دستور العمل های پایداری جهت دستیابی به شهرهای پایدار هوشمند
چکیده
شهری سازی آکنده از چالش های فراوان است. مفاهیم شهر پایدار هوشمند ابزاری را جهت حل این مشکلات پیش روی ما قرار می دهد. از این رو، پژوهشگران طی سالها مشغول انجام تحقیقات بر روی چارچوب های به کار گرفته شده در شکل گیری شهرهای پایدار هوشمند بوده اند تا چالش های شهری سازی که ارائه شده است را برای اجرای مفاهیم شهر پایدار هوشمند ( (SSCCدر کشورهای در حال توسعه کنترل کنند. در مطالعه حاضر، چارچوبی مفهومی جهت کنترل چالش های شهری سازی در اجرای شهرهای پایدار هوشمند در کشورهای در حال توسعه ارائه شده است. مطالعه کنونی با استفاده از رویکرد استقرایی، فلسفه اثبات گرایی پژوهشی را به کار گرفته است. تجزیه و تحلیل عاملی مؤلفه های اصلی برای تحلیل ۷۶ پاسخ بازیابی شده از یک نمونه هدف استفاده شده است. نتایج حاصل از این تحلیل ۴ مؤلفه را به وجود آورد که در حکم دستورالعمل های پایداری برای دستیابی به شهرهای پایدار هوشمند در کشورهای در حال توسعه می باشند. اهمیت اصلی این بررسی در ارائه چارچوبی جهت ارتقای اجرای مفاهیم شهر پایدار هوشمند در کشورهای در حال توسعه نهفته است. این مطالعه با برجسته سازی راهبردهایی برای بهبود هوشمندی شهرها و نشان دادن دستورالعمل های کلیدی پایدار مورد نیاز برای دستیابی به شهر پایدار هوشمند در کشورهای در حال توسعه بر ارزش پیشینۀ پژوهشی شهر پایدار هوشمند می افزاید. همچنین مطالعه حاضر کمبودهای شهری سازی در کشورهای در حال توسعه را آشکار میسازد و مسیرهایی را برای تحقیقات آتی فراهم می کند جایی که مشخص شود فرصت های مطالعاتی آتی در بهبود سازه های توانمند و توسعه ابزارهای سنجش جامع برای تعیین و کنترل شهری سازی شهرهای کشور های در حال توسعه نهفته است. در عمل، این مطالعه چارچوبی با دسترسی آسان ارائه می دهد که نشاندهندۀ این موضوع است که چگونه می توان چالش های شهری سازی را تصویر سازی نمود و راه حل هایی برای پیادهسازی مفهوم شهر پایدار هوشمند در کشورهای در حال توسعه ارائه کرد.
1. مقدمه
فرآیند شهری سازی ترجیحاً باید با پیشبینی آینده تحول اجتماعی و اقتصادی که روشی آسان برای برآورده ساختن نیازهای شهروندان، بهبود انسجام اجتماعی و به حداکثر رساندن منابع است، هماهنگ و سازگار باشد [۶۴،۵۷]. هرچند، رشد سریع و برنامه ریزی نشده مانع توسعه پایدار می شود به منزله نفرینی برای بهرهمندی از مزایای شهری سازی می باشد. بنابراین، به منظور غلبه بر مشکلات شهری سازی و افزودن بر مزایای آن، مفهوم شهر هوشمند پیشنهاد شده است [۲۴،۲۰،۱۷].
Abstract
Urbanisation of cities are fraught with several challenges. Smart sustainable city concepts (SSCC) present means to solve these problems. Therefore, over the years, researchers have been studying frameworks to adopt in the formation of smart sustainable cities to solve urbanisation challenges. In this study, a conceptual framework for controlling urbanisation challenges to implementing SSCC in developing countries is presented. The study adopted positivism research philosophy using deductive approach. Principal component factor analysis was used to analyse 76 responses retrieved from a purposive sample. The emanating results generated four components which serves as sustainability guidelines to achieving smart sustainable cities in developing countries. The primary importance of this study lies in providing a framework to enhance the implementation of SSCC in developing countries. This study adds value to the smart sustainable city literature by highlighting strategies for improving cities’ smartness and showing key sustainability guidelines required for the attainment of a smart sustainable city in a developing country. The study also brings to light deficiencies in urbanisation in developing countries and provide paths for future research, where it was indicated that future research opportunities lie in improving enabling structures in cities and developing comprehensive measurement tools for determining and controlling urbanisation in developing countries’ cities. For the world of practice, the study offers a readily available framework that captures how urbanisation challenges could be conceptualised and solutions could be provided towards the implementation of SSCC in developing countries.
1. Introduction
The process of urbanisation preferably should be geared towards provision of economic and social transformation – an easy way of meeting citizen’s needs, improving social cohesion, and maximising resources [57,64]. However, rapid and unplanned growth impedes sustainable development and acts as anathemise to enjoying the benefits of urbanisation. Therefore, in order to circumvent urbanisation problems and enhance its benefits, the smart city concept has been proposed [17,20,24].
چکیده
1. مقدمه
2. نظریه
1.2 جهان در حال شهری سازی شدن: چالش های پیش روی بهبود
2.2 حل بحران های شهری سازی: تولید مفهوم شهر هوشمند
3.2 چارچوب شهر هوشمند و سازگاری آن در کشورهای در حال توسعه
4.2 مفاهیم شهر هوشمند پایدار برای بهبود سازه های شهری
3. روش ها
4. نتایج و بحث ها
1.4 آزمون های تحلیلی
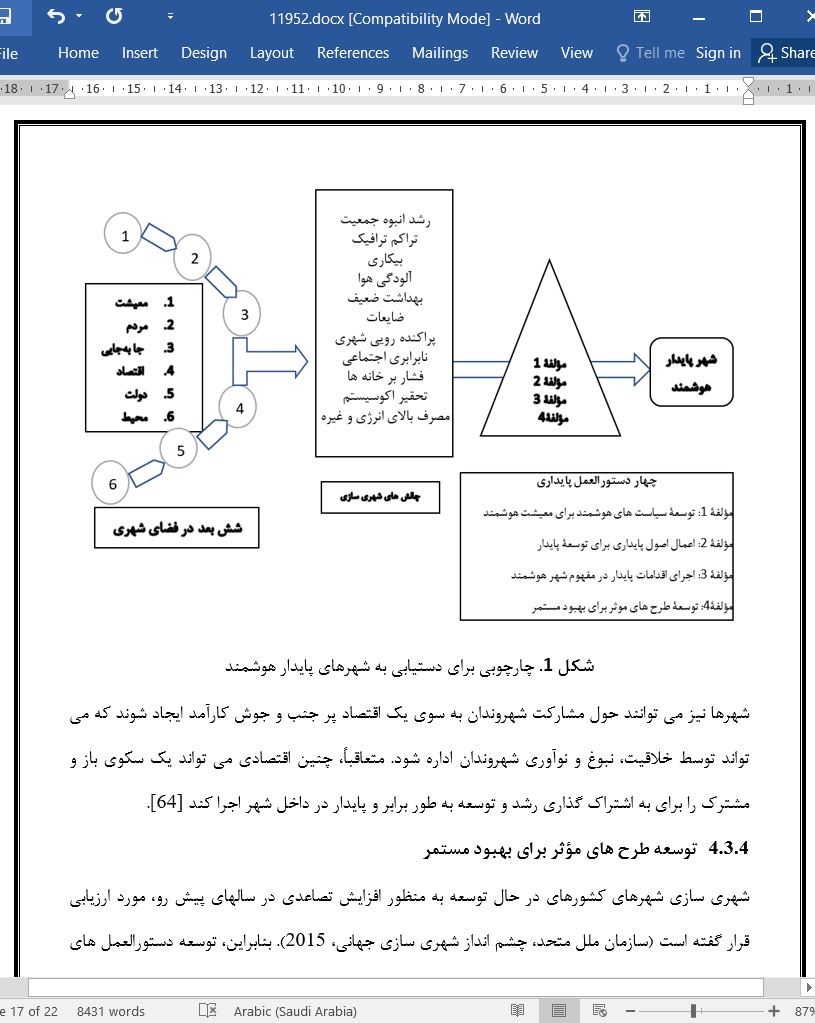
3.4 دستورالعمل های پایداری جهت دستیابی به شهرهای پایدار هوشمند
4.3 چارچوبی برای دستیابی به شهرهای هوشمند پایدار در کشورهای در حال توسعه
5. نتیجه گیری
فهرست منابع
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Theory
2.1. The urbanising world: challenges in the face of improvement
2.2. Solving urbanisation crises: the birth of smart city concept
2.3. Smart city framework and its adoption in developing countries
2.4. Smart sustainable city concepts for improving urban structures
3. Methods
4. Results and discussions
4.1. Analytical tests
4.2. Findings
4.3. Sustainability guidelines to attaining smart sustainable cities
4.4. A framework for the attainment of smart sustainable cities in developing countries
5. Conclusion
Declaration of Competing Interest
Acknowledgements
References
- اصل مقاله انگلیسی با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه