مروری بر نانوالیاف الکتروریسی شده زیست فعال با پایه گیاهان دارویی بعنوان پانسمان زخم
چکیده
در زمان های قدیم، از مواد طبیعی تنها برای پوشاندن زخم استفاده می شد ولی امروزه پانسمان های زخم دارای مواد عامل دار شده اند تا از عفونت جلوگیری کنند، به فرایند بهبود زخم کمک کنند و ترمیم پوست را بهبود بخشند. از بین انواع مختلف پانسمان زخم، نانوالیاف های الکتروریسی شده به دلیل خواص منحصربفرد خود جزء جدیدترین و آینده دارترین پانسمان ها به شمار می روند. این پانسمان ها تشابه مورفولوژیکی با ماتریس برون سلولی طبیعی (ECM) ، نسبت سطح به حجم بالا و تخلخل بیشتر دارند، دارای الیاف منعطف و یکپارچه با ساختار نانو هستند که برای سیستم های تحویل دارو قابل استفاده اند و می توانند ترمیم بافت و انتقال ترشحات زخم را بهتر کنند و قابلیت تنفس برای رشد و تکثیر سلولی را نیز تضمین کنند. این مقاله مروری جدیدترین تحقیقات انجام شده در زمینه ساخت نانوالیاف الکتروریسی شده زیست فعال با پایه گیاهان دارویی بعنوان پانسمان زخم را بررسی می کند. این مقاله خواص درمانی گیاهان دارویی مختلف را نیز مورد بحث قرار می دهد.
1-مقدمه
پوست بزرگ ترین و بیرونی ترین عضو بدن انسان است. در واقع پوست مرز بین بدن انسان و محیط بیرون است که کاربرد آن حفظ دمای بدن در یک حد متعادل، جلوگیری از اتلاف بیش از حد مایعات بدن و ممانعت از حمله پاتوژن ها است (هونگ لی یه، جون ون چنگ) [1,2]. زمانی که پوست آسیب ببیند ممکن است مایعاتی از ناحیه آسیب دیده خارج شود که این مایع به همراه دمای بدن و مواد مغذی موجود می توانند باعث بروز عفونت در زخم شوند که موجب بیمار شدن شخص شده و حتی ممکن است بیمار را بکشد [3]. مواد بیوپزشکی مختلفی با تکنیک های تولید متفاوت برای پوشاندن و بهبود زخم استفاده شده اند. یک پانسمان زخم ایده آل باید ویژگی های اساسی چون زیست سازگاری، غیرسمی بودن، محافظت در برابر عفونت، قابل جذب بودن، تراوایی خوب و تحویل داروی فوری داشته باشد [4-11]. اکثر پانسمان های زخم بر اساس محصولات نساجی به فرم الیاف، نخ، منسوجات بافته شده، بی بافت و قلاب دوزی شده، کامپوزیت ها و نانوالیاف الکتروریسی شده اند. فوم ها، فیلم ها، هیدروژل ها، ماتریس و هیدروکلوییدها نیز استفاده می شوند [8].
4- نتیجه گیری ها
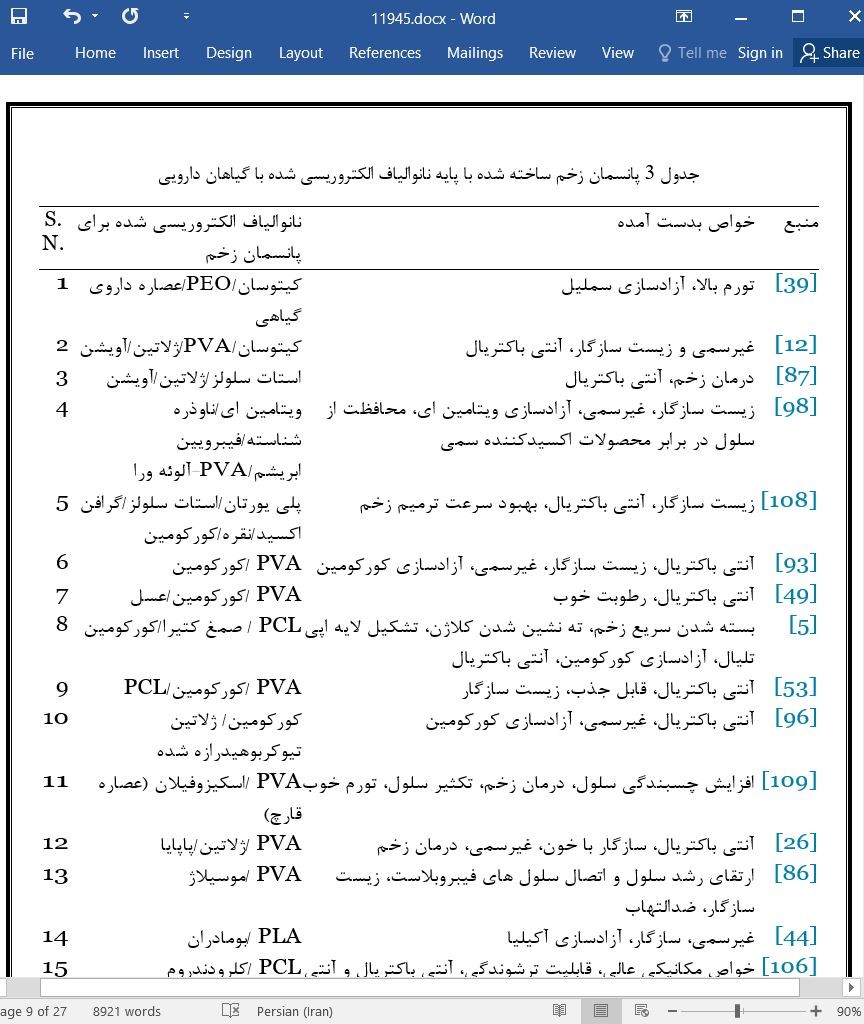
هر روزه اکتشافات جدیدی در زمینه پانسمان های زخم بوجود می آید. در نتیجه تحقیق و توسعه پانسمان های زخم عامل دار کماکان یکی از موضوعاتی است که باید در مورد آن تحقیق شود تا پیش نیازهای زخم های پیچیده و درمان ناپذیر بهتر درک شود. الیاف الکتروریسی شده مورفولوژی خاص، نسبت سطح به حجم بالا و ساختار متخلخل دارند، قابلیت بندآوردن خون و جذب تراوشات زخم را نیز دارند که بعنوان یک حامل دارو و تسریع روند درمان زخم استفاده می شوند. پلیمرهای طبیعی و مصنوعی را می توان برای ساخت الیاف الکتروریسی شده استفاده کرد ولی ترکیبی از پلیمرهای مختلف (طبیعی و مصنوعی) خواص منحصربفردی را برای درمان زخم فراهم خواهند آورد.
Abstract
In the early time, natural materials were used only to cover the wound but nowadays wound dressings contain functionalize materials to prevent infections, assist wound healing process, and improve skin restoration. Among dissimilar forms of wound dressings, electrospun nanofibrous wound dressings are the latest and promising ones due to their unique properties. These dressings have morphological similarity to the natural extracellular matrix (ECM), high surface area to volume ratio, greater porosity, continuous and flexible nano structure fibers applicable for drug delivery systems which can approve tissue regeneration, wound fliuid transportation and ensure breathability for cellular growth and proliferation. This review provides a broad overview of latest medicinal plant incorporated bioactive electrospun nanofibrous wound dressing researches and developments. It also discussed the therapeutic properties of different traditional medicinal plants.
1. Introduction
The skin is the largest and outermost organ of the human body. It is a barrier between human body and the external environment, which has the function of maintaining temperature balance, preventing excessive fluid loss, and preventing pathogens from invasion Hongli Ye, Junwen Cheng [1,2]. Once the skin is damaged, there maybe fluid exudate in the injured area, this fluid with body temperature and nutritions there maybe development of infection in wounds which may bring illness of patients, even lead to passing away [3]. Different biomedical textile materials with different manufacturing techniques are used to cover and heal the wound. An ideal wound dressings must have basic characteristics as biocompatible, non-toxic, protective against infection, absorbable, permeable, and quick drug delivery [4-11]. Most wound dressings are based on textile constructions in the form of fibres, yarns, nonwoven, woven, crochet, knitted and braided fabrics, composites and electrospun nanofibrous materials. Foams, films, hydrogels, matrix, and hydrocolloids are also used [8].
4. Conclusions
Day-by-day there are new understandings and discoveries of textile wound dressings. Consequently, researching and developing new functional wound dressings is still an area of research to meet the requirements of complex and un-healing wounds. Electrospun nanofibrous materials have special morphologies, high surface area to volume ratio and porous structure, haemostasis, capability of absorbing exudates, used as drug carriers, and capability to accelerate wound healing. Both natural and synthetic polymers can be used for electrospun nanofibrous material manufacturing, but combination of different polymers (synthetic and natural) will bring special properties for wound healing.
نکات برجسته
چکیده
1-مقدمه
2- نانوالیاف الکتروریسی شده با پایه پلیمر برای پانسمان زخم
3- نانوالیاف الکتروریسی شده زیست فعال با پایه گیاهان دارویی برای پانسمان زخم
1-3 زردچوبه (کورکوما لونگا)
2-3 آلوئه ورا
3-3 لاوسونیا اینرمیس (حنا)
4-3 آزادیراکتا ایندیکا/ چریش هندی
5-3 زاتاریا مولتی فلورا (آویشن)
6-3 پونه سای جوپاری (Nepeta dschuparensis Bornm)
7-3 گیاه بابونه
8-3 ریشه ایساتیس
9-3 شنبلیله
10-3 ملیلوتوس افیسینالیس (یونجه زرد)
11-3 بومادران لوکانیایی
12-3 ذرت
13-3 انار
14-3 گیاه موسیلاژ (لیزاب)
15-3 گیاه قرنفل
16-3 منگوستن
17-3 پیچ معین التجار (کلرودندروم)
18-3 گیمنما سیلوستر
19-3 پاپایا
4- نتیجه گیری ها
منابع
Highlights
Abstract
Graphical abstract
1. Introduction
2. Polymer based electrospun nanofibrous wound dressings
3. Medicinal plant based bio active electrospun nanofibrous wound dressings
3.1. Turmeric (Curcuma longa)
3.2. Aloe vera
3.3. Lawsonia inermis
3.4. Azadirachta Indica/Neem
3.5. Zataria multiflora
3.6. Nepeta dschuparensis Bornm
3.7. Chamomile plant
3.8. Isatis root
3.9. Fenugreek
3.10. Melilotus officinalis
3.11. Achillea lycaonica
3.12. Corn
3.13. Pomegranate
3.14. Mucilage plant
3.15. Cloves plant
3.16. Mangosteen (Garcinia mangostana linn
3.17. Clerodendrum phlomidis
3.18. Gymnema sylvestre
3.19. Carica papaya
4. Conclusions
References
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه