روش عددی محدود برای مسئله موقعیت یابی و اعزام آمبولانس
چکیده
هدف سیستم های خدمات پزشکی اورژانس (EMS) ، ارائه خدمات پزشکی سریع در موارد اورژانسی می باشد. برنامه ریزی دقیق یک پیش نیاز اصلی برای موفقیت یک سیستم EMS و بخصوص برای کاهش زمان واکنش می باشد. متاسفانه، تقاضا برای خدمات اورژانس بسیار متغیر است و تردید در هنگام برنامه ریزی برای اقدام باید نادیده گرفته شود. چندین روش بهینه سازی برای بررسی مسائل مربوط به برنامه ریزی های EMS مطرح شده است و برای مثال می توان به مسئله موقعیت یابی و اعزام آمبولانس (ALDP) اشاره کرد. به هر حال، بسیاری از مدل ها قطعی هستند و تردید در تقاضا را نادیده می گیرند. در این تحقیق، ما برای بررسی تردید در تقاضا یک روش متقابل ALDP را ارائه و اعتبار سنجی کردیم و از روش عددی محدود استفاده کردیم . بررسی های عددی الهام گرفته از یک مورد واقعی است که نتایج تاثیر گذاری را ارائه کرده است و کاربرد عملی روش را اثبات می کند.
1. مسئله موقعیت یابی و اعزام آمبولانس
سیستم های خدمات پزشکی اورژانس (EMS) در بر گیرنده فعالیت های بالینی و انتقال آمبولانس در واکنش به تماس های اورژانس می باشند.EMS نقش مهمی در سیستم های درمان پیشرفته ایفا می کنند، زیرا واکنش مناسب به تماس های distress می تواند تاثیر قابل توجهی بر شرایط سلامت بیمار داشته باشد. بخصوص اینکه، یکی از مسائل اصلی مربوط به کاهش یا حفظ حد آستانه برای زمان بین دریافت تماس و ورود آمبولانس به منطقه اورژانس می باشد. ادبیات بسط داده شده برای طراحی و مدیریت EMS گسترده است. خوانندگان علاقه مند به تحقیقات (2) و (6) ارجاع داده می شوند زیرا در این تحقیقات طبقه بندی مسائل، فرمولاسیون و روش های حل مسائل EMS مطرح شده اند. جای تعجب نیست اگر بگوییم که در هر دو تحقیق، تردید در تقاضا و وجود آمبولانس بعد از دریافت تماس به عنوان مسائل مهم برای تحقیقات آینده اشاره شده اند.
Abstract
Emergency Medical Services (EMS) systems aim to provide immediate care in case of emergency. A careful planning is a major prerequisite for the success of an EMS system, in particular to reduce the response time. Unfortunately, the demand for emergency services is highly variable and uncertainty should not be neglected while planning the activities. Several optimization models have been proposed in the literature to deal with EMS planning-related problems, e.g. the Ambulance Location and Dispatching Problem (ALDP). However, most of the models are deterministic and neglect demand uncertainty. In this paper, we formulate and validate a robust counterpart of the ALDP to deal with demand uncertainty, exploiting the cardinality-constrained approach. Numerical experiments inspired by a real case show promising results and prove the practical applicability of the approach.
1 The Ambulance Location and Dispatching Problem
Emergency Medical Services (EMS) systems consist of the clinical activities and the ambulance transportation in response to an emergency call. EMS plays an important role in modern health care systems, as an adequate response to distress calls may have a crucial impact on patients’ health conditions. In particular, one of the main issues is to reduce, or to keep under a given threshold, the time between the distress call and the arrival of the ambulance to the emergency site. The body of literature devoted to EMS design and management is huge; we refer the interested reader to [2] and [6], which report classifications of EMS problems, formulations, and solving approaches. Unsurprisingly, both reviews identify uncertainty on the demand and availability of ambulances upon a call arrival as open and important issues to address in future research.
چکیده
1. مسئله موقعیت یابی و اعزام آمبولانس
2. فرمولاسیون مسئله انسجام
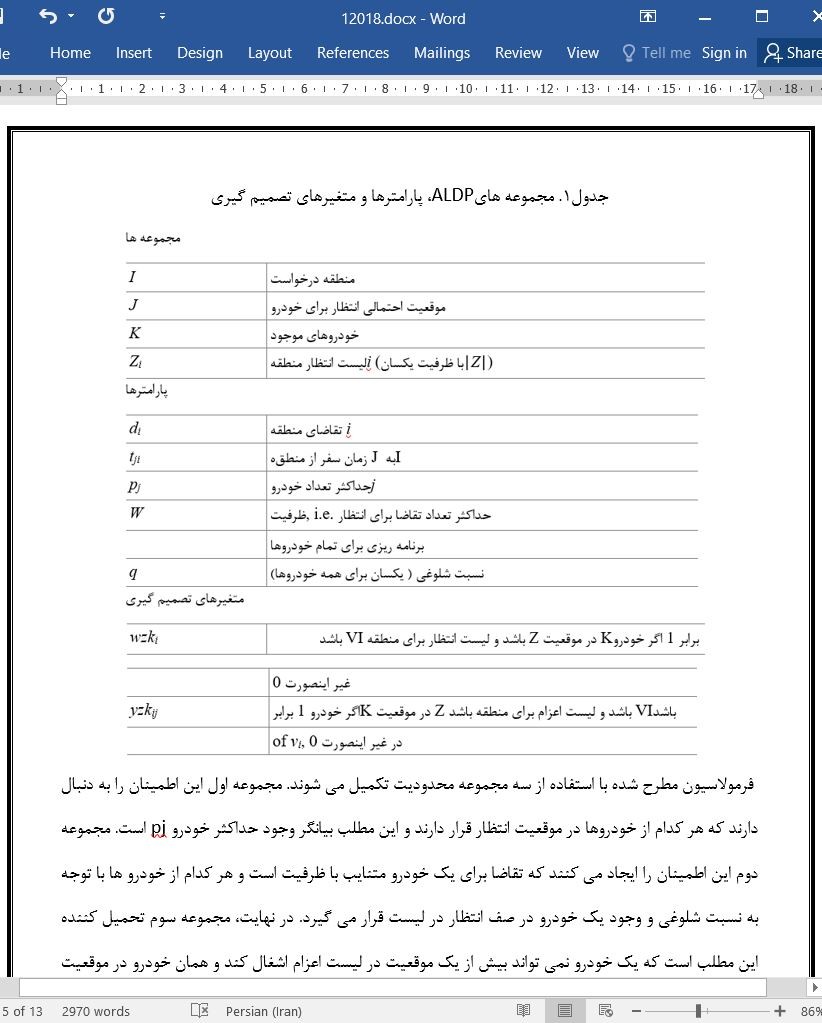
2.1 مجموعه ها، پارامترها و متغیرهای تصمیم گیری
2.2 تابع هدف و محدودیت ها
2.3 فرمولاسیون انسجام دارای محدودیت عددی
3.آزمایشات محاسباتی
3.1 اجرا و ارزیابی جواب ها
4. نتایج
نتیجه گیری
منابع
Abstract
1 The Ambulance Location and Dispatching Problem
2 Robust Problem Formulation
2.1 Sets, Parameters and Decision Variables
2.2 Objective Function and Constraints
2.3 Cardinality-Constrained Robust Formulation
3 Computational Experiments
3.1 Execution and Solutions Evaluation
4 Results
5 Conclusions
References
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه