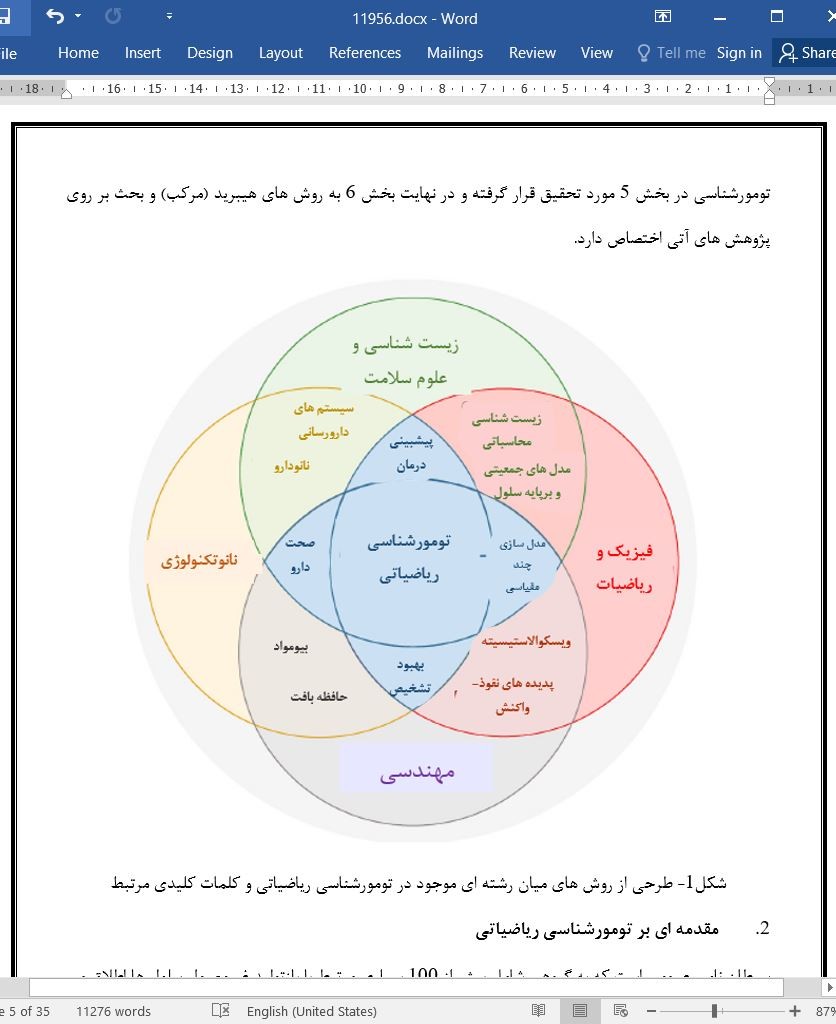
تومورشناسی بر پایه ریاضیات کسری
چکیده
تومورشناسی ریاضیاتی به بررسی پدیده های در ارتباط با سرطان از طریق مدل های ریاضی فراگیر می پردازد. از این رو رویکردهای میان رشته ای شامل مفاهیم گوناگون از زیست شناسی تا علوم مواد، موجب درکی عمیق تر از سیستم های بیولوژیکی وابسته به بیماری می گردد. در این راستا حساب دیفرانسیل کسری (منسوب به مراتب غیرصحیح) شاخه ای از آنالیز ریاضی می باشد که به کمک ابزارهای آن می توان پدیده های پیچیده در مقیاس های متفاوت زمانی و مکانی را توصیف نمود. مدل های مرتبه کسری امکان توصیف و درک بهتر جزئیات تومورشناسی و عوامل بالقوه موثر در حوزه های تصمیم گیری مانند رشد تومور، تکنیک های تشخیص اولیه و روش های درمانی اختصاصی را فراهم می آورد. تحقیق حاضر با دنبال کردن یک دیدگاه پدیدارشناختی (مانند روش های مکانیکی) به بررسی جنبه های گوناگون تومورشناسی بر پایه ریاضیات کسری پرداخته و به مرور و بحث دستاوردهای جدید این حوزه با توجه به کاربردهای آتی آن ها می پردازد.
1. مقدمه
سرطان شامل گروهی از بیماری ها بوده که از جهش غیرنرمال سلول ها نشات گرفته و امکان ظهور آن در تمامی ارگان ها و بافت های بدن وجود دارد. این بیماری دومین علت مرگ و میر در جهان بوده و نرخ زنده ماندن در این بیماری تا حد زیادی به تشخیص به موقع و کیفیت درمان بستگی دارد (سازمان بهداشت جهانی، 2020). حوزه های تومورشناسی آزمایشگاهی، تکنیک های شامل زیست شناسی مولکولی و به تازگی علوم ژنتیک بیشترین پروژه های تحقیقاتی در این موضوع را شامل شده و موجب افزایش دانش پیرامون مشخصه یابی بدخیمی تومور، تشخیص و درمان بیماری می شوند (گاتنبای و مائینی ، 2003). استفاده از فیزیک و ریاضی در موضوعات مربوط به سرطان در چند دهه گذشته افزایش یافته و موجب پیدایش حوزه تحقیقی جدیدی شده است (بیرن ، 2010؛ راکن و اسکات ، 2019).
7. نکات پایانی
برخی ابزارهای ریاضیاتی هم چنان در حال پیدا کردن مسیر خود در حوزه زیست شناسی نظری بوده و حساب دیفرانسیل کسری (به عنوان نمونه مرتبه غیرصحیح) نیز یکی از این موارد می باشد که جنبه های فلسفی و تاریخی آن توجهات زیادی را به خود جلب کرده است. کاربرد حساب دیفرانسیل کسری، همان طور که در این مرور مورد بحث قرار گرفت، به عنوان یک رویکرد قوی و استراتژیک مدل سازی بوده که به فرصت ها و چالش های احتمالی موجود در تومورشناسی ریاضیاتی می پردازد. تومورشناسی بر پایه ریاضیات کسری در کنار دارا بودن فواید شناخته شده تست یا بازتولید مربوط به سناریوهای سیلیکو (که در آزمایش های متناظر بی فایده و یا حتی غیرممکن می باشند)، توانایی کار کردن آسان در مقیاس های ناهمگن، هم چنین بررسی آثار حافظه و دوره های نهفتگی مربوط به شروع و رشد تومور را دارند.
Abstract
Mathematical Oncology investigates cancer-related phenomena through mathematical models as comprehensive as possible. Accordingly, an interdisciplinary approach involving concepts from biology to materials science can provide a deeper understanding of biological systems pertaining the disease. In this context, fractional calculus (also referred to as non-integer order) is a branch in mathematical analysis whose tools can describe complex phenomena comprising different time and space scales. Fractional-order models may allow a better description and understanding of oncological particularities, potentially contributing to decision-making in areas of interest such as tumor evolution, early diagnosis techniques and personalized treatment therapies. By following a phenomenological (i.e. mechanistic) approach, the present study surveys and explores different aspects of Fractional Mathematical Oncology, reviewing and discussing recent developments in view of their prospective applications.
1. Introduction
Cancer embodies a group of diseases that emerge from abnormally mutated cells and can appear in almost any body organ or tissue. It is the second leading cause of death worldwide and survival rates are profoundly related to timely access to quality diagnosis and treatment (World Health Organization, 2020). Experimental oncology and techniques involving molecular biology and, more recently, genetics have dominated most research projects on the subject, increasing the knowledge on malignancies characterization, diagnostic and treatment (Gatenby and Maini, 2003). In the last few decades, physics and mathematics have been increasingly applied to cancer-related problems, thus giving rise to a new research area (Byrne, 2010; Rockne and Scott, 2019).
7. Concluding remarks
There are tools in Mathematics still waiting to establish their way in Theoretical Biology and such is the case of fractional (i.e. non-integer order) calculus, whose historical and philosophical aspects have attracted growing interest. As addressed and discussed in the present review work, the application of fractional calculus indeed arises as powerful and strategic modeling approach in view of prospective challenges and opportunities in Mathematical Oncology. Besides wellknown advantages of either testing or reproducing different in silico scenarios (which could be impractical or even impossible via corresponding in vitro experimentation), Fractional Mathematical Oncology can straightforwardly deal with heterogeneous scales, memory effects and/or dormancy periods related to tumor onset and development.
چکیده
1. مقدمه
2. مقدمه ای بر تومورشناسی ریاضیاتی
3. مدل های قطعی و پیوسته
4. مدل های تصادفی و برپایه سلول: رشد تومور تحت مدل های گسسته
5. تومورشناسی بر پایه ریاضیات کسری
5.1. پایه تئوری حساب دیفرانسیل کسری
5.2- مدل های کسری در ارتباط با سرطان
6. مدل های کسری هیبریدی نوین
7. نکات پایانی
اعلان تعارض منافع
تقدیر و تشکر
مراجع
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. An introduction to Mathematical Oncology
3. Deterministic and continuum models: Tumor growth described by differential equations
4. Cell-based and stochastic models: tumor growth governed by discrete models
5. Fractional Mathematical Oncology
5.1. Fractional calculus basic theory
5.2. Cancer-related fractional models
6. On the prospective fractional hybrid models
7. Concluding remarks
Declaration of competing interest
Acknowledgments
References
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه