مدولاسیون دینامیکی تله گذاری رنگین کمانی نور آهسته و انتشار در موجبر تله گذاری شده
چکیده
یک بررسی عددی از تله گذاری رنگین کمانی نور آهسته در موجبر کریستال فوتونی تله گذاری شده پیشنهاد می کنیم که با اصلاح پارامترهای ساختاری در کریستال های فوتونی با تقارن کم شکل می گیرد. امواج الکترومغناطیسی فرکانس های مختلف در پهنای باند نرمال تقریبا 5% را از طریق تجزیه و تحلیل پراکندگی و شبیه سازی های عددی می توان در موقعیت های مختلف با نام «تله گذاری رنگین کمانی» به دام انداخت. علاوه بر این، موجبر کریستالی فوتونی تله گذاری شده بر روی کاهش پلی استراین ایجاد می شود که در آن شاخص شکست را می توان با تنظیم ولتاژ خارجی براساس اثر الکترواپتیک تنظیم کرد. بنابراین، زمانی که ولتاژ اعمال شده به درستی تعدیل شود، موج تله گذاری شده در موقعیت های مختلف قرار گرفته و حتی منتشر خواهد شد. این ساختار دارای جنبه های کاربردی گسترده در سوئیچ نوری، تقسیم طول موج چندگانه، و سایر دستگاه های ارتباطی نوری دیگر است.
مقدمه
در حال حاضر به لطف ویژگی های امیدوار کننده در ذخیره سازی نوری، ذخیره سازی پنهان نوری، پردازش اطلاعات نوری و سایر حوزه ها، نور آهسته توسط بسیاری از محققان مورد بررسی قرار گرفته است [5-1] که بعنوان فناوری های کلیدی برای ارتباطات نوری آینده و ذخیره سازی اطلاعات در نظر گرفته می شوند. در ابتدا، نور آهسته براساس اثرات کوانتوم مانند وضوح ناشی از الکترومغناطیسی (EIT)، نوسان منسجم جمعیت (CPO)، پراکندگی رامان تحریک شده (SRS) و پراکندگی بریلیون تحریک شده (SBS) تحقق یافت [9-6]. با این حال، دما/فشار کاری بسیار کم و پهنای باند کاری اندک، پیاده سازی های عملی آنها را محدود کرد. کریستال های فوتونی (PC) بعنوان یک ماده مصنوعی جدید، برای تشخیص نور آهسته بیشتر مورد توجه قرار گرفته اند زیرا از دمای اتاق و کوچک سازی مناسب دستگاه پشتیبانی می کنند. [14-10]. به منظور کسب پهنای باند کاری گسترده برای کاربردهای عملی، تلاش های زیادی برای کسب نوارهای پهن بر روی منحنی های پراکندگی با اصلاح محلی شاخص موثر PC انجام شده است [15]. گزارش های اخیر درباره ، «تله گذاری گین کمانی» نور آهسته در برخی مواد مصنوعی (مانند PCها، فرامواد و غیره)، روش جدیدی را برای کاهش سرعت نور در طیف گسترده فرکانس باز کرده است [18-16].
Abstract
We propose a numerical investigation of slow light rainbow trapping and releasing in a tapered photonic crystal waveguide which is formed by linearly modifying the structural parameters in low-symmetric photonic crystals. Through dispersion analysis and numerical simulations, the electromagnetic waves of different frequencies in a normalized bandwith of ~5% can be trapped at different positions, as called “rainbow trapping”. Moreover, the tapered photonic crystal waveguide is created on polystyrene subtract, of which refractive index can be adjusted by tuning the external voltage based on electro-optic effect. Therefore, when the applied voltage is properly modulated, the trapped wave will be captured in different positions even released. The structure has broad application prospects in optical switch, wavelength-division multiplexing, and other optical communication devices.
Introduction
Recently, slow light has been investigated by many researchers, thanks to its promising properties in optical storage, optical caching, optical information processing and other areas [1–5], which are considered to be the key technologies for future all-optical communication and information storage. Initially, slow light was realized based on quantum effects such as electromagnetically induced transparency (EIT), coherent population oscillation (CPO), stimulated Raman scattering (SRS) and stimulated Brillouin scattering (SBS) [6–9]. However, the ultra-low working temperature/pressure and the narrow working bandwidth limited their practical implementations. As a new artificial material to realize slow light, photonic crystals (PCs) have attracted much attention because of their support for room-temperature and their fine device miniaturization [10–14]. In order to obtain wide working bandwidth for practical applications, many efforts have been made in obtaining flat bands on dispersion curves by locally modifying the effective index of PCs [15]. Recent reports on slow light “rainbow trapping” in some artificial materials (such as PCs, metamaterials, etc.) have opened a new way to slow down the speed of light over a wide frequency range [16–18].
چکیده
مقدمه
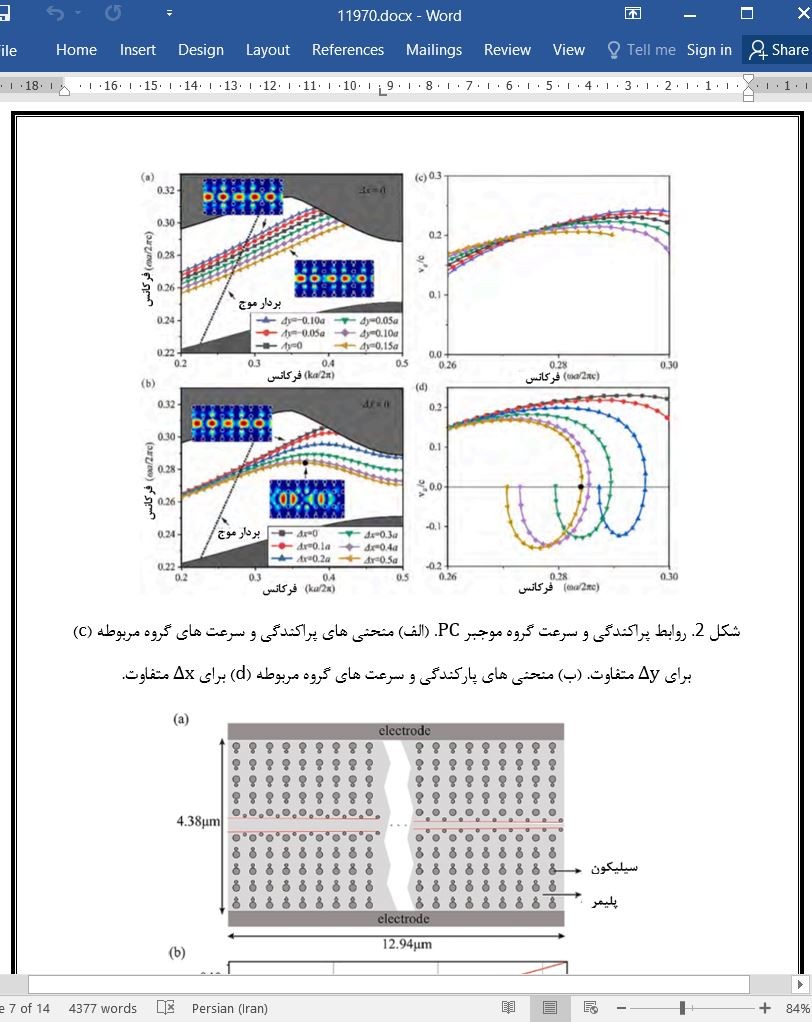
طراحی ساختار و تحلیل پراکندگی
قابلیت سوئیچ کردن تله گذاری رنگین کمانی نور آهسته
نتیجه گیری ها
منابع
Abstract
Introduction
Structure design and dispersion analysis
Switchable slow light rainbow trapping
Conclusions
CRediT authorship contribution statement
Declaration of Competing Interest
Acknowledgements
References
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه