ماهیت موقتی رضایت شغلی کارکنان
چکیده
در زمان جنگ سخت و شدید برای استعداد که طبیعتا خاص صنایع دانش محور است، مسئله رضایت شغلی کارکنان یک مفهوم مدیریتی مهم می باشد. از این نظر، این مطالعه به بررسی عوامل درونی خاصی می پردازد که اساس مفهوم رضایت شغلی و همچنین تداوم رضایت شغلی کارکنان است. بر اساس ادبیات موجود یک مدل نظری از رضایت شغلی طراحی شد که سپس با استفاده از داده های جمع آوری شده از طریق نظرسنجی ها طی ده سال، آزمون شد. نتایج حاصل از آزمون مدل نشان می دهد که انتظارات شغلی کارکنان عامل درونی خاصی ایجاد می کند که رضایت شغلی را از عدم رضایت متمایز می کند. جالب اینکه، نتایج نشان داد که رضایت شغلی قبلی پیش بینی کننده مطمئنی برای رضایت شغلی بعدی نیست.
1. مقدمه
از آنجا که صنعت فناوری اطلاعات بالغ و کامل است، تاثیر آن بر اجتماع و اقتصاد بسیار عمیق و گسترده است. فرآیند ها و مفاهیمی مانند تغییر دیجیتالی، امنیت سایبری، هوش مصنوعی، راه را برای رشد و توسعه در تمام زمینه های جامعه مدرن و به ویژه در حوزه کسب و کار هموار کرده است. این پیشرفت شگرف چالش های زیادی برای کسب و کار و جامعه ایجاد کرده است. به جز مسائل اخلاقی و قانونی رو به افزایش مربوط به امنیت، حریم شخصی و محرمانگی، شرکت های فناوری اطلاعات کنونی با چالش های فناوری و مدیریتی زیادی روبرو هستند-پذیرش تکنولوژی های نوظهور، ایجاد بازار جدید یا رشد بازار موجود، معرفی مدل کسب و کار نوآورانه و غیره. تصمیم گیری عاقلانه درباره این مسائل و مسائل مشابه برای موفقیت کسب و کار، در برخی موارد، حتی صرفا بقای آنها، ضروری است.
4.2. کاربردهای عملی
مدیران کمی هستند که درباره پیشنهادات و مسیرهای نظریه دو عاملی هرزبرگ آگاهی ندارند. یعنی پاداش های بیرونی (پاداش ها و مشوق های مالی و مادی) در بلندمدت کارکنان را برنمی انگیزند. برای ایجاد و حفظ کارکنان راضی و برانگیخته، مدیران باید پاداش های درونی مناسب- کار جالب توجه، محرک و چالشی، و همچنین فرصتی برای رشد شخصی فراهم کنند(هرزبرگ، 2003). نتایج تحقیق به دست آمده، مستقیما چنین گفته ای را تایید می کند که با در نظرگرفتن زمینه خاص تحقیق- شرایط بازار نابالغ و بی ثبات بوسنی و هرزگوین، اهمیت خاصی دارد. نتایج این مطالعه تایید می کند که مدیران منابع انسانی ممکن است و باید بر بهترین شیوه ها تکیه کنند و بینش هایی درباره مدیریت استعداد از محیط کسب و کار توسعه یافته، صرفنظر از شرایط اقتصادی که شرکت تحت آن فعالیت می کند، داشته باشند. به طور خاص، برای جذب و حفظ استعدادهای مد نظر، بخش ها و مدیران منابع انسانی باید مطمئن شوند که رضایت شغلی به طور مستمر برآورده می شود، بنایراین، ارائه پاداش های درونی لازم منجر به سطوح بالای رضایت شغلی و کاهش از دست دادن کارکنان می شود.
Abstract
In a time of persistent and fierce “war for talents,” which is naturally inherent to the knowledge-intensive industries, the issue of employees’ job satisfaction is of the utmost managerial significance. In that respect, this study explores certain intrinsic factors that underlie the job satisfaction concept, as well as the durability of employees’ job satisfaction. Based on the extant literature, a theoretical model of job satisfaction was designed, which was subsequently tested using the data gathered through the surveys conducted over the ten years. The results obtained by model testing show that employees’ job expectations make up that particular intrinsic factor that differentiates job satisfaction from non-satisfaction. More intriguingly, the results showed that prior job satisfaction is not a reliable predictor of later job satisfaction.
1. Introduction
As the IT industry mature, its impact on the economy and society becomes progressively larger and more profound. The processes and concepts like digital transformation, cybersecurity, artificial intelligence, to mention but a few, have paved the way for growth and advancement in all facets of modern society and, particularly, in the realm of business. This immense progress, however, poses many challenges for both business and society. Aside from the growing ethical and legal issues related to privacy, security, and confidentiality, present-day IT companies are also facing numerous technological and managerial challenges – emerging technologies adoption, creating a new market or existing market growth, the introduction of innovative business model, and alike. Wise decision-making concerning these and similar issues is critical for their business success and, in some cases, even their mere existence.
4.2. Practical implications
There are but few managers who do not know about Herzberg’s two-factor theory suggestions and directions. Namely, the extrinsic rewards (financial and material rewards and incentives) will not motivate the employees in the long-run. To create and keep really motivated and satisfied employees, managers must provide them with proper intrinsic rewards – challenging, stimulating, and interesting work, as well as an opportunity for personal growth (Herzberg, 2003). The obtained research results directly support such an assertion, which is particularly important considering the research context’s specificity – quite unstable and immature market conditions of BiH. The study outcomes confirm that HR managers may (and should) rely on the best practices and insights abouttalent managementfrom highly developed business environments, regardless of the economic conditions under which their organizations operate. Specifically, to attract and retain the most wanted talents, HR departments and managers, in general, have to ensure that employees’ job expectations are continuously fulfilled, thus providing the necessary intrinsic rewards that would lead to higher levels of job satisfaction and, likely, lower attrition.
چکیده
1. مقدمه
2. مروری بر ادبیات
2.1. رضایت شغلی کارکنان- مفهوم
2.2. رضایت شغلی کارکان- ویژگی های صنعت فناوری اطلاعات
2.3. رضایت شغلی کارکنان- مدل
3. داده ها و روش شناسی
3.1. طرح تحقیق و معیارها
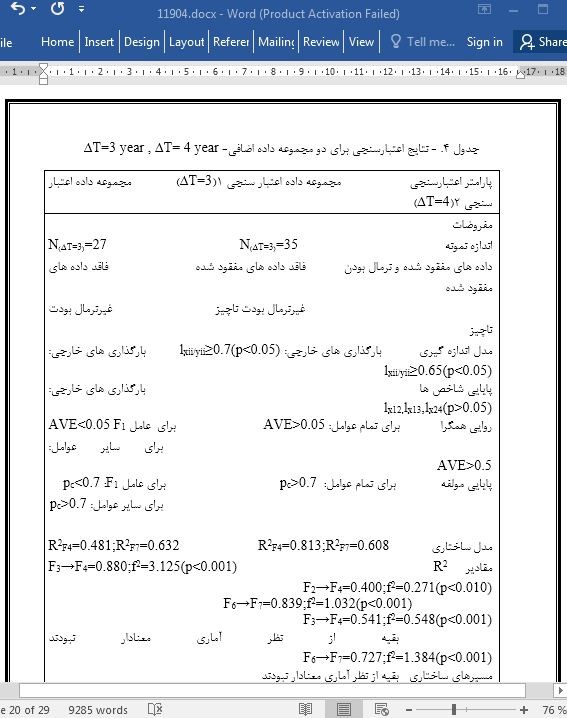
3.2. نتایج
3.3. تفسیر نتایج و بحث
4. نتیجه
4.1. کاربردهای نظری
4.2. کاربردهای عملی
منابع
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature review
2.1. Employees’ job satisfaction – the concept
2.2. Employees’ job satisfaction – the IT industry particularities
2.3. Employees’ job satisfaction – the model
3. Data and methodology
3.1. Research design and measures
3.2. Results
3.3. Interpretation of the results and discussion
4. Conclusion
4.1. Theoretical implications
4.2. Practical implications
References
- اصل مقاله انگلیسی با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه