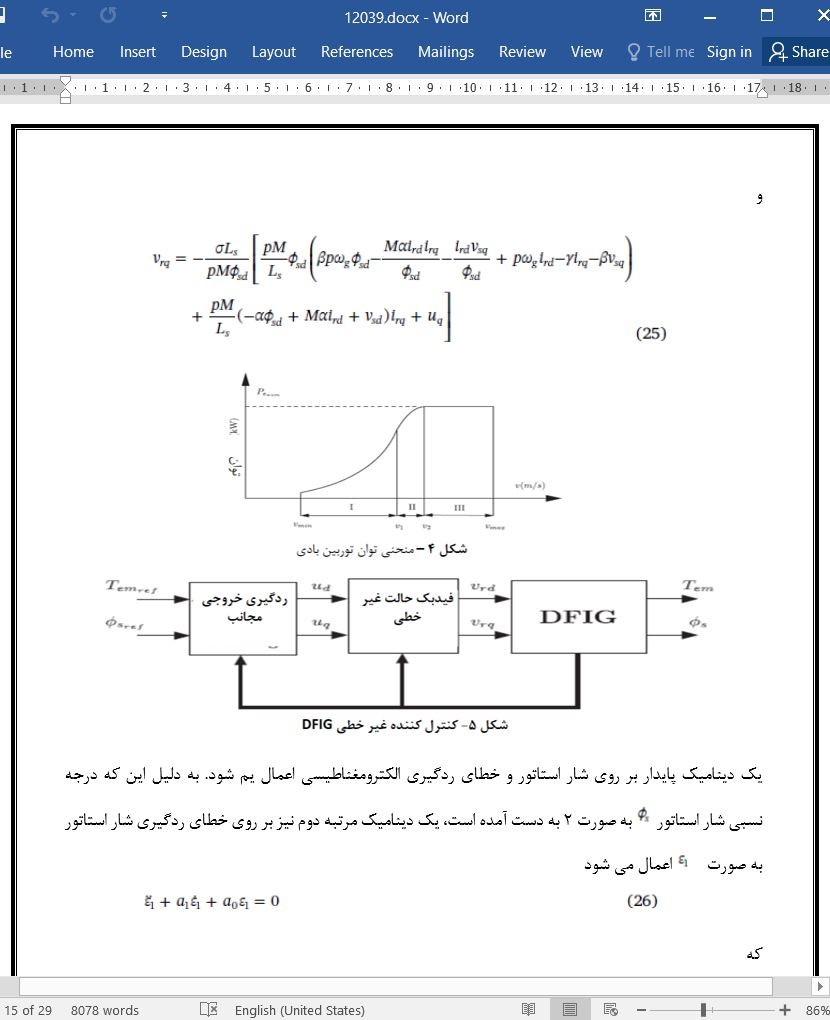
کنترل پیش بینی کننده غیر خطی یک توربین بادی مبتنی بر DFIG برای بهینه سازی کسب توان الکتریکی
چکیده
یک کنترل کننده پیش بینی کننده غیر خطی در این مقاله برای توربین های بادی با سرعت های متغیر ارائه شده است. هدف این مقاله بهینه سازی کسب توان الکتریکی و کاهش بارهای گذرا می باشد. این کنترل کننده تنها در حوزه هایی که سرعت باد در آن ها کم است، قابل استفاده می باشد. این کنترل کننده شامل یک کنترل کننده ژنراتور با تغذیه دوگانه می باشد که با یک کنترل کننده پیش بینی کننده برای توربین های بادی ترکیب شده است. بر خلاف اکثریت مقاله ها و کارهای تحقیقاتی انجام شده بر روی DFIG ها، کنترل کننده غیر خطی به صورت مستقیم با مدل ژنراتور کار می کند بدون این که هیچ گونه فرض ساده سازی برای آن در نظر گرفته شود. این موضوع باعث می شود که ما بتوانیم بعضی از فرضیات مرتبط با مدل های DFIG را کنار بگذاریم. این کنترل کننده DFIG غیر خطی می تواند گشتاور مجانبی و ردگیری شار را فراهم کند. برای قسمت بادی توربین، این کنترل کننده پیش بینی مدل از پیش بینی های خروجی استفاده می کند تا توالی های کنترل بهینه را محاسبه کند. این کنترل کننده نوعی تطابق بین بهینه سازی ثبت توان و کاهش بار را ایجاد می کند. طراحی این کنترل کننده ها در این مقاله به صورت دقیق توضیح داده شده است. کنترل کننده سراسری نیز با پارامتر های آزمایشی واقعی برای توربین های بادی با سرعت متغیر، مورد ارزیابی قرر گرفته است. این کنترل کننده ها با کنترل کننده های PID و LQG نیز مقایسه شده است. شبیه سازی ها در این مطالعه نشان دهنده نتایج رضایت بخش در مقایسه با همین طرح ها می باشد. کنترل کننده پیشنهاد شده می تواند بهینه سازی کسب توان بهتر و کاهش بار بیشتری را فراهم کند. ازین ما را قادر می سازد تا به اهداف طراحی بهتری دست پیدا کنیم
5 جمع بندی
یک کنترل کننده سراسری برای ژنراتور و توربین بادی در این مقاله ارائه شده است. این کنترل کننده برای سرعت متغیر در توربین های بادی مجهز به ژنراتور DFIG مورد استفاده قرار می گیرد. این کنترل کننده متشکل از کنترل کننده غیر خطی برای کنترل کننده DFIG و MPC برای بهینه سازی ثبت توان می باشد. این کنترل کننده ها با استفاده از ساختار کنترل دو حلقه ای با ثابت های زمانی مناسب، به یکدیگر متصل می شوند. این شبیه سازی ها نیز با پارامتر های توربین بادی واقعی و مشخصات سرعت بادی واقعی، تست شده است. آن ها نشان دهنده کارایی کنترل کننده ها از نظر بهینه سازی ثبت توان و کاهش بار کنترل می باشد. عملکرد خوب کنترل کننده ی پیش بینی کننده بر اساس تطبیق خوب طرح کنترل پیش بینی برای سیستم هایی مانند توربین های بادی، تایید شده است. باد به عنوان یک اغتشاش با ورودی فیلتر شده در نظر گرفته می شود. رفتار پیش بینی کنترل کننده MPC امکان واکنش پیش از موعد از کنترل کننده را فراهم می کند که موجب کنترل روان یک سیستم لختی مانند توربین های بادی می شود. کنترل کننده پیش بینی کننده باعث شکل گیری یک تطابق خوب بین سادگی و کارایی می شود. کنترل کننده به صورت کلی در کار های آتی نیز در نظر گرفته می شود. این کار ها شامل حوزه کامل بار برای سرعت بالای باد می شود. این کار ها باید حالت گذار بین بهینه سازی ثبت توان و تنظیم توان را در نظر بگیرد.
Abstract
A nonlinear predictive controller is proposed for a variable speed wind turbine. The objective is power capture optimization and transient loads reduction. The controller acts only on low wind speed area. It consists of a doubly fed induction generator controller coupled with a model predictive aeroturbine controller. Unlike the majority of existing work on DFIG, the nonlinear controller deals directly with the generator model without any simplifying assumptions. This makes it possible to remove some assumptions on the DFIG model. The nonlinear DFIG controller achieves asymptotic torque and flux tracking. For the aeroturbine part, the model predictive controller uses predictions of the output to compute the optimal control sequence. It makes a compromise between power capture optimization and loads reduction. The controllers design procedure is detailed. The global controller is tested with the parameters of a real experimental variable speed wind turbine. It is compared with PID and LQG controllers. The simulations show satisfactory results in comparison with these schemes. The proposed controller achieves better power capture optimization and load reduction. It therefore allows a good achievement of the design objectives.
5. Conclusion
A global controller for both the generator and aeroturbine is proposed. It is applied for a variable speed wind turbine equipped with a DFIG generator. The controller is composed of a nonlinear controller for the DFIG and an MPC controller for the power capture optimization. The two controllers are interconnected using a two-loop control structure with suitable time constants. The simulations are made with the parameters of a real wind turbine and a realistic wind speed profile. They confirm the efficiency of the controller in terms of power capture optimization and control loads reduction. The good performance of the predictive controller are explained by the well adaptation of predictive control scheme for systems like wind turbines. The wind is considered as an filtered-input disturbance. The predictive behavior of the MPC controller allows a premature reaction of the controller for a smooth control of a inertial systems like wind turbine. The predictive controller achieves a good compromise between simplicity and efficiency. A whole controller is to be considered in future works. It will include full load area for high wind speed. It should also take into consideration the transition between power capture optimization and power regulation.
چکیده
1 مقدمه
2 مدل سازی توربین های بادی
2.1 مدل سازی توربین بادی
2.2 مدل سازی ژنراتور
2.3 بهینه سازی ثبت توان
3. پیش بینی غیر خطی برای کنترل کننده توربین بادی
3.1 درگیری خروجی مجانب به صورت غیر خطی با کنترل کننده DFIG
3.2 کنترل کننده توربین بادی به صورت پیش بینی کننده
3.3 کنترل کننده سراسری
4 نتایج شبیه سازی ها
4.1 توصیف فرایند شبیه سازی
4.2 طراحی کنترل کننده DFIG
4.3 کنترل کننده ای متداول توربین های بادی
4.4 طراحی کنترل کننده MPC
4.5 مقایسه کنترل کننده های توربین بادی
4.6 توجیه عملکرد کنترل کننده پیش بینی کننده
5 جمع بندی
منابع
Abstract
Nomenclature
1. Introduction
2. Wind turbine modeling
2.1. Aeroturbine modeling
2.2. Generator modeling
2.3. Power capture optimization
3. Nonlinear predictive wind turbine controller
3.1. Nonlinear asymptotic output tracking DFIG controller
3.2. Predictive aeroturbine controller
3.3. Global controller
4. Simulation results
4.1. Simulation procedure description
4.2. DFIG controller design
4.3. Conventional aeroturbine controllers
4.4. MPC controller design
4.5. Aeroturbine controllers comparison
4.6. Predictive controller performance justification
5. Conclusion
Acknowledgment
Appendix A. Wind turbine parameters values
Appendix B. Direct axis stator voltage vsd time derivative
Appendix C. DIFG Controller parameters design
References
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه