قابلیت اطمینان سازه لرزهای بهبود یافته بر روی ساختمانهای بتنآرمه
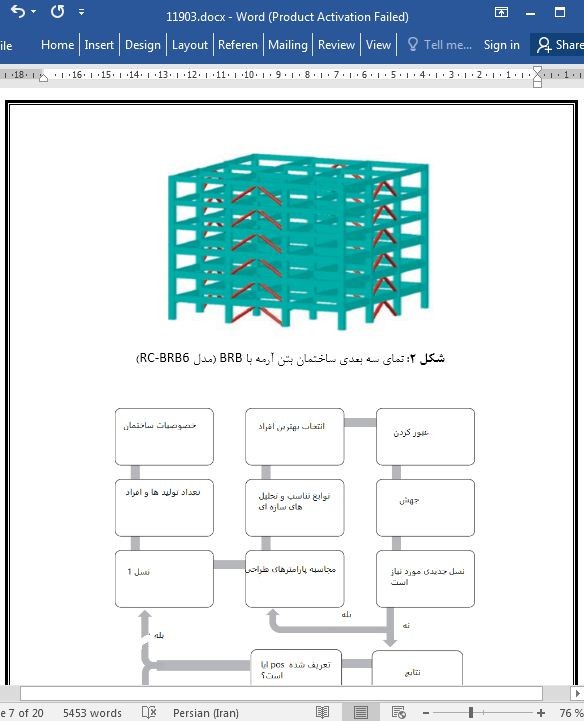
کنترل ارتعاشات و خرابی ساختمانهای بتن مسلح (RC)در برابر زلزله کاری دشوار است. این امر نیاز به استفاده از دستگاههای نوآورانه برای افزایش رفتار لرزهای ساختمانهای بتنی دارد. در این مقاله، ما ساختمانهای بتنآرمه با مهاربندهای کمانش ناپذیر (مهاربندهای کمانش تاب)را برای رسیدن به این هدف طراحی میکنیم. برای این منظور، سه سازه قاب بتن مسلح سنتی با سطوح طبقات ۳، ۶ و ۹ با استفاده از روش شناختهشده الگوریتم ژنتیک مرتبسازی نامغلوب (NSGA - II)به منظور کاهش هزینه و به حداکثر رساندن عملکرد لرزهای طراحی شدهاند. در این مقاله، سازههای بتن مسلح معادل با مهاربندهای کمانش ناپذیر طراحی شدهاند. هر دو سیستم سازهای در معرض چندین تحریک زمین باریک ثبتشده در مکانهای خاک نرم مکزیکوسیتی که در سطوح مختلف شدت از نظر شتاب طیفی در حالت اول ارتعاش سازه (S [ ۱ ])مقیاس گذاری شدهاند، قرار دارند. تحلیل دینامیکی فزاینده، شکنندگی لرزهای و قابلیت اطمینان سازهای بر حسب بیشینه دریفت بین طبقهای برای تمامی ساختمانها محاسبه شدهاست. برای سه سازه انتخابشده و مدلهای معادل با مهاربندهای کمانش ناپذیر، نتیجه گرفته میشود که نرخ افزایش سالانه هنگامی که مهاربندهای کمانش ناپذیر در نظر گرفته میشوند، به طور قابلتوجهی کاهش مییابد.
۱. مقدمه
در چند سال گذشته، تعداد زیادی از ساختمانها به خاطر زلزلههای متوسط و بزرگ آسیبدیده اند.امروزه سیستمهای سازهای به منظور کاهش آسیب لرزهای تکاملیافته اند. امروزه، یکی از پر استفاده ترین سیستمهای سازهای، قابهای بتن مسلح شناخته شدهاست. ساختمانهای بتن مسلح اغلب مورد استفاده قرار میگیرند. با این حال، مهمترین عیب آنها مشکل بودن تعمیرات ان پس از وقوع زلزله است. علاوه بر این، سازههای بتنآرمه واقع در مناطق لرزهای معمولا در معرض جابجایی بین طبقهای پیک بزرگ تولید شده توسط بارهای جانبی قرار میگیرند.
۵. نتیجهگیری
در این مقاله عملکرد لرزهای سه ساختمان بتنی مسلح سنتی و سازههای معادل با مهاربندهای کمانش ناپذیر با استفاده از تحلیل دینامیکی افزایشی، شکنندگی لرزهای و قابلیت اعتماد سازهای مورد ارزیابی قرار گرفتهاست. برای این منظور، حداکثر دریفت بین طبقهای به عنوان پارامتر تقاضای مهندسی انتخاب شدهاست. در این تحقیق، با استفاده از روش تحلیل سلسله مراتبی (ahp)و با استفاده از روش تحلیل سلسله مراتبی (ahp)و با در نظر گرفتن عوامل موثر بر رفتار لرزهای ساختمانها، تاثیر هر یک از این عوامل بر رفتار لرزهای آنها مورد بررسی قرار گرفتهاست. علاوه بر این، عدم قطعیت در پیشبینی پاسخ سازه نیز زمانی که مهاربندهای کمانش ناپذیر در ساختمانهای بتن مسلح استفاده میشوند، کاهش مییابد.
The control of vibrations and damage in traditional reinforced concrete (RC) buildings under earthquakes is a difficult task. It requires the use of innovative devices to enhance the seismic behavior of concrete buildings. In this paper, we design RC buildings with buckling restrained braces (BRBs) to achieve this objective. For this aim, three traditional RC framed structures with 3, 6, and 9 story levels are designed by using the well-known technique nondominated sorting genetic algorithm (NSGA-II) in order to reduce the cost and maximize the seismic performance. .en, equivalent RC buildings are designed but including buckling restrained braces. Both structural systems are subjected to several narrow-band ground motions recorded at soft soil sites of Mexico City scaled at different levels of intensities in terms of the spectral acceleration at first mode of vibration of the structure Sa(T1). .en, incremental dynamic analysis, seismic fragility, and structural reliability in terms of the maximum interstory drift are computed for all the buildings. For the three selected structures and the equivalent models with BRBs, it is concluded that the annual rate of exceedance is considerably reduced when BRBs are incorporated. For this reason, the structural reliability of the RC buildings with BRBs has a better behavior in comparison with the traditional reinforced concrete buildings. .e use of BRBs is a good option to improve strength and seismic behavior and hence the structural reliability of RC buildings subjected to strong earthquake ground motions.
1. Introduction
In the past few years, an extensive amount of buildings has suffered damage due to medium and large earthquakes. Structural systems have evolved in order to reduce seismic damage. Nowadays, one of the most used structural systems is that based on reinforced concrete frames. Reinforced concrete buildings have been frequently used; nevertheless, the main disadvantage of them is the difficulty to be repaired after the occurrence of an earthquake. Furthermore, RC structures located on seismic zones usually are subjected to large peak interstory drift displacements produced by the lateral loads.
5. Conclusions
The seismic performance of three traditional reinforced concrete buildings and equivalent structures with BRBs is assessed through incremental dynamic analysis, seismic fragility, and structural reliability. For this aim, the maximum interstory drift was selected as engineering demand parameter. .e buildings were subjected to several narrowband motions recorded at soft soil of Mexico City. .e results indicate that the maximum interstory drift demand is smaller in the case of the RC-BRB buildings in comparison with the reinforced concrete structures. Moreover, the uncertainty in the structural response prediction also tends to decrease when the BRBs are used in the RC buildings.
۱. مقدمه
2. مهاربندهای مقاوم در برابر کمانش
3. روش شناسی
۳. ۱ طراحی لرزهای مدلهای بتن مسلح RC با استفاده از NSGA - II.
۳.۲ حرکات زمین به صورت زلزله.
۳.۳ ارزیابی قابلیت اطمینان سازه ای.
۴. مقایسه عملکرد لرزهای سازههای بتن مسلح و بتن مسلح - مهاربندهای کمانش ناپذیر: نتایج عددی
۴. ۱ تحلیل دینامیکی افزایشی.
4.2 شکنندگی سازه ای
۴.۳ قابلیت اطمینان سازه ای
۵. نتیجهگیری
منابع
1. Introduction
2. Buckling Restrained Braces
3. Methodology
4. Comparison of the Seismic Performance of the RC and RC-BRB Structures: Numerical Results
4.1. Incremental Dynamic Analyis
4.2. Structural Fragility
4.3. Structural Reliability
5. Conclusions
References
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه