تکنیک های فشرده سازی دایرکتوری برای بهینه سازی فضا در فایل سیستم های EFAT و FAT
چکیده
جدول تخصیص فایل توسعه یافته (ExFAT) نوعی فایل سیستم هستند که در آینده برای ذخیره ساز های تعبیه شده استفاده می شوند. جدول تخصیص فایل(FAT) فایل سیستمی است که در حال حاضر در ذخیره سازهای تعبیه شده مانند کارت های چند رسانه ای (MMC) / دیجیتال امن (SD) / کارت های میکروSD و فلش مموری های NAND و NOR استفاده می شود. MMCها و کارت های SD ، ExFAT را به عنوان فایل سیستم استاندارد برای ذخیره سازی در فلش کارت های بیش از 32 گیگ استفاده می کنند. این مقاله روش های فشرده سازی دایرکتوری را برای فایل سیستم ها FAT و ExFAT بررسی می کند تا فضای کاربر در فایل سیستم ها را افزایش دهد.
1 معرفی
پراستفاده ترین فایل سیستم برای سیستم های خانگی تبلت ، موبایل ها، دوربین های دیجیتال و دستگاه های تعبیه شده ی دیگر برای ذخیره سازی داده و کاربردهای چند رسانه ای مانند تصاویر ویدئویی، بازپخش صوت/تصویر و ضبط ، فایل سیستم FAT [1] می باشد. نسخه اولیه فایل سیستم FAT، FAT12 بود که شرکت مایکروسافت آن را ارائه کرد. بعد از آن FAT16 توسعه پیدا کرد و سپس با نام FAT32 که ظرفیت ذخیره سازی بیشتری را پشتیبانی می کرد. فایل سیستم FAT ابتدا برای استفاده در فلاپی دیسک ها و دیسک-های سخت به وجود آمد. امروزه بیشتر کامپیوترهای خانگی (pc) از فایل سیستم FAT استفاده می کنند. این فایل سیستم به یک فایل سیستم پیش فرض و سازگار با فرمت ذخیره سازی برای دستگاه های تعبیه شده تبدیل شده است. معمولا دستگاه هایی با ساختار FAT با نام رسانه ذخیره سازی قابل حمل در یک pc شناخته می شوند. فلش مموری ها یک انتخاب پیش فرض برای هر دستگاه ذخیره ساز می باشند، زیرا آن ها ارزان قیمت، کوچکتر و ظرفیت ذخیره سازی بیشتری دارند. اگرچه فایل سیستم FAT روش های مدیریت فلش مانند یکسانسازی پوشش و مدیریت بد بلاک را پوشش نمی دهد، دستگاه های تعبیه شده با الگوریتم های اختصاصی مدیریت بلاک فلش این فایل سیستم را پیاده سازی می کنند.
Abstract
The Extend File Allocation Table (ExFAT) is the future file system for embedded storage devices. The File Allocation Table (FAT) file system de-facto file system for embedded storage devices such as Multimedia Cards (MMC) / Secure Digital (SD) / Micro SD cards, NOR, NAND flash memories. The MMC and SD card associations classify the ExFAT as the standard file system for storage flash cards of more than 32 Giga Bytes (GB) of size. This paper implements the directory compaction techniques for both FAT and ExFAT file system to improve the availability of the user space in the file systems.
1. Introduction
The FAT [1] is widely used file system in tablet personal computers, mobile phones, digital cameras and other embedded devices for data storage and multi-media applications such as video imaging, audio/video playback and recording. The initial version of FAT file system was FAT12 by Microsoft Corporation, later it was extended as FAT16 and further as FAT32 to support higher storage capacity. The FAT file system was initially developed to use on floppy disks and hard-drives. Since most of the Personal Computer (PC) s implements the FAT file system, this file system has become a default and world-wide compatible storage format for embedded devices. Usually the device with the implementation of FAT is recognized as removable storage media in a PC. The Flash memories are default choice of any embedded device as they are lowpriced, smaller size and higher storage capacity. Even though FAT file system does not define flash management techniques such as Wear-Levelling and Bad Block management, the embedded devices implements this file system along with the dedicated flash block management algorithms.
چکیده
1 معرفی
2 فشرده سازی دایرکتوری در فایل سیستم FAT و ExFAT
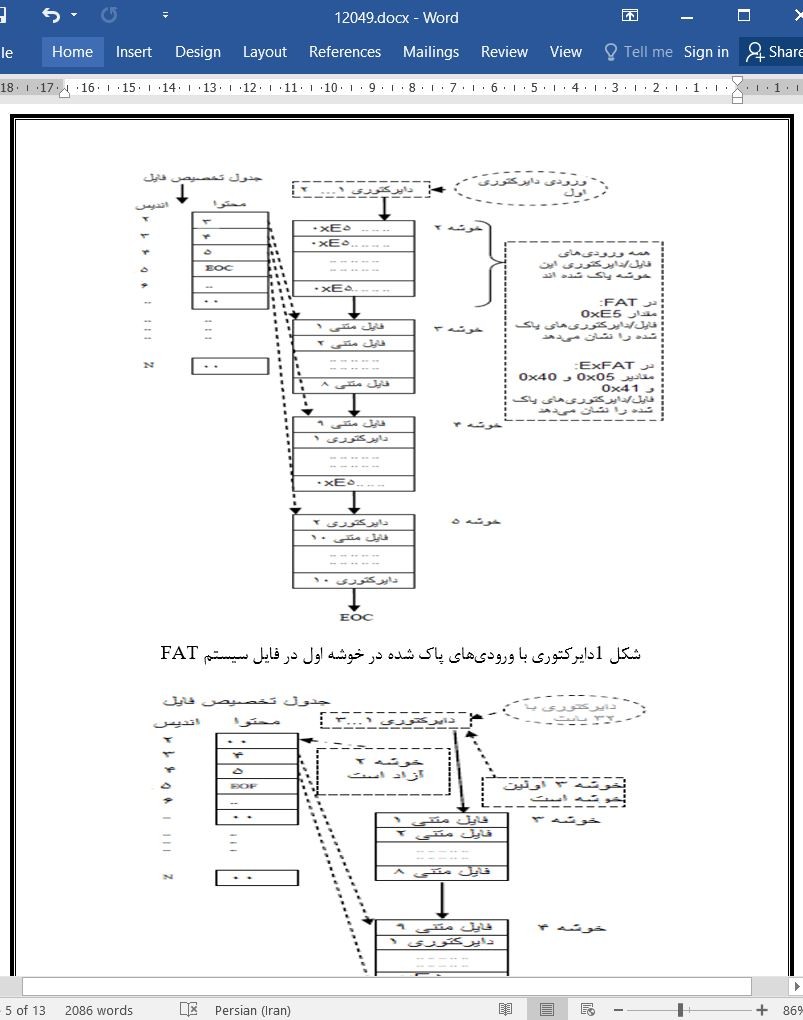
2.1 اولین خوشه در زنجیره خوشه های دایرکتوری
2.2 یک خوشه دلخواه بین اولین و آخرین خوشه در زنجیره خوشه های دایرکتوری
2.3 آخرین خوشه از زنجیره خوشه های دایرکتوری
3 نتیجه گیری
قدردانی
منابع
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Directory compaction in ExFAT and FAT File systems
2.1 First cluster in the clusters chain of the directory
2.2 An arbitrary cluster in between the first and last cluster of the clusters chain of the directory
2.3 Last cluster of the clusters chain of the directory
3. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- اصل مقاله انگلیسی با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه