رده بندی گروه های سنی در شبکه اجتماعی با استفاده از یادگیری عمیق
چکیده
شبکههای اجتماعی دارای حجم زیادی از دادههای قابل دسترس هستند، اما افراد اغلب برخی از دادههای شخصی خود، از قبیل سن، جنسیت و سایر اطلاعات جمعیتشناختی را فراهم نمیکنند. اگرچه تجزیه و تحلیل احساسات، از چنین دادههایی برای توسعه برنامههای کاربردی مفیدی در زندگی روزمره افراد استفاده میکند، در این نوع تجزیه و تحلیل، یا به دلیل تعداد محدود کلمات مشمول در دیکشنریهای لغت یا به دلیل عدم ملاحظه متنوعترین پارامترهایی که میتوانند روی احساسات در جمله تاثیر بگذارند هنوز شکستهایی وجود دارد؛ بنابراین، اگر اطلاعات پروفایل کاربران و ویژگیهای نوشتن آنها را ملاحظه کنیم، میتوانیم نتایج قابل اطمینانتری را به دست آوریم. این تحقیق نشان میدهد که یکی از مهمترین پارامترهای مشمول در پروفایل کاربر، گره سنی است، که نشان دهنده این است که رفتارهای معمولی در میان کاربران گروه سنی یکسان وجود دارند، به ویژه زمانی که این کاربران درباره موضوعی یکسان مینویسند. تجزیه و تحلیل دقیقی با 7000 جمله برای تعیین این موضوع انجام شد که کدام ویژگیها، از قبیل استفاده از نشانهگذاری، تعداد کاراکترها، اشتراکگذاری رسانهها، موضوعات و غیره، مهم هستند؛ و کدام ویژگیها را میتوان برای ردهبندی گروههای سنی نادیده گرفت. الگوریتمهای مختلف یادگیری ماشین برای ردهبندی گروههای سنی نوجوان و بزرگسال آزمایش میشوند و شبکه عصبی پیچشی عمیق دارای بهترین عملکرد است به طوری که به دقت 95/0 در آزمایشهای معتبرسازی میرسد. علاوهبراین، به منظور اعتبارسنجی سودمندی مدل پیشنهادی، مفهوم سنجش شدت احساسات (eSM) اجرا شده است. در اعتبارسنجی کارایی، آزمونهای ذهنی انجام میشوند و مدل eSM با مدل پیشنهادی به میانگین مربع خطا و ضریب همبستگی پیرسون به ترتیب 0.25 و 0.94، بالاتر از متریک eSM دست یافت، درحالی که اطلاعات گروه سنی در دسترس نبودند.
۱. مقدمه
امروزه، با استفاده مداوم از اینترنت، کاربران ساعتها در حال بازدید از سایتهای تجارت الکترونیک، خواندن اخبار و بیان نظرات و احساسات خود در قالب کامنت در شبکههای اجتماعی در مورد موضوعات مختلف هستند. این نظرات را میتوان برای ارزیابی رضایت مشتری ارزیابی کرد که اطلاعاتی بسیار مفید برای ارائهدهندگان خدمات و تامین کنندگان محصول هستند. گلدسمیت و همکاران [1]، رفتار افراد در استفاده از اینترنت برای تجارت الکترونیک را بررسی نموده و بر اهمیت ارزیابی رضایت مشتری در این نوع خدمات تأکید کردند.
7. نتیجه
به منظور به دست آوردن پارامترهای مربوطه، تعداد زیادی از جملات (7000) به صورت کیفی مورد تجزیه و تحلیل قرار گرفت تا ویژگیهای گروههای سنی نوجوانان و بزرگسالان با توجه به سبک نوشتاری و تاریخچه پروفایل هر کاربر مشخص شوند. نتایج تجربی نشان میدهند که پارامترهای مورد استفاده در این تحقیق میتوانند به دقت بالایی در تعیین گروههای سنی کاربران توییتر دست یابند. برخی از پارامترها حذف شدهاند زیرا بر نتایج ردهبندی نهایی تأثیر نمیگذارد، و در نتیجه روشن است که نباید مورد توجه قرار گیرند یا اعمال شوند.
ABSTRACT
Social networks have a large amount of data available, but often, people do not provide some of their personal data, such as age, gender, and other demographics. Although the sentiment analysis uses such data to develop useful applications in people’s daily lives, there are still failures in this type of analysis, either by the restricted number of words contained in the word dictionaries or because they do not consider the most diverse parameters that can influence the sentiments in a sentence; thus, more reliable results can be obtained, if the users profile information and their writing characteristics are considered. This research suggests that one of the most relevant parameter contained in the user profile is the age group, showing that there are typical behaviors among users of the same age group, specifically, when these users write about the same topic. A detailed analysis with 7000 sentences was performed to determine which characteristics are relevant, such as, the use of punctuation, number of characters, media sharing, topics, among others; and which ones can be disregarded for the age groups classification. Different learning machine algorithms are tested for the classification of the teenager and adult age group, and the deep convolutional neural network had the best performance, reaching a precision of 0.95 in the validation tests. Furthermore, in order to validate the usefulness of the proposed model for classifying age groups, it is implemented into the enhanced sentiment metric (eSM). In the performance validation, subjective tests are performed and the eSM with the proposed model reached a root mean square error and a Pearson correlation coefficient of 0.25 and 0.94, respectively, outperforming the eSM metric, when the age group information is not available.
I. INTRODUCTION
Nowadays, with the constant use of the Internet, users spend hours browsing on e-commerce sites, reading news about sports, journalism and entertainment, and expressing their opinions and sentiments in the form of comments on social networks about diverse topics. These comments can be analyzed to assess customer satisfaction that is a very useful information for service providers and product suppliers. Goldsmith et al. [1] explores the behavior of people that uses Internet for e-commerce and stresses the importance for evaluating the customer satisfaction in this type of services.
VII. CONCLUSION
In order to obtain the most relevant parameters, an extensive number of sentences (7000) were analyzed qualitatively, to determine the characteristics of teenager and adults age groups, considering the writing style and both users’ history and profile. The experimental results show that the parameters used in this research can reach a high accuracy for determining the age groups of Twitter users.
چکیده
۱. مقدمه
۲. کارهای مشابه
A. ارتباط بین گروه سنی و ویژگیهای نوشتاری
B. تجزیه و تحلیل احساسات
C. یادگیری ماشین
۳. مدل پیشنهادی برای ردهبندی گروههایسنی
A. پردازش دادههای استخراج شده از شبکههای اجتماعی
B. فاز ردهبندی
4. استفاده از مدل پیشنهادی در معیار شدت احساسات
A. آزمونهای ذهنی در محیط آزمایشگاهی
B. آزمونهای ذهنی در نظارت شده از راه دور
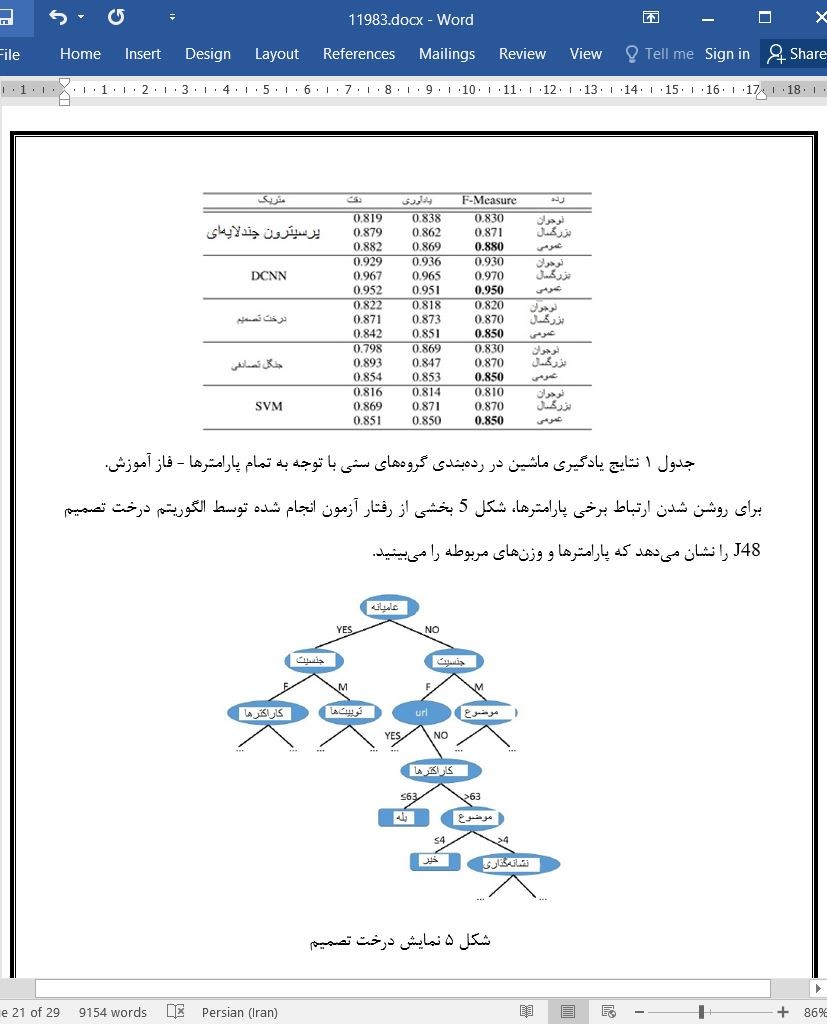
5. نتایج
A. یادگیری ماشین برای مدل ردهبندی
B. بررسی سودمندی مدل ارائه شده در معیارهای شدت احساسات
6. بحث
7. نتیجه
منابع
ABSTRACT
I. INTRODUCTION
II. RELATED WORK
A. RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN THE AGE GROUP AND THE CHARACTERISTICS OF THE WRITING
B. SENTIMENT ANALYSIS
C. MACHINE LEARNING
III. PROPOSED MODEL FOR CLASSIFYING AGE GROUPS
A. DATA TREATMENT EXTRACTED FROM SOCIAL NETWORKS
B. CLASSIFICATION PHASE
IV. APPLICATION OF THE PROPOSED MODEL IN A SENTIMENT INTENSITY METRIC
A. SUBJECTIVE TESTS IN A LABORATORY ENVIRONMENT
B. SUBJECTIVE TESTS MONITORED REMOTELY
V. RESULTS
A. MACHINE LEARNING FOR CLASSIFYING MODEL
B. EVALUATION OF THE USEFULNESS OF THE PROPOSED MODEL IN SENTIMENT INTENSITY METRICS
VI. DISCUSSIONS
VII. CONCLUSION
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
REFERENCES
- اصل مقاله انگلیسی با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه