مالکیت معنوی ارزش آفرینی شرکت های نوآفرین در فناوری های توانمندساز کلیدی
چکیده
ما نحوه مدیریت حفاظت از مالکیت معنوی (IP) رسمی و غیررسمی ارزش آفرینی از سوی شرکت های نوآفرین فعال در فناوری های توانمندساز کلیدی، KET، را مورد مطالعه قرار دادیم. شش جنبه کلیدی کمکرسان مدیران در ایجاد استراتژی های IP موثر برای شرکت های نوآفرین فعال در این فناوری های به شدت پیچیده شناسایی شدند. با پانزده شرکت نوآفرین که به عنوان شرکت های نانوفناوری شناخته می شوند با پرسش های بازی درباره ارزش آفرینی از طریق حفاظت از نوآوری ها مصاحبه گردید. شرکت های نوآفرین در جنوب سوئد که در حال حاضر یک قطب بزرگی برای KET محسوب می گردد، فعالیت می کنند. یافته های ما شش جنبه کلیدی کمکرسان مدیران در KET را به ویژه در بخش شرکت های نوآفرین نانوفناوری در ایجاد استراتژی های IP موثر نشان می دهد. در وهله نخست، تهیه نقشه محیط فناوری و بازار تجاری مهم است. اغلب شرکت های نوآفرین نانوفناوری مصاحبه شونده اظهار نمودند که خواهان افزایش سهم بازار هستند اما تنها چهار شرکت از پانزده شرکت نوآفرین عملاً استراتژی هایی را برای نقشه برداری بازار تجاری تدوین نمودند. غفلت از تمرکز بر تقاضای بازار تجاری و تمرکز صرف بر روی نوآوری، موانع آتی شرکت های نوآفرین نانوفناوری محسوب می شوند. در وهله دوم، توجه و تعیین ارزش های واقعی حائز اهمیت در شکوفایی شرکت های نوآفرین نانوفناوری و متعاقباً برنامه ریزی استراتژیک IP رسمی و غیررسمی، سودمند خواهد بود. در وهله سوم، حفاظت از جنبه های مختلف یک نوآوری با انواع مختلف IP برای ارزش آفرینی موثر شرکت های نوآفرین نانوفناوری سودمند می باشد. عوامل مهمی که باید در هنگام انتخاب نحوه حفاظت از جنبه های مختلف نوآوری مد نظر قرار گیرند عبارتند از: نیازهای بازار، امکان فعالیت پیرامون راه حل و نیز ریسک مهندسی معکوس نوآوری. در وهله چهارم، به دلیل پیچیدگی نانوفناوری، شرکت های نوآفرین از توجه به جنبه هایی از نوآوری بهره مند می شوند که مهندسی معکوس این اسرار تجاری دشوار می باشد. به عنوان نمونه چنین جنبه هایی عبارتند از: دانش فنی مربوط به فرآیند تولید و سایر فنون زیربنایی که به بیمانندی محصول اضافه نموده اما مستقیماً از خود محصول مشتق نمی شوند. نکته قابل توجه آنکه، تنها پنج شرکت از پانزده شرکت نوآفرین نانوفناوری واقعاًٌ استراتژی هایی را برای نحوه مدیریت اسرار تجاری خود تدوین نمودند. در وهله پنجم، در ارزش آفرینی، حفاظت رسمی از جنبه های نوآوری که تقاضای بازار را برآورده ساخته و جنبه هایی که احتمالاً رقبا برای توسعه محصولات خود بدان نیاز دارند، سودمند می باشد. بنابراین، حفاظت از جنبه هایی که با مباحث فروش مرتبط بوده و یا مبنای توافقنامه های صدور مجوز را تشکیل می دهند، از طریق ثبت اختراع برای شرکت های نوآفرین نانوفناوری سودمند خواهد بود. تمام شرکت های نوآفرین نانوفناوری مورد مطالعه دارای ثبت اختراع هستند اما به طور شگفت آوری تنها هفت شرکت از پانزده شرکت نوآفرین دست به ثبت اختراع جنبه هایی زده اند که در بازار آن ها ارزش آفرینی تجاری دارند. در وهله ششم، برای شرکت های نوآفرین نانوفناوری برخورداری از طرحی درباره نحوه ارزش آفرینی از طریق دستیابی واقعی به این حقوق حائز اهمیت می باشد. طرح مزبور ممکن است در بر گیرنده مواردی همچون نحوه حمایت حقوق مزبور از افزایش فروش، تشکیل مبنایی برای برنامه زمان بندی صدور مجوز، ارزش افزایی شرکت و غیره باشد. طرح نحوه ارزش آفرینی این حقوق، مبنایی برای روند بررسی حفظ و یا عدم حفظ حقوق خاص مالکیت معنوی محسوب می گردد.
پیامدهای عملی
به منظور طراحی استراتژی های موثر IP برای شرکت های نوآفرین نانوفناوری، شش جنبه مهم با توجه به شرایط واقعی کسب و کار مشخص گردید. شش بُعد زیر از طریق تجزیه و تحلیل توانمندسازهای مزبور برای یافتن شباهت ها ایجاد شدند. با مرتب سازی کلیه توانمندسازهای ارزش، این توصیه ها می تواند به مدیران اجرایی در شرکت های نوآفرین نانوفناوری در طراحی استراتژی های IP موثر و ترکیب موثر IP رسمی و غیررسمی برای ارزش آفرینی استراتژیک و مالی کمک نمایند.
نخست، توصیه می شود نقشه محیط فناوری و بازار تجاری ترسیم گردد. غفلت از تمرکز بر تقضاهای بازار تجاری می تواند موانع آتی شرکت های نوآفرین نانوفناوری در هنگام ایجاد استراتژی های موثر IP باشد. عوامل مهمی را که باید در هنگام انتخاب محوه حفاظت از جنبه های مختلف نوآوری مد نظر قرار داد عبارتند از: نیازهای بازار، امکان فعالیت پیرامون راه حل و نیز ریسک مهندسی معکوس نوآوری. در هنگام ایجاد استراتژی های IP مطابق با نقشه فنی و تجاری، شرکت های نوآفرین نانوفناوری می توانند به آزادی عمل در بازار دست یافته و از توانایی منع و مسدود کردن رقبا برخوردار شوند.
Abstract
We have studied how start-up companies operating within key enabling technologies, KETs, manage formal and informal intellectual property (IP) protection for generating value. Six key aspects helping executives to create effective IP strategies for start-ups in these highly complex technologies have been identified. 15 start-ups defined as nanotechnology companies have been interviewed with open questions regarding value generated through protecting innovations. The start-ups operate in southern Sweden which currently is a KET heavy hub. Our findings indicate six key aspects to help executives within KETs, specially within the nanotechnology start-up sector, to create effective IP strategies. First, it is important to map the technological environment and the commercial market. Most of the interviewed nanotechnology start-ups expressed that they want to increase in market share however, only four out of fifteen start-ups actually had set strategies for mapping the commercial market. Neglecting to focus on commercial market demands and merely on the innovation itself can present a future hindrance for nanotechnology start-ups. Second, it is beneficial for nanotechnology start-ups to consider and determine which actual values are important in order for them to thrive, and thereafter strategically plan formal and informal IP accordingly. Third, protecting different aspects of an innovation with different types of IP is beneficial for nanotechnology start-ups to effectively generate value. Important factors to consider when choosing how to protect different aspects of innovations are, what the market needs, the possibility to work around the solution, as well as risk of reverse engineering the innovation. Fourth, due to the complexity within nanotechnology, start-ups may benefit from treating aspects of an innovation that are difficult to reverse engineer as trade secrets. Such aspects include e.g. know-how related to the production process and other underlying know-how which add to the product’s uniqueness but which not directly derivable from the product itself. Notably, only five out of fifteen nanotechnology start-ups have set strategies for how to manage their trade secrets. Fifth, to generate value, it is beneficial to formally protect aspects of an innovation that fulfill market demands as well as aspects that competitors likely would need to develop their products. Thus, aspects which are associated with sales arguments or which could form the basis for licensing agreements are beneficial to protect by patents for nanotechnology start-ups. All the studied nanotechnology start-ups have patents, but surprisingly only seven out of fifteen start-ups stated have patented aspects that generate commercial value on their market. Sixth, it is important for nanotechnology start-ups to have a plan for how the rights attained actually should generate value. This plan may encompass anything from how the rights support increased sales, form the basis for a licensing schedule, increase the value of the company, etc. The plan for how the rights should generate value is also the basis for a review procedure concerning whether to maintain a specific IP right or not.
Practical implications
In order for nanotechnology start-ups to create effective IP strategies the finding indicate six important aspects to consider in real business situations. The following six aspects were constructed through analyzing the identified value enablers to find similarities. By sorting out all value enablers, this recommendation can help executives within the nanotechnology start-up sector to create effective IP strategies and to effectively combine formal and informal IP to generate both strategic and financial values.
First, it is recommended to map the technological environment and the commercial market. Neglecting to focus on commercial market demands can be a future hindrance for nanotechnology start-ups when trying to create effective IP strategies. Important factors to consider when choosing how to protect different aspects of innovations are, whatthe market needs, the possibility to work around the solution, as well as risk of reverse engineering the innovation. When IP strategies are created in accordance to the technological and commercial mapping, nanotechnology start-ups can attain freedom to operate the market and have the ability to hinder and block competitors.
چکیده
مقدمه
نتایج
ارزش های استراتژیک و ابعاد مربوطه
بُعد 1: اطمینان پذیری از طریق شناسایی مشروط
بُعد ۲: توانایی افزایش سهم بازار
بُعد 3: داشتن حضور رقابتی در بازار
ارزش های مالی و ابعاد مربوطه
بُعد ۴: تخصیص موثر منابع
بُعد ۵: درآمد مستقیم حاصل از معاملات بازار
بُعد ۶: توانایی دستیابی به سرمایه گذاران
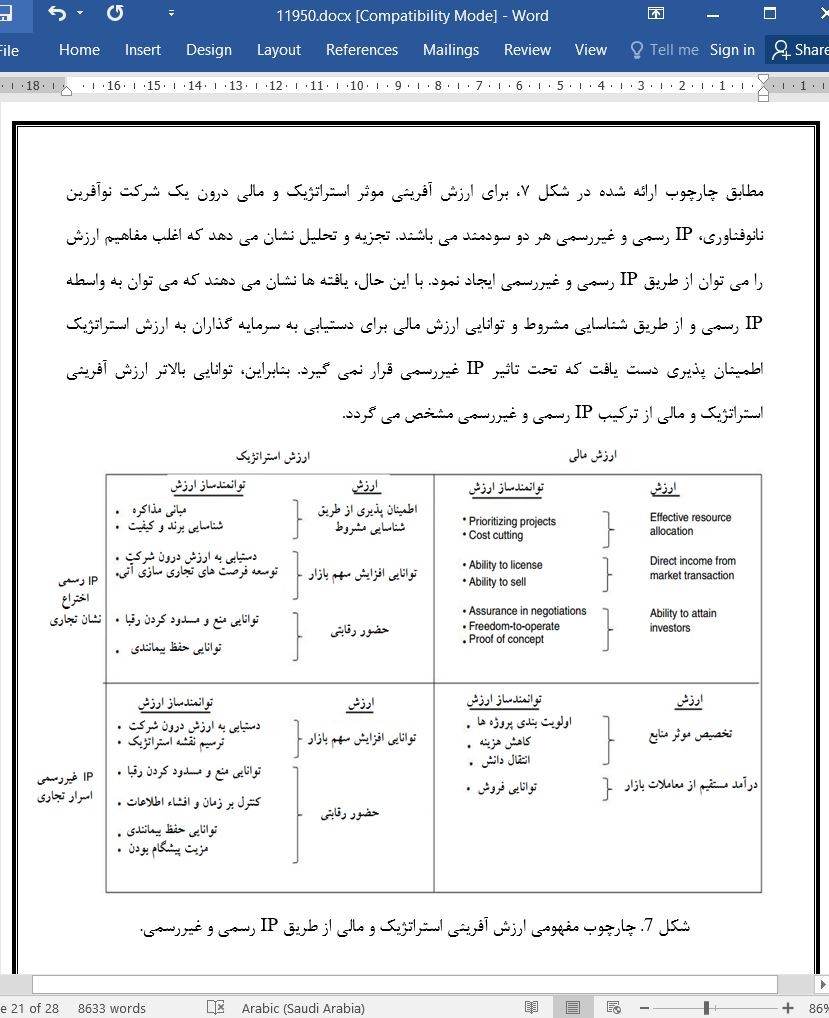
چارچوب مفهومی استراتژی های موثر IP
ترکیبی از IP رسمی و غیررسمی و توانمندسازهای مربوطه
بحث و نتیجه گیری
پیامدهای عملی
تضاد منافع
تقدیر و تشکر
ضمیمه A. داده های تکمیلی
منابع
Abstract
Introduction
Results
Strategic values and corresponding dimensions
Dimension 1: Trustworthiness through qualified recognition
Dimension 2: Ability to increase in market share
Dimension 3: Having a competitive presence on the market
Financial values and corresponding dimensions
Dimension 4: Effective resource allocation
Dimension 5: Direct income from market transactions
Dimension 6: Ability to attain investors
Conceptual framework for effective IP strategies
Combination of formal and informal IP and corresponding enablers
Discussion and conclusions
Practical implications
Conflicts of interest
Acknowledgements
Appendix A. Supplementary data
References
- اصل مقاله انگلیسی با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه