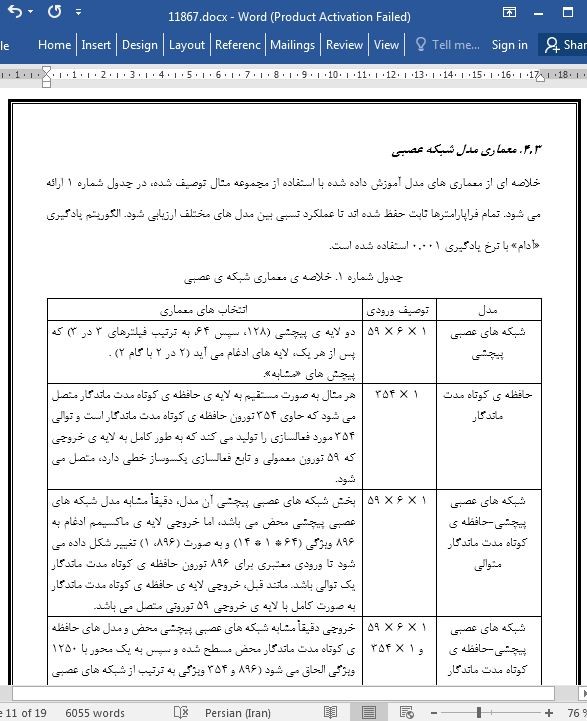
4.3. معماری مدل شبکه عصبی
4.4. رگرسیون کمترین مربعات معمولی
5. نتایج
5.1. خطای مجذور میانگین و دقت
5.2. پیش بینی
6. بحث
منابع
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Problem statement and background
1.2. Scope of the research and research question
2. Review of relevant literature
2.1. Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN)
2.2. Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) and combined Neural Networks
3. Data
4. Methodology
4.1. Description of ”image input” for CNN
4.2. Example generation and assembling training, validation and test sets
4.3. Neural network model architecture
4.4. Ordinary Least Squares regression
5. Results
5.1. Mean Squared Error and Accuracy
5.2. Prediction
6. Discussion
References
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه