کووید 19 و بحران مدیریت کسب و کار: یک مطالعه تجربی در SMEها
چکیده
بیماری همه گیر کووید 19 بسیاری از شرکت ها را وادار به تعطیلی کرده، و منجر به اختلال بی سابقه ای در تجارت در اکثر بخش های فعالیت اقتصادی در سراسر جهان شده است. اگرچه زنجیره های تأمین جهانی تحت تأثیر قرنطینه عمومی قرار گرفته اند، اما به دلیل ویژگی های خاص آنها، شرکت های کوچک و متوسط (SME ها) با اقدامات انجام شده برای جلوگیری از گسترش ویروس به شدت تحت تأثیر قرار گرفته اند. هدف از این پژوهش این است که چگونه این شرکت ها با اختلال ناشی از تعطیلی، از نظر جمعیت و زندگی روزمره آنها جهت انجام فعالیت های اقتصادی خود سروکار دارند. برای این منظور، یک روش کیفی (توصیفی و استقرایی) با استفاده از نمونه گیری گلوله برفی با پرسشنامه ای در پرتغال در طی قرنطینه به کار رفت. نتایج به دست آمده نشان می دهد که SME ها با یک سری مشکلات از قطع عملکردهای خود مواجه هستند، که منجر به مشکلات نقدینگی جدی با تأثیر بر تداوم آینده آنها و حفظ مشاغل شده است. علاوه بر این، اهمیت اقدامات دولت برای حمایت از این شرکت ها در امروز و آینده را نشان داد، اگرچه تعداد شرکت هایی که به آنها وفادار هستند به طور قابل توجهی تحت تأثیر معیارهای شایستگی و سرعت پاسخگویی مؤسسات است. سهم اصلی این تحقیق در تأیید این امر است که نقاط ضعف SME ها مانع اصلی برای یک پاسخ مقاوم به این بحران، از قبیل نقدینگی محدود آنها، منابع انسانی، دیجیتال سازی و استفاده از فناوری اطلاعات هستند. این ضعف ها و/یا تهدیدها پیش از این در جریان های مختلف نظری ناشی از نظریه سازمانی نشان داده شده بود، بنابراین اصالت این مشارکت در این واقعیت قرار دارد که مدیران این SME ها از مهارت و ویژگی های دیگری از قبیل ظرفیت های پویا جهت مدیریت کسب و کار در یک بحران بی نظیر و ادامه عملیات خود، حتی در صورت مواجهه با انسداد جهانی برخوردار هستند. مفاهیم نظریه و عمل، محدودیت ها و پیشنهادات برای تحقیقات آینده نیز ارائه شده است.
1. مقدمه
در 11 مارس 2020، سازمان جهانی بهداشت (WHO) اعلام کرد که جهان با یک بیماری همه گیر ناشی از کروناویروس جدید، به نام کووید 19 مواجه است که به طور تصاعدی منتشر خواهد شد. در این موقعیت، از تمام کشورها خواسته شد تا درتلاش برای کاهش شیوع آن قرنطینه عمومی را اجرا کنند ]1[، و این یک فرایند طولانی بوده است. بقا وابسته به نحوه مدیریت خروج از این بحران است ]2[، زیرا همانطورکه توسط بالدوین و ودر استدلال شد ]3[، بحران سلامتی عمومی گسترش می یابد و بر کل اقتصاد تأثیر خواهد گذاشت. بحران بیماری همه گیر فعلی متفاوت از بحران های قبلی (به عنوان مثال، طوفان ها، بحران مالی 2008) است، زیرا آنها در یک لحظه خاص و در مکان هایی معین پدیدار شده اند، درحالیکه کووید 19 در مقیاس جهانی توسعه یافته و کنترل آن به سرعت به اقتصادها در سراسر جهان و فعالیت های کسب و کار آنها (کسب و کار ملی و بین المللی) خسارت زده است ]5[. این رابطه علّی بین ظهور قرنطینه جهانی و عواقب اقتصادی و بهداشتی آن تأثیر خاصی بر شرکت های خرد، کوچک و متوسط، خواه خانوادگی یا غیر خانوادگی داشته است ]10 – 6[.
Abstract
The COVID-19 pandemic has forced many firms to close, causing an unprecedented interruption in trade in most sectors of economic activity worldwide. Although global supply chains have been affected by the general lockdown, due to their particular characteristics, small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) have been hit most severely by the measures implemented to prevent the spread of the virus. This study aims to determine how these firms coped with the disruption caused by the closure, in terms of population and their daily lives to carry out their economic activities. For this purpose, a qualitative methodology (descriptive and inductive) was used through the use of snowball sampling with a questionnaire in Portugal during the lockdown. The results obtained show that SMEs face a series of difficulties from interrupting their operations, which has caused serious liquidity problems, with effects on their future continuity and maintaining jobs. Additionally, it showed the importance of government measures to support these firms today and in the future, although the number of firms adhering to them is considerably affected by the eligibility criteria and the speed of institutions’ response. The main contribution of this research lies in confirming that the weaknesses in SMEs are the principal obstacle to a resilient response to this crisis, such as their limited liquidity, human resources, digitalization, and use of information technology. These weaknesses and/or threats had already been indicated in the various theoretical currents stemming from Organizational Theory, so the originality of this contribution lies in the fact that the managers of these SMEs are endowed with other skills and characteristics, such as, for example, dynamic capacities to manage business in an unparalleled crisis and to continue their operations, even when faced with a global blockage. Implications for theory and practice, limitations, and suggestions for future research are also presented.
1. Introduction
On 11 March 2020, the World Health Organisation (WHO) announced that the world was facing a pandemic caused by a new coronavirus, called COVID-19, which would disseminate exponentially. In these circumstances, all countries were urged to implement a general lockdown in an attempt to slow down its spread [1], and this has been a lengthy process. Survival depends on how the exit from this crisis will be managed [2], as the public health crisis will spread to and influence the whole economy, as argued by Baldwin and Weder [3]. The current pandemic crisis is different from previous crises (e.g., hurricanes, the financial crisis of 2008), as those emerged at a specific moment and in certain places, whereas COVID-19 has developed on a world scale, and controlling it has quickly damaged economies worldwide [4] and their business activities (national and international business) [5]. This causal relation between the emergence of a global lockdown and its economic and sanitary consequences has had a particular effect on micro-, small- and medium-sized firms, whether family-owned or not [6–10].
چکیده
1. مقدمه
2. مرور مقالات
2.1. چالشی که SME ها در پاسخ به بیماری همه گیر با آن مواجه هستند
2.2. پیامدهای کسب و کار و مدیریت SME
3. روش شناسی
3.1. نوع پژوهش
3.2. جمع آوری داده ها و نمونه
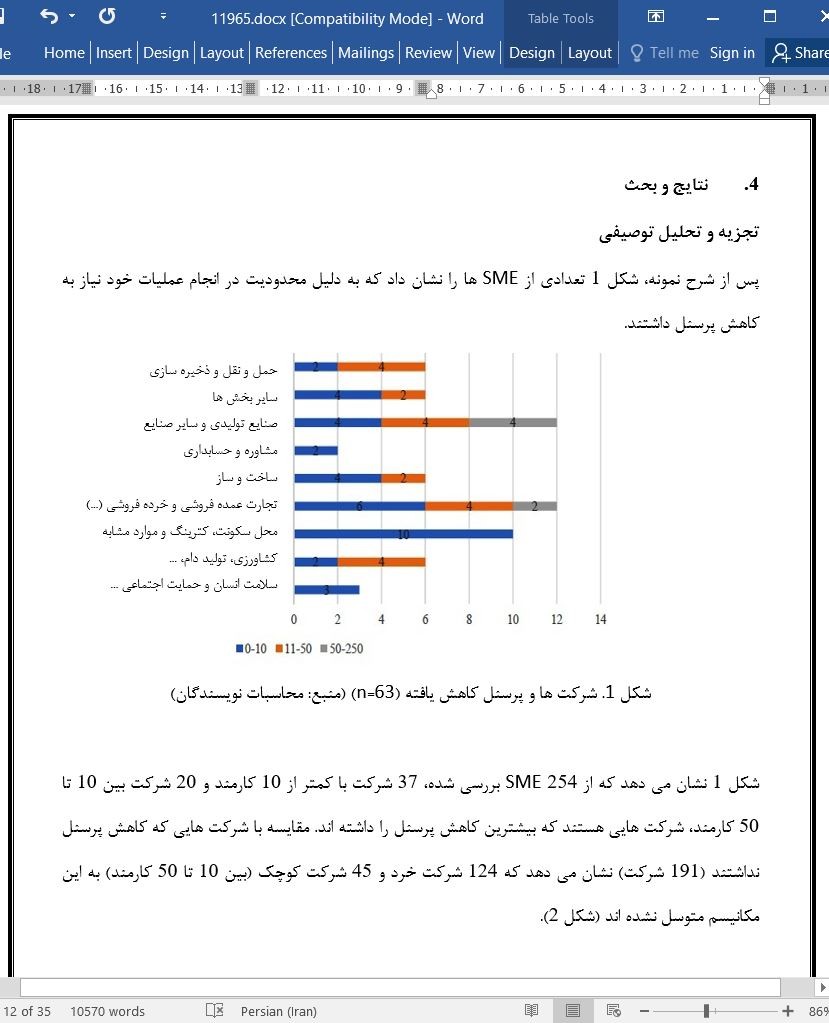
4. نتایج و بحث
تجزیه و تحلیل توصیفی
5. تجزیه و تحلیل محتوا
6. نتایج
7. مفاهیم
8. محدودیت ها و راه های آینده
پیوست A پرسشنامه ای پیرامون تأثیر کووید 19 بر شرکت های پرتغالی
منابع
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Challenge Faced by SMEs in Responding to the Pandemic
2.2. Consequences for Sme Business and Management
3. Methodology
3.1. Type of Research
3.2. Data Collection and Sample
4. Results and Discussion
Descriptive Analysis
5. Content Analysis
6. Conclusions
7. Implications
8. Limitations and Future Avenues
Appendix A Questionnaire on the Impact of COVID-19 on Portuguese Firms
References
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه