کاربرد الگوریتم های داده کاوی برای زوال عقل در افراد مبتلا به ایدز
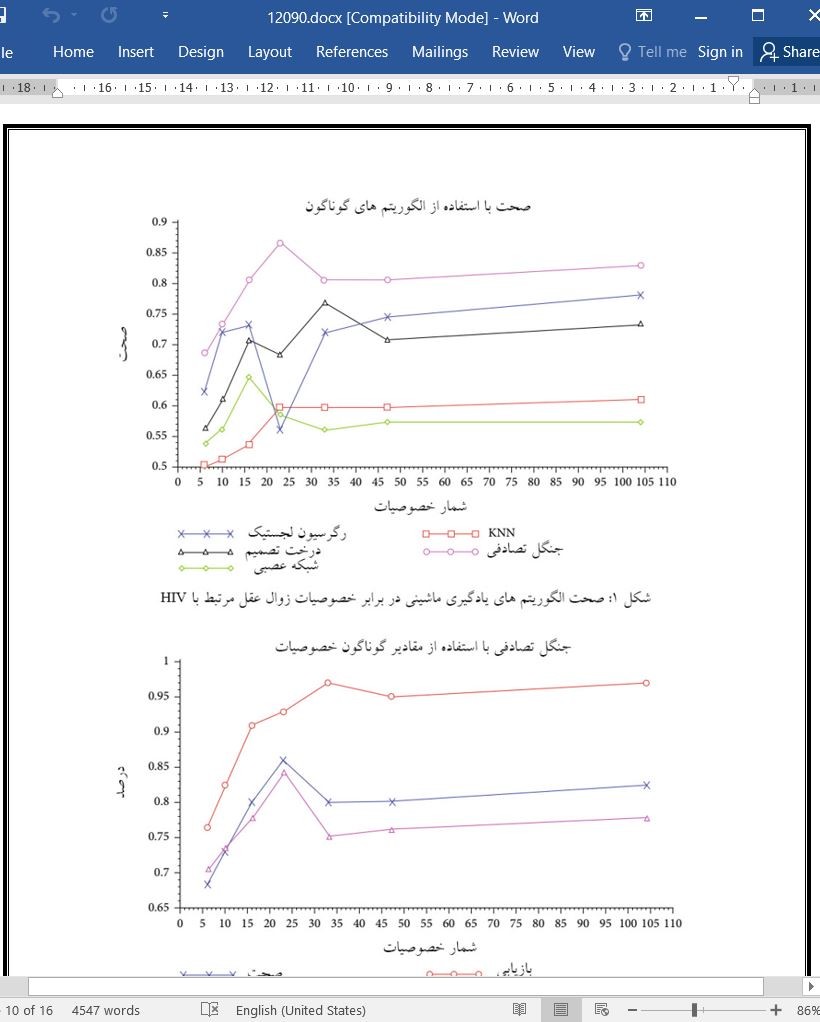
زوال عقل باعث اختلال در کارکردهای حرکتی، رفتاری، و هوشی فرد می شود به طوری که او را از انجام فعالیت های مؤثر روزمره بازمی دارد. پژوهش کنونی بر آن بود که بهترین الگوریتم عمل کننده و مرتبط ترین خصوصیات را با استفاده از داده کاوی شناسایی کند تا بدین وسیله افراد مبتلا به ایدزی که در خطر جدی زوال عقل هستند را طبقه-بندی نماید. در این راستا، الگوریتم تحلیل مؤلفه های اصلی (PCA) مورد استفاده قرار گرفت و آزمایش هایی به شکل مقایسه ای میان الگوریتم های یادگیری ماشینی زیر انجام شد: رگرسیون لجستیک، درخت تصمیم، شبکه ی عصبی، KNN (k همسایه ی نزدیک تر) و جنگل تصادفی. پایگاه داده ی مورد استفاده در این مطالعه بر پایه ی گردآوری داده ی 270 انسان مبتلا به ایدز تدوین گردید و ادامه ی کار در درمانگاه یک بیمارستان مرجع بیماری های واگیردار و انگلی در ایالت سیرا برزیل از ژانویه تا آوریل 2019 پیگیری شد. همچنین، عملکرد الگوریتم ها به ازای 14 ویژگی و خصوصیت موجود در پایگاه داده تجزیه و تحلیل شدند؛ آنگاه با کاهش ابعاد، در کیفیت الگوریتم های یادگیری ماشینی بهبودی حاصل شد و مشخص گردید که در جریان آزمون ها، حتی حدود 30 درصد تنوع از میان رفت. افزون بر این، هنگام در نظر گرفتن تنها 23 ویژگی و خصوصیت، دقت الگوریتم ها در جنگل تصادفی برابر 86 درصد، در رگرسیون لجستیک برابر 56 درصد، در درخت تصمیم برابر 68 درصد، در KNN برابر 60 درصد، و در شبکه ی عصبی برابر 59 درصد بود. معلوم گردید که الگوریتم جنگل تصادفی نسبت به بقیه کارامدتر است به طوری که به دقت 84 درصدی و صحت 86 درصدی دست یافت.
1. مقدمه
داده کاوی (MD) یکی از فرایندهای واکاوی داده ها است که با استفاده از راهبردهایی همچون الگوریتم های یادگیری، هوش مصنوعی (AI) یا طبقه بندی ها آماری، که می توانند روابط پنهان و داده های صحیح را آشکار کنند، قادر به پیش بینی و استخراج الگوهای منسجم است [1 و 2].
کاربرد داده کاوی در سامانه های اطلاعات سلامت، خواه حوزه های عمومی و خواه خصوصی، است که از طریق فرایند انتخاب، پیش پردازش و تبدیل داده ها می توان الگوها را یافت و با تفسیر آن ها دانش تولید کرد. با استفاده از این روش و بر پایه ی الگوهای مسائل سلامت و درمان های مراقبتی برای بیماری های گوناگون، متخصص بهداشت بیمار را شناسایی، توصیف، و راهنمایی خواهد کرد.
Dementia interferes with the individual’s motor, behavioural, and intellectual functions, causing him to be unable to perform instrumental activities of daily living. This study is aimed at identifying the best performing algorithm and the most relevant characteristics to categorise individuals with HIV/AIDS at high risk of dementia from the application of data mining. Principal component analysis (PCA) algorithm was used and tested comparatively between the following machine learning algorithms: logistic regression, decision tree, neural network, KNN, and random forest. The database used for this study was built from the data collection of 270 individuals infected with HIV/AIDS and followed up at the outpatient clinic of a reference hospital for infectious and parasitic diseases in the State of Ceará, Brazil, from January to April 2019. Also, the performance of the algorithms was analysed for the 104 characteristics available in the database; then, with the reduction of dimensionality, there was an improvement in the quality of the machine learning algorithms and identified that during the tests, even losing about 30% of the variation. Besides, when considering only 23 characteristics, the precision of the algorithms was 86% in random forest, 56% logistic regression, 68% decision tree, 60% KNN, and 59% neural network. The random forest algorithm proved to be more effective than the others, obtaining 84% precision and 86% accuracy.
1. Introduction
Data mining (MD) is one of the data exploration processes capable of predicting and extracting consistent patterns by using strategies such as learning algorithms, such as artificial intelligence (AI), or classification in statistics, which can reveal hidden relationships and accurate data [1, 2].
The application of MD is in health information systems, in the public and private spheres, which, through a process of selection, preprocessing, and data transformation, one can discover patterns and generate knowledge through their interpretations. With this method, the health professional will identify, characterise, and guide the patient based on patterns of health problems and care therapies for different diseases [2].
1. مقدمه
2. روش شناسی
3. نتایج و بحث
4. نتیجه گیری و پژوهش های آینده
منابع
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusion and Future Works
Acknowledgments
References
- اصل مقاله انگلیسی با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه