طرحی کارآمد برای اینترنت صنعتی اشیاء با استفاده از امضای فاقد گواهی
اخیراً، رمزنگاری منحنی بیضوی (HECC) معطوف به دستگاههای کممصرفی مانند اینترنت صنعتی اشیا (IIoT) شده است. همان طور که همه می دانیم، رمزنگاری منحنی بیضوی قابلیت استفاده از کلید با اندازه کوچک را دارد که این امر میتواند برای محیط IIoT مناسب باشد. ما با الهام از ویژگی فوق الذکر HECC، با استفاده از امضای بدون گواهی و با کمک HECC طرحی کارآمد ارائه کردهایم. اثبات شده که رویکرد ارائه شده، در برابر چالش های حمله کنندگان نوع ۱ و نوع ۲، غیرقابل جعل است. ما امنیت این رویکرد طراحی شده را از طریق اعتبارسنجی خودکار پروتکل های امنیتی اینترنت و برنامه های کاربردی (AVISPA) آزمایش کردیم. همچنین، هزینه های محاسباتی و ارتباطی را با طرح هایی که از پیش موجود بودند، مقایسه کردیم و از تحلیلمان مشاهده نمودیم که طرح ما از نظر محاسباتی، کارآمد است و به هزینه پایین محاسباتی نیاز دارد.
1 مقدمه
اینترنت اشیا (IOT) شبکه ای از دستگاه های متصل به صورت فیزیکی است که فناوری های تعبیه شده مانند RFID، حسگرها و دیگر دستگاه های هوشمند [۱،۲] که با استفاده از اینترنت [۳، ۴] برای برقراری ارتباط با محیط های خارج، با هم شبکه شده اند را در خود جای داده است. از طرفی، اینترنت اشیا از طریق پیوند دادن شهرها با سیستم های کامل رشد یافته، در حال گسترش حوزه خود است. این سیستم های هوشمند، برای ترکیب آیتم های معمول ما با دستگاه های هوشمند طراحی شده اند تا سیستم خودکار کاملا هوشمندی (AIS) ایجاد کنند که پتانسیل کاهش تلاش های انسانی را دارد. براساس گزارش اخیر Ericsson، تا سال ۲۰۲۲[۵] ۱۸ بیلیون دستگاه هوشمند IoT به اینترنت متصل خواهند شد. این روند نوآورانه نوین راه را برای یکپارچه سازی این فناوری های نوآورانه در حوزه های مختلفی مانند بهداشت و درمان، داده کاوی، حمل و نقل، و تجارت و بازرگانی [۶-۱۰] هموار نموده است. IoT از زمان اولین ارائه خود [۱۱] در میان جامعه تحقیقاتی هم در زمینه آموزش و هم در زمینه صنایع، تحسین زیادی برانگیخت [۱۲].
9 نتیجه گیری
این مطالعه، با استفاده از امضای فاقد گواهی (غیررسمی) و با کمک سیستم رمزنگاری منحنی هایپرلیپتیک (HCC)، طرحی کارآمد برای IIoT ارائه می کند. جعل ناپذیری رویکرد ارائه شده در برابر چالش های مهاجمین نوع اول و نوع دوم به اثبات رسیده است. امنیت کار پیشنهادی از طریق ابزار محبوب «AVISPA» تست شده است. تحلیل تطبیقی جامعی در برابر طرح های مربوطه انجام شد که ارجحیت طرح پیشنهادی ما هم از نظر هزینه های ارتباطی و هم از نظر هزینه های محاسباتی نسبت به آن ها را نشان داد. براساس ادعاهای فوق، استدلال می نماییم که طرح طراحی شده بهترین گزینه برای دستگاه های دارای منابع محدود از نظر مصرف هزینه خواهد بود.
Currently, hyperelliptic curve cryptography (HECC) got attractions towards low power devices such as Industrial Internet of things (IIoT). As we all know, it has the capability of utilizing low key size, which can be suitable for IIoTenvironment. Inspired by the aforementioned property of HECC, we proposed an efficient scheme for IIoT using certificateless signature with the help of HECC. the presented approach is proven to be unforgeable against the challenges of type I and type II attackers. We tested the security of the designed approach through Automated Validation of Internet Security Protocols and Applications (AVISPA). We also performed the computational and communicational cost comparisons with already existed schemes, and it is observed from our analysis that our scheme is computationally efficient and needs low communication cost.
1. Introduction
Internet of Things (IoT) is a network of physical interconnected devices, which incorporate embedded technologies such as RFID, sensors, and other smart devices [1, 2], networked together for communicating with the external environments via the Internet [3, 4]. On the other hand, IoT is growing its scope through linking cities to mature smart systems. these smart systems are designed to combine our routine items with smart devices to create a fully automated intelligent system (AIS) that has the potential to reduce human effort. According to a recent Ericsson report, about 18 billion smart IoT devices will be connected to the Internet by 2022 [5]. This new innovative trend has paved the way for integrating these innovative technologies into various fields such as healthcare, data mining, transportation, and commerce [6–10]. Since its first proposal [11], IoT has attained considerable admiration among the research community in both pedagogy and industries [12].
9. Conclusion
this study presents an efficient scheme for IIoT using certificateless signature with the help of the hyperelliptic curve cryptosystem (HCC). the presented approach is proven to be unforgeable against the challenges of type I and type II attackers. the security of the proposed work is tested through a popular tool “AVISPA.” A comprehensive comparative analysis against relevant schemes has been given which shows how our proposed scheme is better in terms of both communication and computation costs from them. Based on the above claims, we argue that the designed scheme will be the best option for the resource-limited devices in terms of cost consumptions.
1 مقدمه
1.1 انگیزه و همکاری
1.2 نقشه راه مقاله
2 مطالعات مرتبط
3 مقدمات
3.1 مسئله لگاریتمی گسسته منحنی هایپرلیپتیک
۳.۲. مدل تهدید
4 مدل شبکه
5 طرح پیشنهادی امضای فاقد گواهی
۵.۱. ساخت طرح امضای فاقد گواهی (CLSC)
6. تحلیل امنیت
۶.۱. قضیه A (جعل ناپذیری)
6.2 قضیه جعل ناپذیری
۶.۳. قضیه حمله ضد بازپخش
6.4 قضیه حمله مرد میانه
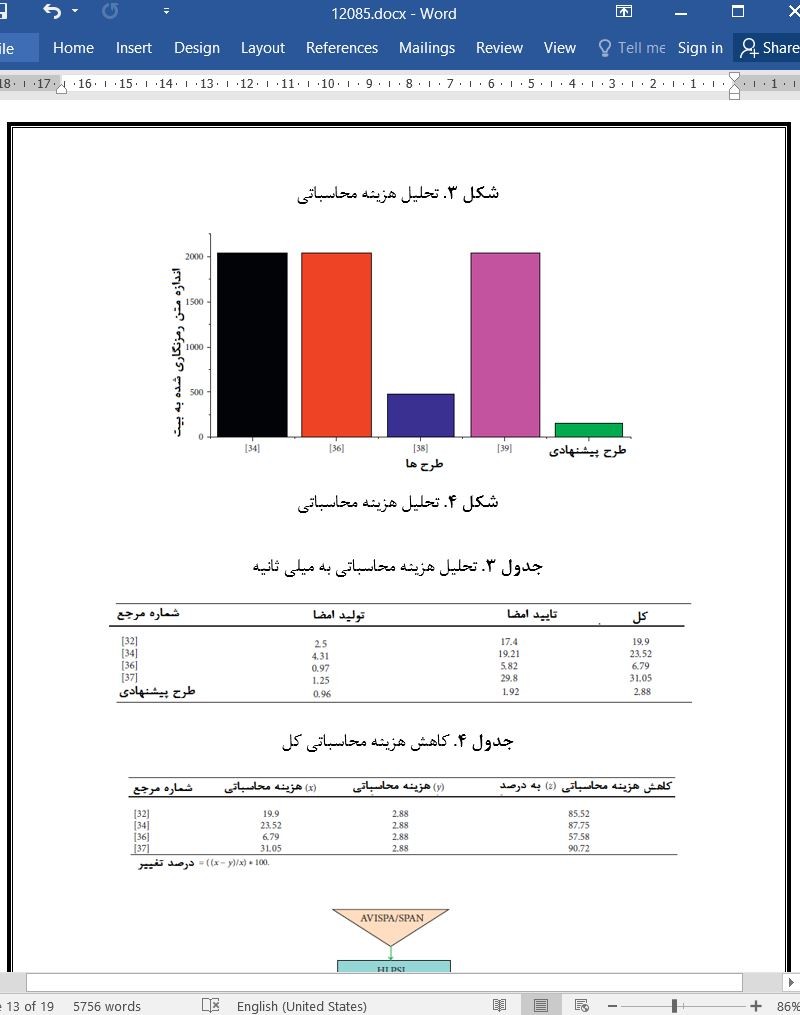
7 تحلیل عملکرد
7.1 هزینه محاسباتی
8. مطالعه شبیه سازی (ضمیمه)
9. نتیجه گیری
تضاد در منافع
منابع و مآخذ
1. Introduction
1.1 Motivation and Contribution. Inspired
1.2 Road Map of the Article
2. Related Work
2.1 Outcomes of the Literature
3. Preliminaries
3.1 Hyperelliptic Curve Discrete Logarithm Problem (HDLP)
3.2 Threat Model
4. Network Model
5. Proposed Certificateless Signature Scheme
5.1 Certificateless Signature Construction (CLSC) Scheme
6. Security Analysis
6.1 Theorem A (Unforgeability)
6.2 Theorem Unforgeability
6.3 Theorem of Antireplay Attack
6.4 Theorem of Man-in-the-Middle Attack
7. Performance Analysis
7.1 Computational Cost
8. Simulation Study (Appendix)
Conflicts of Interest
References
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه